reference:
- https://blog.csdn.net/shiyongyue/article/details/75103446
- http://blog.rongpmcu.com/gpiozi-xi-tong-he-pinctrlzi-xi-tong/
- https://www.cnblogs.com/Cqlismy/p/11891789.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/hellokitty2/p/12500546.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/ccwzhu/article/details/103079297
- pinctrl:https://www.cnblogs.com/hellokitty2/p/12501493.html
内核相关文档
Documentationdevicetreeindingspinctrlpinctrl-bindings.txt
Documentationgpiogpio.txt
Documentationdevicetreeindingsgpiogpio.txt
背景
随着内核的发展,linux驱动框架在不断的变化。在早期,GPIO子系统存在之前,我们驱动需要在代码中配置寄存器来使用GPIO引脚。
此后,出现了gpio子系统,后来又出现了pinctrl子系统。
有些平台的实现没有使用内核提供的pinctrl子系统,而是继续采用在内核提供pinctrl子系统前自己实现的那套机制来pinmux操作,如Ti的omap平台;
有些平台则基于pinctrl子系统来实现pinmux、pinconf的控制。
介绍
GPIO子系统可以说是Linux中最简单的子系统。
- GPIO(General Purpose Input Output):负责管理整个系统各gpio输入输出管脚的使用情况,同时通过sys文件系统导出了调试信息和应用层控制接口。
- Pinctrl(Pin Control):负责管理SOC中各pin的状态,比如输出电流能力、是否有内部上拉或者下拉,是否有功能复用等参数。
要想操作GPIO引脚,需要先把所用引脚配置成GPIO功能,这个通过pinctrl子系统来实现。然后可以根据设置的引脚的方向来读取引脚的值和设置输出值。
在BSP工程师实现好GPIO子系统后,我们就可以在设备树中指定GPIO引脚,在驱动中使用GPIO子系统的标准函数来获取GPIO、设置GPIO方向、读取/设置GPIO的值。这样的驱动代码是于单板无关的。
gpio子系统
gpio子系统内部实现主要提供了两类接口:
-
一类给bsp工程师,用于注册gpio chip(也就是所谓的gpio控制器驱动)
-
另一部分给驱动工程师使用,为驱动工程师屏蔽了不同gpio chip之间的区别,驱动工程师调用的api的最终操作流程会导向gpio对应的gpio chip的控制代码,也就是bsp的代码。
核心实现
gpio子系统的实现源码在drivers/gpio文件夹下,主要文件有:
在安卓系统中,实现源码在
kernel/drivers/gpio
| 文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| devres.c | 针对gpio api增加的devres机制的支持 |
| gpiolib.c | gpio子系统的核心实现 |
| gpiolib-of.c | 对设备树的支持 |
| gpiolib-acpi.c | 和acpi相关,不分析 |
| gpio-xxx.c | 根据平台的不同,所对应的gpio控制 |
gpio子系统提供了两层接口,一层给上层驱动工程师调用,一层给下层bsp工程师调用。
上层使用前,当然先得bsp工程师完成对应的动作。
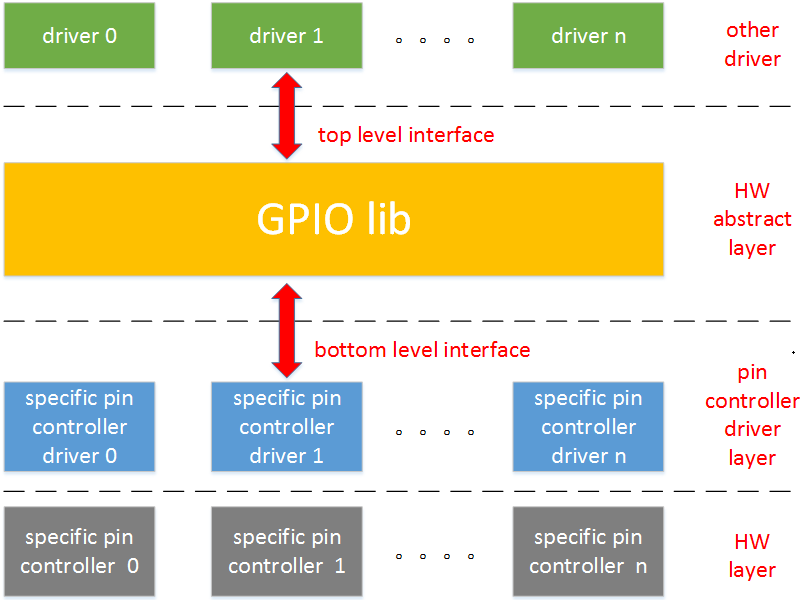
GPIO子系统有两套接口:
-
一是基于描述符(
descriptor-based)的,相关api函数都是以"gpiod_"为前缀,它使用gpio_desc结构来表示一个引脚。 -
另一种是老(
legency)的,相关api函数都是以"gpio_"为前缀,它使用一个整数来表示一个引脚,强烈建议不要使用legacy的接口函数。
其实,
legacy gpio大部分api就是基于描述符api来实现的,我们可以看到很多legacy api内部的实现调用了to_desc。
// 1.获取GPIO
gpiod_get;
gpiod_get_index;
gpiod_get_array;
devm_gpiod_get;
devm_gpiod_get_index;
devm_gpiod_get_array;
// 2.设置方向
gpiod_direction_input;
gpiod_direction_output;
// 3.读值、写值
gpiod_get_value;
gpiod_set_value;
// 4. 设为中断(如果必要)
request_irq(gpiod_to_irq(gpio_desc)...); //将gpio转为对应的irq,然后注册该irq的中断handler
// 5.释放GPIO
gpiod_put;
gpiod_put_array;
devm_gpiod_put;
devm_gpiod_put_array;
前缀为"
devm_"的含义是设备资源管理,这是一种自动释放资源的机制。思想:“资源是属于设备的,设备不存在时资源就可以自动释放”。
背景:在Linux驱动开发过程中,先申请了GPIO,再申请内存,如果内存申请失败,那么在返回之前就需要先释放GPIO资源。如果使用的是devm相关函数,在内存申请失败时可以直接返回,设备的销毁函数会自动地释放已经申请了的GPIO资源。
因此,建议使用devm相关函数操作GPIO。
gpio控制api( descriptor)
使用基于描述符的接口时,GPIO被作为一个描述符来使用。
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
// 更多相关的说明可以参考 Documentation/gpio/consumer.txt
获取一个或一组GPIO
struct gpio_desc * gpiod_get(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
/*
在允许GPIO不存在时,可以使用gpiod_get_optional()和gpiod_get_index_optional()函数。
这两个函数在没有成功分配到GPIO的时候返回NULL而不是-ENOENT。
*/
struct gpio_desc * gpiod_get_optional(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
struct gpio_descs {
unsigned int ndescs; // 数量
struct gpio_desc *desc[]; // 每一个 desc 的情况
}
// 返回gpio_descs 注意:不是 gpio_desc
struct gpio_descs * gpiod_get_array(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
/*多个Pin时需要附带index参数。*/
struct gpio_desc * gpiod_get_index(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
unsigned int idx,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
struct gpio_desc * gpiod_get_index_optional(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
unsigned int index,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
struct gpio_desc * devm_gpiod_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
struct gpio_desc * devm_gpiod_get_index(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
unsigned int idx,
enum gpiod_flags flags);
描述:必须通过调用gpiod_get()函数族来获取对应的描述符。
参数解析:
- con_id:字符串类型,即GPIO的名字;
一般需要查看设备树中的定义。除此之外,我们还可以在设备树文件里添加参数(
GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW、GPIO_OPEN_DRAIN、GPIO_OPEN_SOURCE)来触发该接口内部设置gpio,具体的参数格式和具体的gpio chip driver有关,一般可以在Documentation/devicetree/bindings/gpio里找到对应平台的方法。
有关DeviceTree情况中con_id参数的更详细说明请参阅Documentation/gpio/board.txt
例如:
在SD卡驱动看到的去查找名字为cd-gpios的gpio:
// simple.c:
ctx->cd_gpio = devm_gpiod_get_optional(dev, "cd", 0);
在使用SD卡驱动的主dts就有cd pin的定义:
// xxx.dts:
cd-gpios = <&gpio2 12 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
- index:逻辑下标。将一个GPIO设备(DESC)下的多个Pin看成一个数组,此时index是数组成员下标。
内核文档有个例子,比如gpio如下定义:
led-gpios = <&gpio 15 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>, /* red */
<&gpio 16 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>, /* green */
<&gpio 17 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; /* blue */
如果index是0,那么对应的就是gpio 15;如果index是1,那么对应就是gpio 16,以此类推。
- flags:用于可选地指定GPIO的方向和初始值,它的值可以是:
GPIOD_ASIS或0表示根本不初始化GPIO。需要随后使用专门的函数设置方向GPIOD_IN初始化GPIO作为输入。GPIOD_OUT_LOW将GPIO初始化为输出,值为0。GPIOD_OUT_HIGH将GPIO初始化为输出,值为1。GPIOD_OUT_LOW_OPEN_DRAIN:与GPIOD_OUT_LOW相同,但强制以开漏的方式使用GPIOD_OUT_HIGH_OPEN_DRAIN:与GPIOD_OUT_HIGH相同,但强制以开漏的方式使用
最后两个标志用于必须开漏方式的情况,比如GPIO被用作I2C时,如果该GPIO尚未在映射(参见board.txt)中被配置为开漏方式,将被强制配置为开漏方式并给出WARNING。
这两个函数都返回有效的GPIO描述符或可被IS_ERR()检查的错误代码(它们永远不会返回NULL指针)。
返回值:成功返回一个GPIO描述符;失败返回错误编码,可以使用IS_ERR()进行检查错误原因。
- 返回-ENOENT只会发生在当且仅当没有为设备/功能/索引三元组成功分配GPIO的时候。
- 其他错误代码用于已成功分配GPIO,但在试图获得它的时候发生了错误的情况:这可以用于区分错误原因是可选GPIO参数错误还是GPIO缺失这两种情况。
释放
void gpiod_put(struct gpio_desc *desc);
void gpiod_put_array(struct gpio_descs *descs); // 对应 get*array
void devm_gpiod_put(struct device *dev, struct gpio_desc *desc);
void devm_gpiod_put_array(struct device *dev, struct gpio_descs *descs);
描述:释放之前通过get获取的GPIO描述符
注意:在释放之后,严格禁止使用被释放的描述符;也不允许在使用gpiod_get_array()获取的数组中单独使用gpiod_put()释放描述符。
设置方向
注意:GPIO没有默认方向。因此,使用GPIO前必须首先设置其方向,否则将导致未定义的行为!
// 设置GPIO为输入还是输出
int gpiod_direction_input(struct gpio_desc *desc);
int gpiod_direction_output(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value);
// 查询GPIO的当前方向:返回0表示输出,1表示输入,或错误代码(如果出错)
int gpiod_get_direction(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
描述:使用设备驱动必须首先确定GPIO的方向。如果在调用gpiod_get* ()时,flag指定了nodirection,就可以调用上面的某个gpiod_direction_*()函数来设置方向:
参数解析:
- value:对于输出GPIO,提供的值将成为初始输出值;用于避免系统启动期间的信号故障。
返回值:成功返回值为零,否则返回值为负的错误代码。
该返回值应该被检查,因为之后获取/设置GPIO引脚值
get/set调用不会返回错误,所以错误的配置是有可能的。您通常应该在任务上下文进行这些调用。但是,对于自旋锁安全(Spinlock-Safe)的GPIO,可以作为板级设置初期的一部分,在启用任务之前使用它们。
使用单个GPIO
/*
Spinlock-Safe的GPIO访问
意义:如果操作GPIO可能导致sleep,那么同步机制不能采用spinlock,因为spinlock要求不能sleep
*/
// 读取输出引脚的值时,返回的值应该是引脚上的值。由于包括开漏信号和输出延迟在内的问题,它并不总是匹配指定的输出值。
int gpiod_get_value(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
void gpiod_set_value(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value);
描述:大多数GPIO控制器可通过存储器读/写指令访问。在不能睡眠的环境下调用。
不能睡眠的环境:内部hard(非线程的)IRQ handler、类似的上下文中完成的操作(即原子操作中)。
参数解析:
- value:布尔值,零为低,非零为高。
返回值:get/set调用不会返回错误,因为“无效的GPIO”应该在这之前就从gpiod_direction_*()中得知。
但请注意,并非所有平台都可以读取输出引脚的值;对于那些不能读取的平台,函数永远返回零。另外,使用这些函数访问需要睡眠才能安全访问的GPIO(见下文)是错误的操作。
/* 允许睡眠的GPIO访问 */
// 判断是否允许睡眠:返回非零 代表 可以睡眠:
int gpiod_cansleep(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
// 获取、设置GPIO的值。
int gpiod_get_value_cansleep(const struct gpio_desc * desc);
void gpiod_set_value_cansleep(struct gpio_desc * desc,int value);
描述:有些GPIO控制器必须使用基于消息的总线(如I2C或SPI)访问。读取或写入这些GPIO值的命令需要等待到达队列的头部以传输命令并获得其响应。这样就需要允许睡眠,导致这类GPIO的访问不能在内部IRQ处理程序内(原子上下文)完成。
访问这样的GPIO需要一个可以休眠的上下文,例如一个threaded IRQ处理程序,并且必须使用上述访问函数访问函数(而不是没有带cansleep()后缀的)。
除了可以睡眠,无法在hardIRQ处理程序访问的特点以外,这些调用与Spinlock-Safe的调用相同。
使用gpio的时候需要了解一下低有效和开漏语义,见附录。
使用一组GPIO
## 获取值
int gpiod_get_array_value(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
int gpiod_get_raw_array_value(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
int gpiod_get_array_value_cansleep(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
int gpiod_get_raw_array_value_cansleep(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
## 设置值
void gpiod_set_array_value(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
void gpiod_set_raw_array_value(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
void gpiod_set_array_value_cansleep(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
void gpiod_set_raw_array_value_cansleep(unsigned int array_size,
struct gpio_desc **desc_array,
int *value_array);
描述:如果相应的芯片驱动器支持,这些函数将尝试同时访问属于同一存储体或芯片的GPIO。在这种情况下,可以预期显著改善的性能。如果无法同时访问,GPIO将按顺序访问。用来获取、设置GPIO的值。
参数解析:
- array_size - 数组元素的数量
- desc_array - GPIO描述符数组,可以是任意一组GPIO
如何理解“任意”:
我们可以先使用
gpiod_get()和gpiod_get_array()的任意组合来获得描述符后,放入一个我们自己构建数组中,再将其传递给上述函数)。同时,如果为了获得最佳性能,属于同一芯片的GPIO应该在描述符数组中是连续的。
- value_array - 存储GPIO值(get)的数组或要分配给GPIO的值数组(set)
返回值:
gpiod_get_array_value()及其变体成功时返回0,错误返回负数。gpiod_get_value()在成功传递GPIO值时返回0或1。使用数组函数时,GPIO值存储在value_array中,而不是作为返回值传回。
小例子:
struct gpio_descs *my_gpio_descs = gpiod_get_array(...);
if(!my_gpio_descs)
return ERROR...
gpiod_set_array_value(my_gpio_descs->ndescs, my_gpio_descs->desc,
my_gpio_values);
配置为中断(可选)
int gpiod_to_irq(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
描述:获取与给定GPIO相对应的IRQ编号。
返回值:返回IRQ编号或负的errno代码(很可能是因为该特定GPIO不能用作IRQ)。
注意:
- 使用未使用
gpiod_direction_input()设置为输入的GPIO,或者使用最初不是来自gpiod_to_irq()的IRQ编号,是错误的操作。 - gpiod_to_irq()不允许休眠。
从gpiod_to_irq()返回的非错误值可以传递给request_irq()或free_irq()。
它们通常通过特定于板的初始化代码存储到平台设备的IRQ资源中。
注意,IRQ触发选项是IRQ接口的一部分,例如, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING,
导出到应用空间(可选)
drivers/gpio/gpiolib.c
/**
* gpiod_export - export a GPIO through sysfs
* @gpio: gpio to make available, already requested
* @direction_may_change: true if userspace may change gpio direction
* Context: arch_initcall or later
*
* When drivers want to make a GPIO accessible to userspace after they
* have requested it -- perhaps while debugging, or as part of their
* public interface -- they may use this routine. If the GPIO can
* change direction (some can't) and the caller allows it, userspace
* will see "direction" sysfs attribute which may be used to change
* the gpio's direction. A "value" attribute will always be provided.
*
* Returns zero on success, else an error.
*/
int gpiod_export(struct gpio_desc *desc, bool direction_may_change)
gpiod_export提供了用户层的访问,主要用于驱动工程师调试或者应用程序控制。
描述:将该gpio的信息通过sys文件系统导出,这样应用层可以直接查看状态、设置状态等。
参数解析:
- direction_may_change: 用来标记这个gpio的输入输出方向是否可以改变。
如果该gpio已经设置了输入或者输出,那么它的
direction_may_change为false。
兼容
旧的GPIO系统使用基于标号的结构而不是基于描述符。可以使用如下两个函数进行相互转换:
int desc_to_gpio(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
struct gpio_desc *gpio_to_desc(unsigned gpio);
注意:不能使用一套API的方法释放另一套API获取的设备。
附录:GPIO子系统其他内容
低有效和开漏语义
介绍
一般情况下,使用GPIO子系统的开发者并不需要关心GPIO对外的实际电平,因此,gpiod_set_value_xxx()或 gpiod_set_array_value_xxx() 这样的函数都以逻辑值操作。
这些函数会将低电平有效的性质考虑在内。也就是说,低电平有效,物理值0对应逻辑值的1。
如果我们事先告知内核某一个GPIO是低电平有效(
active_low)这些函数内部会进行处理,就不再需要我们关心“到底是不是电平1有效还是电平0有效”,
例如,如果设置了GPIO的低电平有效属性,并且gpiod_set_(array)_value_xxx()传递了逻辑值1(“asserted”),则物理线路电平将被驱动为低电平。
这同样适用于开漏或开源输出:它们并不输出高电平(开漏)或低电平(开源),它们只是将输出切换到高阻抗值。使用者应该不需要关注。
有关的详细信息,请参阅driver.txt中关于开漏的细节。
总结:
| 函数(示例) | 线路属性 | 物理线路 |
|---|---|---|
| gpiod_set_raw_value(desc, 0); | - | 低电平 |
| gpiod_set_raw_value(desc, 0); | - | 高电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 0); | 默认(高电平有效) | 低电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 1); | 默认(高电平有效) | 高电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 0); | 低电平有效 | 高电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 1); | 低电平有效 | 低电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 0); | 开漏 | 低电平 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 1); | 开漏 | 高阻态 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 0); | 开漏 | 高阻态 |
| gpiod_set_value(desc, 1); | 开漏 | 高电平 |
接口
当然,如果你硬是要知道GPIO此时的电平值(的确需要管理GPIO线路物理状态),可以使用下面的一组函数来达到你要的目的。
但应尽可能避免去读原始值,尤其是系统无关的驱动程序,它们只需要关心逻辑值。
下面的一组调用忽略GPIO的低有效或开漏属性,设置什么值,物理值就是什么什么值:
raw-value的意思就是不在乎DTS里面的ACTIVE,我set 高电平,就是高电平。
int gpiod_get_raw_value(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
void gpiod_set_raw_value(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value);
int gpiod_get_raw_value_cansleep(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
void gpiod_set_raw_value_cansleep(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value);
int gpiod_direction_output_raw(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value);
还可以使用以下方法查询GPIO的低有效属性:
int gpiod_is_active_low(const struct gpio_desc *desc);
请注意,这些函数只能在使用者明白自己在做什么的情况下使用;驱动程序一般不应该关心线路物理状态或开漏语义。
在设备树中设置低有效
假设我们在DTS里面这样设置
reset-gpios = <&gpio3 RK_PA3 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
然后我们这样调用:
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(gc5025->reset_gpio, 1);
因为DTS里面的active 状态是 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW,所以这个代码输出的是 低电平。
系统唤醒功能
这个功能与
ACPI有关。有关详细信息,请参阅
Documentation/acpi/gpio-properties.txt
在ACPI系统上,GPIO由设备的_CRS配置对象列出的GpioIo()/ GpioInt()资源描述。这些资源不提供GPIO的连接ID(名称),因此有必要为此目的使用附加机制。
符合ACPI 5.1或更新版本的系统可能可以提供_DSD配置对象,它可以用于提供_CRS中的GpioIo()/ GpioInt()资源描述的特定GPIO的连接ID。如果是这种情况,它将由GPIO子系统自动处理。但是,如果不存在_DSD,则GpioIo()/ GpioInt()资源与GPIOconnection ID之间的映射需要由设备驱动程序提供。
附录:legacy-api
#include <linux/gpio.h>
还有一组用于允许睡眠场景的
api没有给出,更多相关的说明可以参考Documentation/gpio/gpio-legacy.txt
使用流程:
- 申请、释放:
gpio_request、gpio_free - 设置GPIO方向:
gpio_direction_input、gpio_direction_output - 获取设置GPIO值:
gpio_get_value、gpio_set_value - (可选)设置为中断:
gpio_to_irq - (可选)导出到
sys文件系统:gpio_export
判断
/*
* "valid" GPIO numbers are nonnegative and may be passed to
* setup routines like gpio_request(). only some valid numbers
* can successfully be requested and used.
*
* Invalid GPIO numbers are useful for indicating no-such-GPIO in
* platform data and other tables.
*/
static inline bool gpio_is_valid(int number)
{
return number >= 0 && number < ARCH_NR_GPIOS;
}
描述:来判断获取到的gpio号是否是有效的,只有有效的gpio号,才能向内核中进行申请使用,因此,当我们从设备树的设备节点获取到gpio号,可以使用该函数进行判断是否有效。
参数解析:
- numb:需要判断的GPIO号。
返回值:合法为1,否则为0。
申请、释放
/* Always use the library code for GPIO management calls,
* or when sleeping may be involved.
*/
extern int gpio_request(unsigned gpio, const char *label);
extern void gpio_free(unsigned gpio);
/**
* struct gpio - a structure describing a GPIO with configuration
* @gpio: the GPIO number
* @flags: GPIO configuration as specified by GPIOF_*
* @label: a literal description string of this GPIO
*/
struct gpio {
unsigned gpio;
unsigned long flags;
const char *label;
};
int gpio_request_one(unsigned gpio, unsigned long flags, const char *label);
int gpio_request_array(struct gpio *array, size_t num);
void gpio_free_array(const struct gpio *array, size_t num);
/* CONFIG_GPIOLIB: bindings for managed devices that want to request gpios */
int devm_gpio_request(struct device *dev, unsigned gpio, const char *label);
int devm_gpio_request_one(struct device *dev, unsigned gpio,
unsigned long flags, const char *label);
void devm_gpio_free(struct device *dev, unsigned int gpio);
以
gpio_request为例,gpio_request_one、gpio_request_array是它的扩展,devm_为前缀的是gpio devres机制的实现。
描述:请求一个/一组gpio。
参数解析:
- gpio:gpio号,可以通过sdk开发包说明文档查看,或者查看设备树文件,也可以在
gpio chip驱动的实现中找到。 - flags:可以指定
GPIOF_OPEN_DRAIN、GPIOF_OPEN_SOURCE、GPIOF_DIR_IN、GPIOF_EXPORT等标志- 如果指定了
GPIOF_DIR_IN,那么后面就不需要自己再额外调用gpio_direction_input或者gpio_direction_output了, - 如果指定了
GPIOF_EXPORT,后面就不需要自己调用gpio_export了。
- 如果指定了
- label:向系统中申请GPIO使用的标签,类似于GPIO的名称
- array,num:是
gpio_request_array对gpio_request_one的封装,用于处理同时申请多个gpio的情形。 - dev:带有
devm_前缀,用于带设备资源管理版本的函数,因此在使用上面的函数时,需要指定设备的struct device指针,生命周期与设备相同。
返回值:成功返回0。
意义:gpio_request主要做了以下动作:
- 检查是否已经被申请,没有的话,标记为已申请
- 填充label到该pin数据结构,用于debug
- 如果chip driver提供了request回调,调用它
- 如果chip driver提供了get_direction回调,调用它,通过它更新pin数据结构,标明gpio方向
用法举例:
static struct gpio leds_gpios[] = {
{ 32, GPIOF_OUT_INIT_HIGH, "Power LED" }, /* default to ON */
{ 33, GPIOF_OUT_INIT_LOW, "Green LED" }, /* default to OFF */
{ 34, GPIOF_OUT_INIT_LOW, "Red LED" }, /* default to OFF */
{ 35, GPIOF_OUT_INIT_LOW, "Blue LED" }, /* default to OFF */
{ ... },
};
err = gpio_request_one(31, GPIOF_IN, "Reset Button");
if (err)
...;
err = gpio_request_array(leds_gpios, ARRAY_SIZE(leds_gpios));
if (err)
...;
gpio_free_array(leds_gpios, ARRAY_SIZE(leds_gpios));
设置方向
//设置gpio方向为输入/输出
gpio_direction_input 或者gpio_direction_output ---------<2> ;
static inline int gpio_direction_input(unsigned gpio)
{
return gpiod_direction_input(gpio_to_desc(gpio));
}
static inline int gpio_direction_output(unsigned gpio, int value)
{
return gpiod_direction_output_raw(gpio_to_desc(gpio), value);
}
描述:当我们使用gpio_request()函数族向系统中申请了GPIO资源后,可以使用上面的函数进行GPIO的方向设置:
- 函数
gpio_direction_input()用来设置GPIO的方向为输入 - 函数
gpio_direction_output()用来设置GPIO的方向为输出,并且通过value值可以设置输出的电平。
意义: gpio_direction_input或者gpio_direction_output主要是回调gpio chip driver提供的direction_input或者direction_output来设置该gpio寄存器为输入、输出。
导出
// include/asm-generic/gpio.h
/*
* A sysfs interface can be exported by individual drivers if they want,
* but more typically is configured entirely from userspace.
*/
static inline int gpio_export(unsigned gpio, bool direction_may_change)
{
return gpiod_export(gpio_to_desc(gpio), direction_may_change);
}
gpio_export提供了用户层的访问,主要用于驱动工程师调试或者应用程序控制。
描述:将该gpio的信息通过sys文件系统导出,这样应用层可以直接查看状态、设置状态等。
参数解析:
- direction_may_change: 用来标记这个gpio的输入输出方向是否可以改变。
如果该gpio已经设置了输入或者输出,那么它的
direction_may_change为false。
使用
static inline int gpio_get_value(unsigned int gpio)
{
return __gpio_get_value(gpio);
}
static inline void gpio_set_value(unsigned int gpio, int value)
{
__gpio_set_value(gpio, value);
}
描述:当我们将GPIO的方向设置为输入时,可以使用上面的函数gpio_get_value()来获取当前的IO口电平值,当GPIO的方向设置为输出时,使用函数gpio_set_value()可以设置IO口的电平值。
申请中断
static inline int gpio_to_irq(unsigned int gpio)
{
return __gpio_to_irq(gpio);
}
描述:用于获取该gpio对应的中断号,这个需要设备树里的该gpio节点描述使用哪个中断号
并不是所有的gpio都可以触发中断的。
意义:回调gpio chip driver提供的to_irq。
例子
设备树(高通msm平台):
dev_gpio {
status = "okay";
compatible = "dev-gpio";
label = "test_gpio";
gpios = <&msm_gpio 68 0>;
};
驱动程序:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
struct gpio_platform_data {
const char *label;
unsigned int gpio_num;
enum of_gpio_flags gpio_flag;
};
struct gpio_drvdata {
struct gpio_platform_data *pdata;
bool gpio_state;
};
static ssize_t ctrl_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct gpio_drvdata *ddata = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
int ret;
if (ddata->gpio_state)
ret = snprintf(buf, PAGE_SIZE - 2, "%s", "enable");
else
ret = snprintf(buf, PAGE_SIZE - 2, "%s", "disable");
buf[ret++] = '
';
buf[ret] = '�';
return ret;
}
static ssize_t ctrl_store(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count)
{
struct gpio_drvdata *ddata = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
bool state = ddata->gpio_state;
if (!strncmp(buf, "enable", strlen("enable"))) {
if (!state) {
gpio_set_value(ddata->pdata->gpio_num, !state);
ddata->gpio_state = !state;
goto ret;
}
} else if (!strncmp(buf, "disable", strlen("disable"))) {
if (state) {
gpio_set_value(ddata->pdata->gpio_num, !state);
ddata->gpio_state = !state;
goto ret;
}
}
return 0;
ret:
return strlen(buf);
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(ctrl, 0644, ctrl_show, ctrl_store);
static ssize_t gpio_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct gpio_drvdata *ddata = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
int ret;
ret = snprintf(buf, PAGE_SIZE - 2, "gpio-number: GPIO_%d",
ddata->pdata->gpio_num - 911);
buf[ret++] = '
';
buf[ret] = '�';
return ret;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(gpio, 0444, gpio_show, NULL);
static struct attribute *gpio_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_ctrl.attr,
&dev_attr_gpio.attr,
NULL
};
static struct attribute_group attr_grp = {
.attrs = gpio_attrs,
};
static struct gpio_platform_data *
gpio_parse_dt(struct device *dev)
{
int ret;
struct device_node *np = dev->of_node;
struct gpio_platform_data *pdata;
pdata = kzalloc(sizeof(*pdata), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pdata) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to alloc memory of platform data
");
return NULL;
}
ret = of_property_read_string(np, "label", &pdata->label);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to read property of lable
");
goto fail;
}
pdata->gpio_num = of_get_named_gpio_flags(np, "gpios",
0, &pdata->gpio_flag);
if (pdata->gpio_num < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "invalid gpio number %d
", pdata->gpio_num);
ret = pdata->gpio_num;
goto fail;
}
return pdata;
fail:
kfree(pdata);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
static int gpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct gpio_drvdata *ddata;
struct gpio_platform_data *pdata;
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct device_node *np = dev->of_node;
int ret;
printk("[%s]==========gpio_probe start==========
", __func__);
if (!np) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to find device node of gpio device
");
return -ENODEV;
}
ddata = kzalloc(sizeof(*ddata), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ddata) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to alloc memory for driver data
");
return -ENOMEM;
}
pdata = gpio_parse_dt(dev);
if (IS_ERR(pdata)) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to parse device node
");
ret = PTR_ERR(pdata);
goto fail1;
}
/* gpio初始化 */
if (gpio_is_valid(pdata->gpio_num)) {
/* 申请gpio资源 */
ret = gpio_request(pdata->gpio_num, pdata->label);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to request gpio number %d
",
pdata->gpio_num);
goto fail2;
}
/* 设置gpio的方向(输出) */
ret = gpio_direction_output(pdata->gpio_num, 0);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to set gpio direction for output
");
goto fail3;
}
/* 在sysfs中导出gpio(方向不能改变) */
ret = gpio_export(pdata->gpio_num, false);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to export gpio %d
", pdata->gpio_num);
goto fail3;
}
/* 设置gpio电平值(高电平) */
gpio_set_value(pdata->gpio_num, 1);
}
ddata->gpio_state = false;
ddata->pdata = pdata;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, ddata);
ret = sysfs_create_group(&dev->kobj, &attr_grp);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to create sysfs files
");
goto fail3;
}
printk("[%s]==========gpio_probe over==========
", __func__);
return 0;
fail3:
gpio_free(pdata->gpio_num);
fail2:
kfree(pdata);
fail1:
kfree(ddata);
return ret;
}
static int gpio_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct gpio_drvdata *ddata = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct gpio_platform_data *pdata = ddata->pdata;
sysfs_remove_group(&pdev->dev.kobj, &attr_grp);
/* 释放已经申请的gpio资源 */
if (gpio_is_valid(pdata->gpio_num))
gpio_free(pdata->gpio_num);
kfree(pdata);
pdata = NULL;
kfree(ddata);
ddata = NULL;
return 0;
}
static struct of_device_id device_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "dev-gpio",},
{ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, device_match_table);
static struct platform_driver dev_gpio_driver = {
.probe = gpio_probe,
.remove = gpio_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "dev-gpio",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = device_match_table,
},
};
module_platform_driver(dev_gpio_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("HLY");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
当驱动模块加载的时候,由于嵌入了platform_driver这个驱动框架中,所以看起来复杂一点,实际上根据上面的注释进行参考即可:
- 需要获取要使用的GPIO号,然后需要向系统申请使用GPIO资源
- 资源申请成功后,我们需要设置GPIO的方向(输入或者输出),
- 此外,还能使用gpio_export()函数在sysfs中导出GPIO,导出的好处在于可以方便地debug代码,
- 当驱动模块卸载时,需要将已经申请的GPIO资源进行释放掉
另外,在设备节点中导出了ctrl和gpio属性文件,便可以很方便地在应用层进行设备的GPIO控制了。
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/schips/p/linux_subsystem_using_gpio_ss.html