什么是集合?
记得在高中《数学》课本中的定义是:一般地,我们把研究对象统称为元素;把一些元素组成的总体叫做集合,也简称集。
在java中,把数据以某种特定的排列方式放到一起构成集合,这种数据的结构在JAVA中被体现为集合。在JAVA的集合中有对应的结构算法,JAVA中集合中使用的数据结构有,链表,散列存储,映射,树等等。
什么是集合框架?
集合框架是为表示和操作集合而规定的一种统一的标准的体系结构。
为什么要使用集合框架?
数组相信大家也不会陌生。那么我们为什么要是用数组呢?当我们需要保持一组一样(类型相同)的元素的时候,我们应该使用一个容器来保存,数组就是这样一个容器。但是,数据有一个不足,那就是定义数组时一定要确定数组的长度。然而,在开发中我们经常需要动态的来保存我们的数据,因此数组肯定是不行了。那么怎么办呢?数据结构!使用数据结构的知识可以达到以上要求,但是对于一般开发者来讲数据结构的实现相对繁琐,因此产生了java中的集合(它就是对一些实现好了的数据结构的包装,使用方便,最重要的是解决了类集框架本身不受对象数组长度的限制)。
集合框架简介:
三大特性:
- 这种框架是高性能的,对基本类集(动态数组、链表、树、离散表)的实现是高效率的。所以很少需要人工对这些“数据引擎”编写代码。
- 框架必须允许不同类型的类集以相同的方式和高度(解释:方式是指对于对象的操作形式,如add();高度是指类集中的元素类型都是统一的)互操作方式工作。
- 类集必须是容易扩展和修改的。因此,类集框架被设计成包含了一组标准接口。
常用接口及其继承关系:

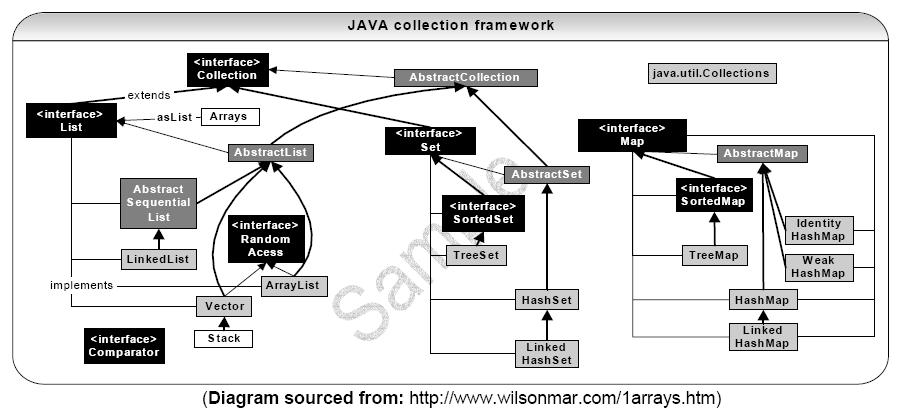
(以上两张图片均来自于网络)
从图看可能有点乱,来个简单的:
Collection
├List
│├LinkedList
│├ArrayList
│└Vector
│ └Stack
└Set
Map
├Hashtable
├HashMap
└WeakHashMap
|
有序否 |
允许元素重复否 |
||
|
Collection |
否 |
是 |
|
|
List |
是 |
是 |
|
|
Set |
AbstractSet |
否 |
否 |
|
HashSet |
|||
|
TreeSet |
是(用二叉树排序) |
||
|
Map |
AbstractMap |
否 |
使用key-value来映射和存储数据,Key必须惟一,value可以重复 |
|
HashMap |
|||
|
TreeMap |
是(用二叉树排序) |
||
集合框架的简单使用:
List接口:
ArrayList的使用:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list_test=null; Collection<String> coll_test=null; list_test=new ArrayList<String>(); coll_test=new ArrayList<String>(); System.out.println("add remove 操作:"); list_test.add("add");//添加元素 coll_test.add("coll"); list_test.add(0, "first");//在指定位置添加元素 list_test.addAll(coll_test);//添加添加一组元素 list_test.addAll(0, coll_test);//在指定位置添加一组元素 System.out.println(list_test); list_test.add("remove first and add"); list_test.remove(1);//删除指定位置的元素 list_test.remove("add");//删除指定内容的元素 System.out.println(list_test); System.out.println("输出list内容:"); for(int i=0;i<list_test.size();i++){ System.out.print(list_test.get(i)+" "); } System.out.println(" "+"将集合变为对象数组:"); String str[]=list_test.toArray(new String[] {}); for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++){ System.out.print(str[i]+"、"); } Object obj[]=list_test.toArray(); for(int i=0;i<obj.length;i++){ String temp=(String)obj[i]; System.out.print(temp+"、"); } System.out.println(" "+"集合操作前是否为空?"+list_test.isEmpty()); System.out.println("判断元素是否存在:"); System.out.println(list_test.contains("coll")?""coll"字符串存在!":""coll"字符串不存在!"); List<String> strlist=list_test.subList(1, 3); System.out.println("截取集合为:"); for(int i=0;i<strlist.size();i++){ System.out.print(strlist.get(i)+"、"); } System.out.println(" "+"查找coll字符串的位置:"+list_test.indexOf("remove first and add")); } }
运行结果:
Vector类的使用:
如果直接使用的是List接口进行操作,则几乎和ArrayList没有任何区别。但因为出现较早,有些List接口中没有的方法,如:addElement(E o)方法,是最早的想集合中添加元素的操作,但在JDK1.2之后此方法功能与List中的add()方法是一致的。
是用旧方法:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector<String> list=new Vector<String>(); list.addElement("001"); list.addElement("002"); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ System.out.print(list.get(i)+"、"); } } }
运行结果:
Vector与ArrayList的区别请参考另一篇文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/scetopcsa/articles/3703571.html
LinkedList的使用:
LinkedList表示的是一个链表的操作类,此类实现了List和Queue两个接口。Queue接口是Collection的子接口。
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<String> link=new LinkedList<String>(); link.add("001"); link.add("002"); link.add("003"); link.add("004"); System.out.println("初始化链表:"+link); link.addFirst("000"); link.addLast("00n"); System.out.println("增加头尾后:"+link); System.out.println("element方法找到表头:"+link.element()); System.out.println("链表内容:"+link); System.out.println("peek方法找到表头(不删除表头):"+link.peek()); System.out.println("链表内容:"+link); System.out.println("poll方法找到表头(删除表头):"+link.poll()); System.out.println("链表内容:"+link); System.out.println("以FIFO的方式输出:"); int t=link.size(); for(int i=0;i<t;i++){ System.out.print(link.poll()+"、"); } System.out.println(" 操作最后"+link); } }
运行结果:
Set接口:
Set接口也是Conllection接口的子接口,与List接口的定义没有太大的区别,但是与Collection或是List接口不同的是,Set接口中不能加入重复的元素。
Set接口常用的子类:
散列的存放:HashSet(不能存放重复的元素,采用散列的存储方式,所以没有顺序)
有序的存放:TreeSet(有序排放)(TreeSet对于对象的排序,以后再详谈)
SortedSet接口:TreeSet中实现了SortedSet接口,此接口主要是用于排序操作,即实现此接口的子类都是属于排序的子类。
下面是常用方法的例子:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<String> allset=new HashSet<String>(); allset.add("C"); allset.add("A"); allset.add("Z"); allset.add("A"); allset.add("O"); System.out.println(allset); Set<String> treeset=new TreeSet<String>(); treeset.add("A"); treeset.add("A"); treeset.add("D"); treeset.add("Z"); treeset.add("Q"); System.out.println(treeset); SortedSet<String> sortset=new TreeSet<String>(); sortset.add("A"); sortset.add("A"); sortset.add("D"); sortset.add("B"); sortset.add("Z"); sortset.add("S"); sortset.add("P"); System.out.println(sortset); System.out.println("第一个元素:"+sortset.first());//返回集合中的第一个元素 System.out.println("最后一个元素:"+sortset.last());//返回最后一个元素 System.out.println("headSet元素:"+sortset.headSet("D"));//返回从开始到指定元素的集合 System.out.println("tailSet元素:"+sortset.tailSet("S"));//从指定元素到最后 System.out.println("subSet元素:"+sortset.subSet("B", "P"));//返回指定对象间的元素 } }
运行结果如下:

集合的输出:
如果要输出Collection、Set集合中的内容,可以将其转换成对象数组输出,而使用List则可以直接通过get()方式输出,但是这些都不是标准的集合输出方式。
在类集中提供了的常见输出方式有迭代输出、foreach等
迭代输出:
Iterator是专门的迭代输出接口,所谓的迭代输出就是将元素一个个进行判断,判断是否有内容,如果有内容则把内容取走。
Iterator有三个常用方法,均已注释出。
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> all = new ArrayList<String>(); all.add("nihao"); all.add(":"); all.add("你好"); Iterator<String> iter = all.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) {// iter.hasNext()判断是否有下一个值 System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");// iter.next()取出当前值 } } }
运行结果:
删除方法:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> all = new ArrayList<String>(); all.add("nihao"); all.add(":"); all.add("你好"); Iterator<String> iter = all.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) {// iter.hasNext()判断是否有下一个值 String str = iter.next(); if (str.equals(":")) { iter.remove();// 删除当前元素 } } System.out.println("删除后的集合:" + all); } }
运行结果:
需要注意的是:不要把集合自带的remove()删除方法和Iterator的remove()方法弄混了。
Iterator的子接口ListIterator可实现双向输出,而Iterator为单向输出。另外,ListIterator的add()、set()方法分别可以实现增加和替换集合中的元素。
foreach输出的简单用法:
foreach除了可以完成数组的输出,对于集合也同样支持。
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> all = new ArrayList<String>(); all.add("nihao"); all.add(":"); all.add("你好"); for(String str:all){ System.out.print(str+" "); } } }
运行结果:
Map接口:
子类HashMap的简单使用:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> map = null; map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("sctop", "www.scetop.com"); map.put("top", "www.scetop.com");// 增加内容 System.out.println("取出内容:" + map.get("top"));// 输出内容 if (map.containsKey("top")) {// 查找指定的key是否存在 System.out.println("Key值top存在"); } else { System.out.println("Key值top不存在"); } if (map.containsValue("www.scetop.com")) {// 查找指定的value是否存在 System.out.println("搜索Value值存在"); } else { System.out.println("搜索Value值不存在"); } Set<String> keys = map.keySet();// 得到全部的KEY // 迭代输出 Iterator<String> iter = keys.iterator(); System.out.print("输出全部的key值:"); while (iter.hasNext()) { String str = iter.next(); System.out.print(str + "、"); } Collection<String> values = map.values();// 得到全部的values Iterator<String> iter1 = values.iterator(); System.out.print(" " + "输出全部的value:"); while (iter1.hasNext()) { String str = iter1.next(); System.out.print(str + "、"); } } }
运行如下:
map的旧子类中有一个hashtable,但在使用上与hashmap没有太大的不同。
Hashtable和HashMap的区别:
| 序号 | 比较点 | HashMap | Hashtable |
| 1 | 推出时间 | JDK1.2之后推出的,属于新的操作类 | JDK1.0时推出,属于旧类 |
| 2 | 性能 | 采用异步处理方式,性能更高 | 采用同步处理方式,性能较低 |
| 3 | 线程安全 | 属于非线程安全的操作类 | 属于线程安全的操作类 |
| 4 | 空键 | 允许将KEY设置为null | 不允许将KEY设置为null,会出现null pointer exception |
另外,子类TreeMap的使用也与上面的使用方法并无大异,值得注意的是:TreeMap的主要特点是可以按照KEY排序,而前者不能。






