一.冒泡
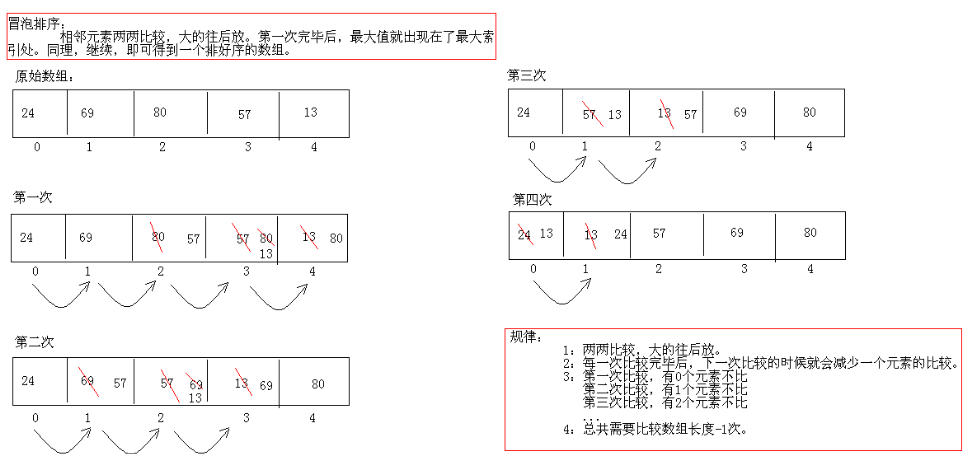
def sort(alist): length = len(alist) for j in range(length-1): for i in range(length-1-j): if alist[i] > alist[i+1]: temp = alist[i] alist[i] = alist[i+1] alist[i+1] = temp return alist
alist = [3,8,5,7,6,4,1,2] print(sort(alist))
结果为:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
二.选择
- 选择排序改进了冒泡排序,每次遍历列表只做一次交换。为了做到这一点,
一个选择排序在他遍历时寻找最大的值,并在完成遍历后,将其放置在正确的位置。
找到最大元素,放到最后位置
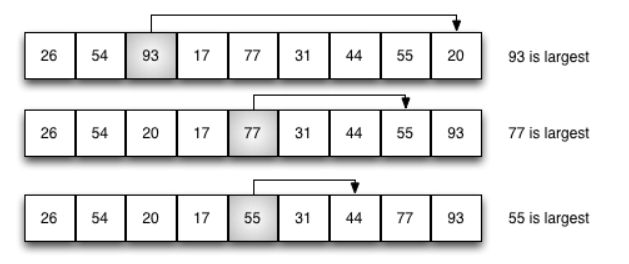
def sort(alist): length = len(alist) for j in range(length-1,0,-1): #数据中最大元素的下标 max_index = 0 #该循环就可以定位到最大元素值的索引(max_index) for i in range(1,j+1): if alist[i] > alist[max_index]: max_index = i #将最大值放置到列表最后的位置 alist[max_index],alist[j] = alist[j],alist[max_index] return alist
alist = [3,8,5,7,6,4,1,2] print(sort(alist))
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
三.插入
- 插入排序的主要思想是每次取一个列表元素与列表中已经排序好的列表段进行比较,
然后插入从而得到新的排序好的列表段,最终获得排序好的列表。比如,待排序列表为
[49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49],则比较的步骤和得到的新列表如下:
(带有背景颜色的列表段是已经排序好的,红色背景标记的是执行插入并且进行过交换的元素)

def sort(alist): for j in range(1,len(alist)): i = j while i>0: if alist[i] < alist[i-1]: alist[i],alist[i-1] = alist[i-1],alist[i] i = i-1 else: break return alist
alist = [49,38,65,97,76,13,27] print(sort(alist))
# [13, 27, 38, 49, 65, 76, 97]
四.希尔
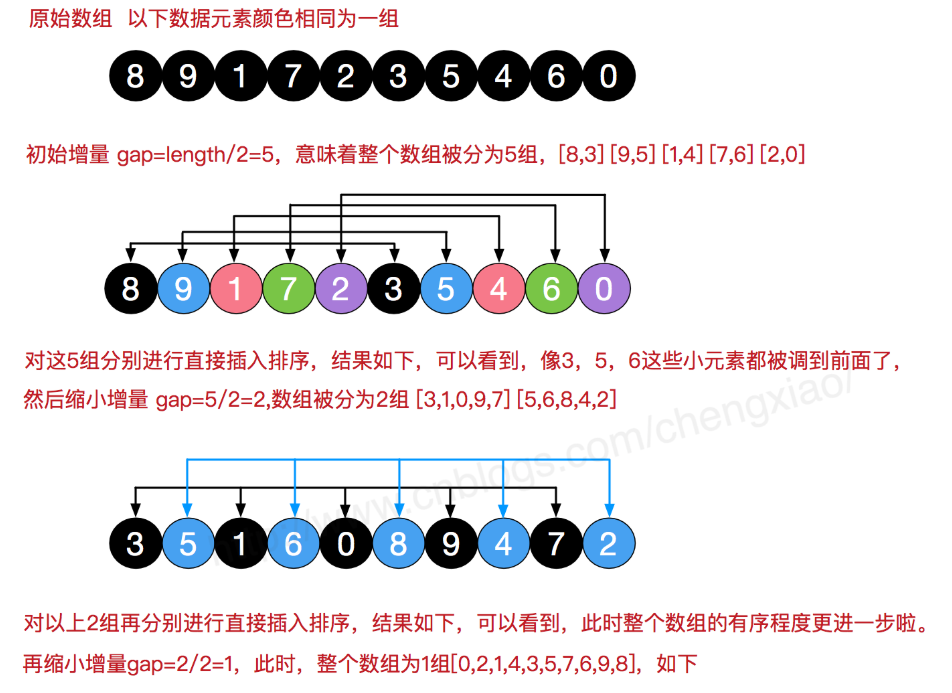
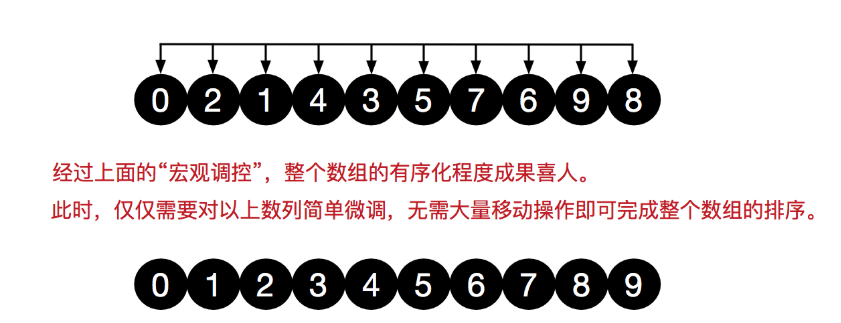
def sort(alist): gap = len(alist) // 2 while gap >= 1: for j in range(gap,len(alist)): i = j while i>0: if alist[i] < alist[i-gap]: alist[i],alist[i-gap] = alist[i-gap],alist[i] i = i-gap else: break #缩减增量 gap = gap//2 return alist
alist = [49,38,65,97,76,13,27] print(sort(alist))
# [13, 27, 38, 49, 65, 76, 97]
五.快排
左右假象两个游标 1.先让0位置的元素为中间值 2.从右边开始比较,比它大的不变,小的放在前面前面游标位置 3.小时就在从左边开始小的不变,大的放在右边游标位置 4.最后中间的空位,放开始的0位置的值
def sort(alist,start,end): low = start high = end mid = alist[0] if low >= high: return while low < high: while low < high: #判断的话要从右往左 if alist[high] > mid: high -= 1 else: alist[low] = alist[high] break while low < high: #判断的话要从左往右 if alist[low] < mid: low += 1 else: alist[high] = alist[low] break alist[low] = mid #mid左侧的子列表 sort(alist,start,low-1) #mid右侧的子列表 sort(alist,low+1,end) return alist
alist = [49,38,65,97,76,13,27,55] print(sort(alist,0,len(alist)-1))
# [13, 27, 38, 49, 13, 13, 13, 55]