NumPy(Numerical Python) 是 Python 语言的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。
一.创建
1. 使用np.array() 创建
导入模块:
import numpy as np
①一维数据创建
np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
结果为:
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
②二维数组创建
np.array([[1,2,3.2],[4,5,6]])
array([[ 1. , 2. , 3.2], [ 4. , 5. , 6. ]])
注意: numpy默认ndarray的所有元素的类型是相同的
如果传进来的列表中包含不同的类型,则统一为同一类型,优先级:str>float>int
2.使用np 的 routlines 函数创建
①np.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None) 等差数列
np.linspace(0,100,num=51)
结果为:
array([ 0., 2., 4., 6., 8., 10., 12., 14., 16., 18., 20., 22., 24., 26., 28., 30., 32., 34., 36., 38., 40., 42., 44., 46., 48., 50., 52., 54., 56., 58., 60., 62., 64., 66., 68., 70., 72., 74., 76., 78., 80., 82., 84., 86., 88., 90., 92., 94., 96., 98., 100.])
②np.arange([start, ]stop, [step, ]dtype=None)
np.arange(0,100,2)
结果为:
array([ 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98])
③np.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
np.random.randint(0,100,size=(5,6))
结果为:
array([[46, 91, 10, 79, 98, 47], [66, 41, 99, 7, 69, 22], [99, 51, 25, 49, 82, 59], [ 6, 20, 28, 33, 63, 66], [29, 58, 91, 46, 60, 57]])
④np.random.random(size=None)
np.random.random((5,5))
结果为:
array([[ 0.44483672, 0.14777086, 0.83894078, 0.50285068, 0.27617434], [ 0.96386475, 0.11509807, 0.83173289, 0.93913778, 0.74246338], [ 0.71150576, 0.09607129, 0.04946329, 0.72253115, 0.65797176], [ 0.47363412, 0.2775543 , 0.40101206, 0.05375956, 0.30270107], [ 0.05198828, 0.62509195, 0.42600588, 0.18691781, 0.54398897]])
#指定变化因子,生成的数据就不会变化了
np.random.seed(90) np.random.randint(0,100,size=(5,6))
array([[91, 29, 31, 67, 39, 68], [58, 37, 18, 74, 96, 51], [30, 80, 18, 77, 82, 9], [ 0, 0, 10, 95, 12, 4], [26, 9, 48, 70, 75, 80]])
二.属性
4个必记参数:
ndim:维度
shape:形状(各维度的长度)
size:总长度
dtype:元素类型
#使用matplotlib.pyplot获取一个numpy数组,数据来源于一张图片
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline
cat_img_arr = plt.imread('./cat.jpg')
plt.imshow(cat_img_arr)

#查看形状:
cat_img_arr.shape
#结果为:
(456, 730, 3)
#查看元素类型:
cat_img_arr.dtype
结果为:
dtype('uint8')
三.基本操作
#生成数组
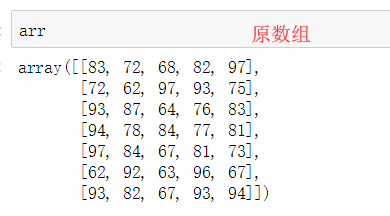
arr = np.random.randint(60,100,size=(7,5))
array([[75, 90, 93, 74, 91], [62, 62, 83, 88, 62], [78, 61, 92, 67, 82], [66, 73, 62, 61, 66], [93, 73, 72, 67, 93], [79, 71, 98, 69, 62], [64, 94, 98, 83, 74]])
1.索引
①获取第一行
arr[0]
array([75, 90, 93, 74, 91])
②获取前两行
arr[[0,1]]
array([[75, 90, 93, 74, 91], [62, 62, 83, 88, 62]])
2.切片
①获取前两行
arr[0:2]
array([[75, 90, 93, 74, 91], [62, 62, 83, 88, 62]])
②获取前两列
arr[:,0:2] #逗号左边表示行 右边表示列
array([[75, 90], [62, 62], [78, 61], [66, 73], [93, 73], [79, 71], [64, 94]])
③获取前两行和前两列
arr[0:2,0:2]
array([[75, 90], [62, 62]])
④行倒序
arr[::-1]
array([[64, 94, 98, 83, 74], [79, 71, 98, 69, 62], [93, 73, 72, 67, 93], [66, 73, 62, 61, 66], [78, 61, 92, 67, 82], [62, 62, 83, 88, 62], [75, 90, 93, 74, 91]])
⑤列倒序
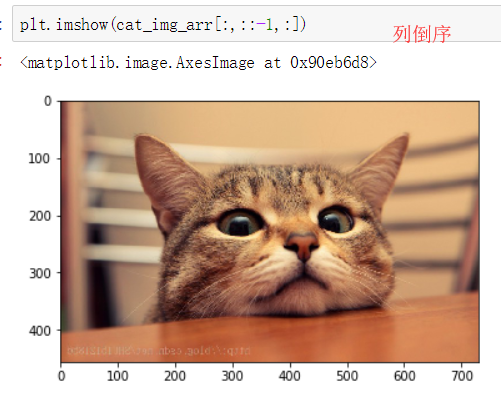
arr[:,::-1]
array([[91, 74, 93, 90, 75], [62, 88, 83, 62, 62], [82, 67, 92, 61, 78], [66, 61, 62, 73, 66], [93, 67, 72, 73, 93], [62, 69, 98, 71, 79], [74, 83, 98, 94, 64]])
⑥全部倒序
arr[::-1,::-1]
array([[74, 83, 98, 94, 64], [62, 69, 98, 71, 79], [93, 67, 72, 73, 93], [66, 61, 62, 73, 66], [82, 67, 92, 61, 78], [62, 88, 83, 62, 62], [91, 74, 93, 90, 75]])
⑦将图片的数组倒叙


3.变形
①将多维数组变形成一维数组
arr1 = arr.reshape((35,))
array([75, 90, 93, 74, 91, 62, 62, 83, 88, 62, 78, 61, 92, 67, 82, 66, 73, 62, 61, 66, 93, 73, 72, 67, 93, 79, 71, 98, 69, 62, 64, 94, 98, 83, 74])
②将一维数组变形成多维数组
arr1.reshape((5,7))
# -1 表示自动补充,这两种结果一样 arr1.reshape((-1,7))
array([[75, 90, 93, 74, 91, 62, 62], [83, 88, 62, 78, 61, 92, 67], [82, 66, 73, 62, 61, 66, 93], [73, 72, 67, 93, 79, 71, 98], [69, 62, 64, 94, 98, 83, 74]])
4.级联
①将两个数组进行级联
np.concatenate((arr,arr),axis=1)
array([[75, 90, 93, 74, 91, 75, 90, 93, 74, 91], [62, 62, 83, 88, 62, 62, 62, 83, 88, 62], [78, 61, 92, 67, 82, 78, 61, 92, 67, 82], [66, 73, 62, 61, 66, 66, 73, 62, 61, 66], [93, 73, 72, 67, 93, 93, 73, 72, 67, 93], [79, 71, 98, 69, 62, 79, 71, 98, 69, 62], [64, 94, 98, 83, 74, 64, 94, 98, 83, 74]])
②合并图片
arr_3 = np.concatenate((cat_img_arr,cat_img_arr,cat_img_arr),axis=1) arr_9 = np.concatenate((arr_3,arr_3,arr_3),axis=0) plt.imshow(arr_9)

级联需要注意的点: 级联的参数是列表:一定要加中括号或小括号
维度必须相同
形状相符:在维度保持一致的前提下,如果进行横向(axis=1)级联,必须保证进行级联的数组行数保持一致。如果进行纵向(axis=0)级联,必须保证进行级联的数组列数保持一致。
可通过axis参数改变级联的方向
5.切分


四.聚合操作
np.sum 求和 np.prod np.nanprod Compute product of elements np.mean 平均 np.std np.nanstd Compute standard deviation np.var np.nanvar Compute variance np.min 最小 np.max 最大 np.argmin np.nanargmin Find index of minimum value np.argmax np.nanargmax Find index of maximum value np.median np.nanmedian Compute median of elements np.percentile np.nanpercentile Compute rank-based statistics of elements np.any N/A Evaluate whether any elements are true np.all N/A Evaluate whether all elements are true np.power 幂运算
示例:
arr.mean(axis=1)
array([ 84.6, 71.4, 76. , 65.6, 79.6, 75.8, 82.6])
五.排序
np.sort()与ndarray.sort()都可以,但有区别:
np.sort()不改变输入值
ndarray.sort()本地处理,不占用空间,但改变输入值