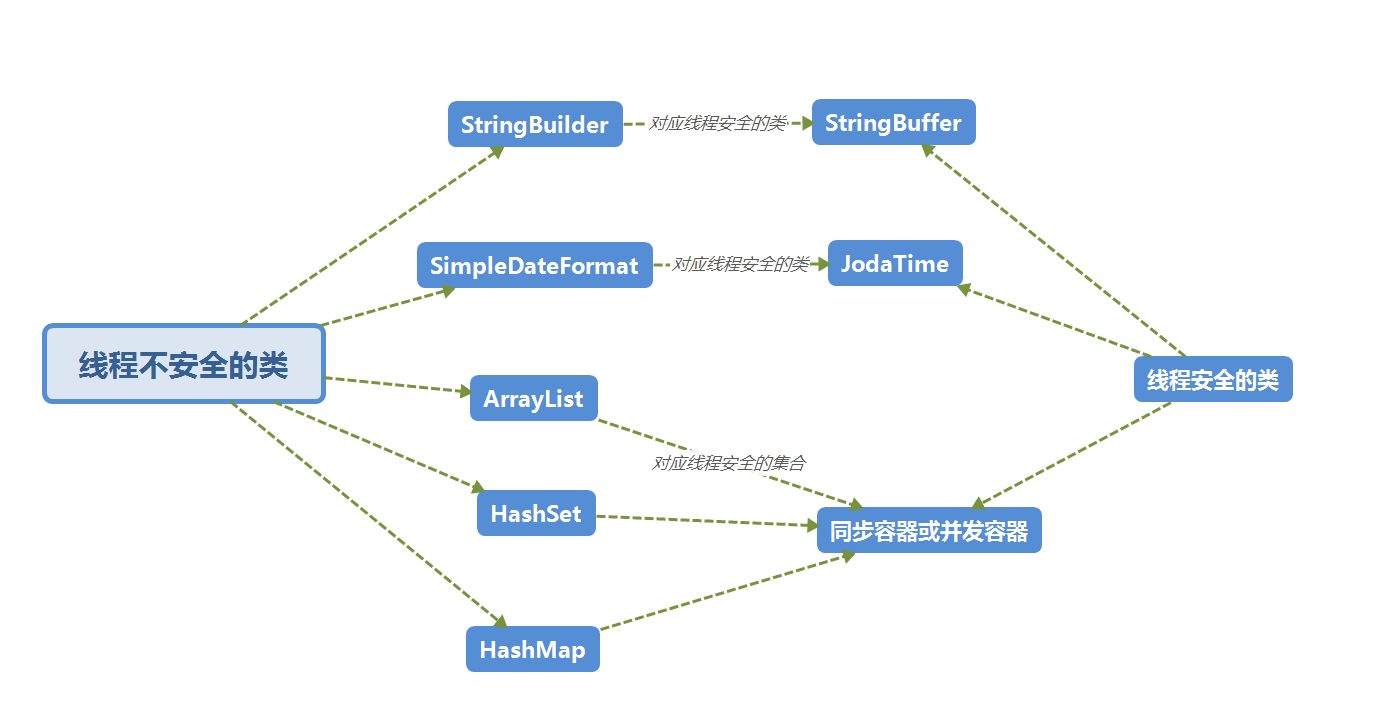
什么是线程不安全的类呢?
如果一个类的对象同时被多个线程访问,如果不做特殊的同步或并发处理,很容易表现出线程不安全的现象,比如抛出异常、逻辑处理错误等,这种类我们就称为线程不安全的类
常见线程不安全的类有哪些呢
下图中,我们只画出了最常见的几种情况,我们常见的Collections集合都是线程不安全的
StringBuilder-demo
@Slf4j public class StringExample1 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; public static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); private static void update() { stringBuilder.append("1"); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}",stringBuilder.length()); } }
我测试的时候输出为,4985(因为线程不安全,所以每次的输出可能是不同的),如果StringBuilder类为线程安全的话,输出应该为5000
StringBuffer-demo
@Slf4j public class StringExample2 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; public static StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); private static void update() { stringBuffer.append("1"); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}",stringBuffer.length()); } }
输出为5000,且多次测试结果均为5000,证明StringBuffer类是线程安全的,通过看StringBuffer的实现可发现,其所有的实现都是加了synchronized关键字的,虽然可以保证线程安全但是性能是有损耗的,这也证明了StringBuilder的存在价值,如果定义StringBuilder为局部变量时是没有线程安全问题的,这就用到了上篇博客我们讲的堆栈封闭原理
simpleDateFormat-demo1
@Slf4j public class DateFormatExample1 { private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd"); //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; private static void update() { try { simpleDateFormat.parse("20180208"); } catch (ParseException e) { log.error("parse exception",e); } } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); } }
运行结果如下:

因为simpleDateFormat为线程不安全的类,所以在多线程访问的时候出现了异常
simpleDateFormat-demo2
@Slf4j public class DateFormatExample2 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; private static void update() { try { //用堆栈封闭的方式 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd"); simpleDateFormat.parse("20180208"); } catch (ParseException e) { log.error("parse exception",e); } } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); } }
此demo为demo1的改进版,将SimpleDateFormat声明为局部变量,运用了堆栈封闭的方式保证了线程安全,运行此demo是没有异常抛出的
jodatime-demo
import org.joda.time.DateTime; import org.joda.time.format.DateTimeFormat; import org.joda.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; @Slf4j public class DateFormatExample3 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; private static DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormat.forPattern("yyyyMMdd"); private static void update(int i) { log.info("{},{}",i,DateTime.parse("20180208", dateTimeFormatter).toDate()); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); } }
此demo引用了joda.time包,保证了线程安全,在实际的开发中,我们更推荐做日期转换的时候使用此包,这种处理方法不仅能保证线程安全,而且还有其它的优势。我导入的包如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
</dependency>
以下我们做ArrayList,HashMap,HashSet的实例演示,它们都是线程不安全的,还好我们一般都将它们定义为局部变量(堆栈封闭),如果我们将它们定义为成员变量或static修饰的变量,在多个线程同时访问的时候就很容易出问题。
ArrayList-demo
@Slf4j public class ArrayListExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); private static void update(int i) { list.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", list.size()); } }
如果是线程安全的输出应该为5000,实际输出为4945,且每次运行输出的值可能不一样,所以它是线程不安全的
HashSet-demo
@Slf4j public class HashSetExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //HashSet是线程不安全的 private static Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); private static void update(int i) { set.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", set.size()); } }
输出为4985,是线程不安全的(线程安全的话输出为5000)
HashMap-demo
@Slf4j public class HashMapExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //HashMap是线程不安全的 private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); private static void update(int i) { map.put(i,i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", map.size()); } }
输出为4886(且每次运行输出值可能不同),是线程不安全的(线程安全的话输出为5000)
线程不安全的写法
典型的线程不安全的写法是:先检查,再执行
if(condition(a)){handle(a);} 就算a是一个线程安全的类所对应的对象,对a的处理handle(a)也是原子性的,但由于这两步之间的不是原子性的也会引发线程安全问题,如A、B两个线程都通过了a的判断条件,A线程执行handle(a)之后,a已经不符合condition(a)的判断条件了,可是此时B线程仍然要执行handle(a),这就引发了线程安全问题。