通常我们保证线程安全策略的方式有以下几种:
a、不可变对象
b、线程封闭
c、同步容器
d、并发容器
不可变对象

可参考string类,可以采用的方式是将类声明为final,将所有成员都声明为私有的,对变量不提供set方法,将所有可变成员声明为final,通过构造器初始化所有成员,进行深度拷贝,在get方法中不直接返回对象本身,而是返回对象的拷贝。
关于final,我们详细说明一下

final-demo
@Slf4j public class ImmutableExample1 { private final static Integer a = 1; private final static String b = "2"; private final static Map<Integer, Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap(); static { map.put(1, 2); map.put(3, 4); map.put(5, 6); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 被final修饰的基本数据类型无法改变 // a = 2; // b = "2"; // 引用对象,此引用无法指向别的对象,但可修改该对象的值 map.put(1,3); log.info("{}", map.get(1)); } //final可修饰传递进来的对象 private void test(final int a) { } }
此demo需要我们注意的是,final修饰引用类型时,虽然不能将引用再指向别的对象,但可修改该对象的值;此外final还可修饰参数,这样传递进来的参数a无法被修改。此demo不是线程安全的
除了final可以定义不可变对象,java提供的Collections类,也可定义不可变对象,Collections.unmodifiableXXX传入的对象一经初始化便无法修改,XXX可表示Collection、List、Set、Map等,谷歌提供的Guava类,也有类似的功能,ImmutableXXX,XXX同样可表示Collection、List、Set、Map等
Collections-demo
@Slf4j public class ImmutableExample2 { private static Map<Integer, Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap(); static { map.put(1, 2); map.put(3, 4); map.put(5, 6); //此处理后的map的值是不可以修改的 map = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map); } public static void main(String[] args) { // map.put(1,3); log.info("{}", map.get(1)); } }
输出如下:

可见,用Collections.UnmodifiableMap修饰的对象是不可修改的,如果尝试修改对象的值,在程序运行时会抛出异常,此方法的实现可参考源码(其实就是将一个新的集合的所有更新方法变为抛出异常) 此demo是线程安全的。
ImmutableSet-demo
public class ImmutableExample3 { //以下为不可变对象的集合 private final static ImmutableList<Integer> list = ImmutableList.of(1, 2, 3); private final static ImmutableSet set = ImmutableSet.copyOf(list); private final static ImmutableMap<Integer, Integer> map = ImmutableMap.of(1,2,3,4); private final static ImmutableMap<Integer, Integer> map2 = ImmutableMap.<Integer, Integer>builder() .put(1, 2).put(3, 4).put(5, 6).build(); public static void main(String[] args) { // 此时不同意再添加新的元素 map2.put(1, 3); } }
输出如下:

此demo是线程安全的,开发时如果我们的对象可以变为不可变对象,我们尽量将对象变为不可变对象,这样可以避免线程安全问题
线程封闭
线程封闭就是把对象封装到一个线程里,只有一个线程可以看到这个对象,这样就算这个对象不是线程也不会有线程安全问题
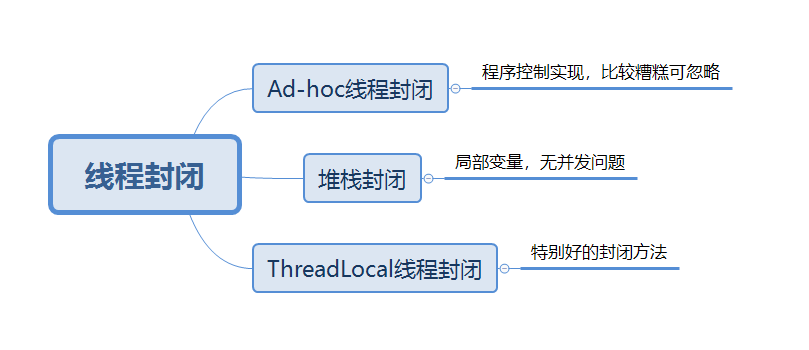
关于堆栈封闭,我们自己定义的局部变量被多个线程访问时,每个局部变量都会被拷贝一份放到线程的栈中去,这样每个线程操作的对象相当于是不同的,所以不会有线程安全问题(全局变量容易引发并发问题);ThreadLocal使用map实现了线程封闭,map的key是线程id,map的值是封闭的对象
THreadLocal-demo
定义RequestHolder类来操作ThreadLocal:
public class RequestHolder { //只有当项目重新启动的时候,threadLocal中存储的值才会被释放 private final static ThreadLocal<Long> requestHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void add(Long id) { requestHolder.set(id); } public static Long getId() { return requestHolder.get(); } public static void remove() { requestHolder.remove(); } }
注意,如add方法,只需传入需要封闭的对象即可,key值会自动取线程id放入,get和remove方法类似
定义HttpFilter类处理请求:
@Slf4j public class HttpFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; log.info("do filter,{},{}", Thread.currentThread().getId(), request.getServletPath()); RequestHolder.add(Thread.currentThread().getId()); //使请求继续被处理,不要拦住不动 filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } @Override public void destroy() { } }
配置启动类:
@SpringBootApplication public class ConcurrencyApplication extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConcurrencyApplication.class, args); } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean httpFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); registrationBean.setFilter(new HttpFilter()); registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/threadLocal/*"); return registrationBean; } @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new HttpInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/*"); } }
拦截以threadLocal开头的url,并利用Interceptor拦截所有的接口
定义Interceptor
@Slf4j public class HttpInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { log.info("preHandle"); return true; } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { RequestHolder.remove(); log.info("afterCompletion"); return; } }
此Interceptor的作用是当接口处理后,移除ThreadLocal中对应的值
定义Controller来进行验证
@Controller @RequestMapping("/threadLocal") public class ThreadLocalController { @RequestMapping("/test") @ResponseBody public Long test() { return RequestHolder.getId(); } }
同步容器
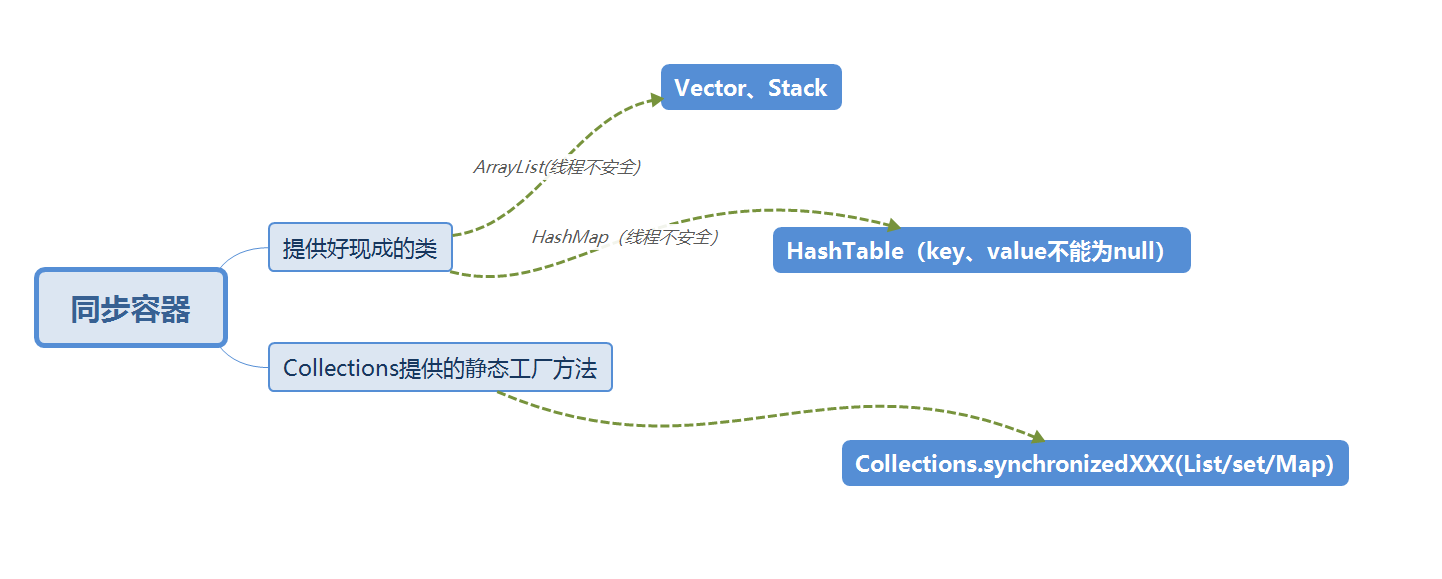
我们都知道ArrayList、HashMap等为线程不安全的,上图标识了它们对应的同步处理的容器
Vector-demo1
@Slf4j public class VectorExample1 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static Vector<Integer> list = new Vector<>(); private static void update(int i) { list.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", list.size()); } }
执行结果为5000,但是并不能说是线程安全的,同步容器不能保证在所有的情景下都保证线程安全,可参考Vector-demo2
Vector-demo2
public class VectorExample2 { private static Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { while (true) { for (int i = 0; i < vector.size(); i++) { vector.add(i); } Thread thread1 = new Thread() { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < vector.size(); i++) { vector.remove(i); } } }; Thread thread2 = new Thread() { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { vector.get(i); } } }; thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } }
输出如下:

表明某一线程访问的数据,可能被其他线程remove掉,导致出现下标越界异常,此demo是线程不安全的
HashTable-demo1
@Slf4j public class HashTableExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //Hashtable是线程安全的 private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new Hashtable<>(); private static void update(int i) { map.put(i,i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", map.size()); } }
运行结果为5000,此demo为线程安全的
Collections-List-demo1
@Slf4j public class CollectionsExample1 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static List<Integer> list = Collections.synchronizedList(Lists.newArrayList()); private static void update(int i) { list.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", list.size()); } }
运行结果为5000,是线程安全的
Collections-Set-demo1
@Slf4j public class CollectionsExample2 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static Set<Integer> set = Collections.synchronizedSet(Sets.newHashSet()); private static void update(int i) { set.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", set.size()); } }
返回结果为5000,是线程安全的
Collections-Map-demo1
@Slf4j public class CollectionsExample3 { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //Hashtable是线程安全的 private static Map<Integer, Integer> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>()); private static void update(int i) { map.put(i,i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", map.size()); } }
返回结果为5000,是线程安全的
并发容器J.U.C
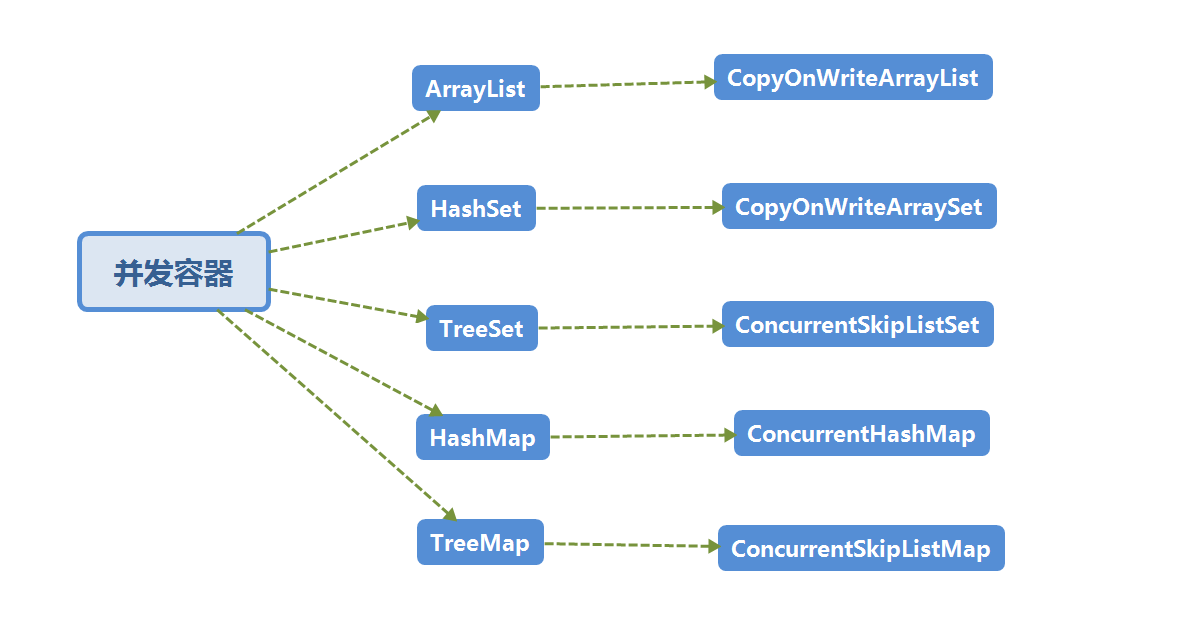
以上是常见的不安全的容器类,对应的并发容器类,我们以demo的方式进行演示
CopyOnWriteArrayList、CopyOnWriteArraySet因为需要copy数组,需要消耗内存,可能引发yonggc胡哦哦这fullgc,并且不能做到实时性,适合读多写少的情景
ConcurrentSkipListSet 支持自然排序,并且可以在构造的时候自己定义比较器,可以保证每一次的操作是原子性的,比如add()、remove等,但是对于批量操作,如addAll()等并不能保证原子性(需要自己手动做同步操作,如加锁等)
ConcurrentHashMap针对读操作做了大量的优化,这个类具有特别高的并发性,高并发场景下有特别好的表现
ConcurrentSkipListMap与ConcurrentHashMap相比的key是有序的,它支持更高的并发,它的存取时间和线程数是没有关系的,在一定的数据量下,并发的线程越多ConcurrentSkipListMap越等体现出它的优势来
CopyOnWriteArrayList-demo
public class CopyOnWriteArrayListExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static List<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); private static void update(int i) { list.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", list.size()); } }
运行结果为5000,是线程安全的
CopyOnWriteArraySet-demo
@Slf4j public class CopyOnWriteArraySetExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static Set<Integer> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>(); private static void update(int i) { set.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", set.size()); } }
运行结果为5000,是线程安全的
ConcurrentSkipListSet-demo
@Slf4j public class ConcurrentSkipListSetExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //arraylist是线程不安全的 private static Set<Integer> set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet<>(); private static void update(int i) { set.add(i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", set.size()); } }
输出为5000,是线程安全的
ConcurrentSkipListMap-demo
@Slf4j public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //HashMap是线程不安全的 private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>(); private static void update(int i) { map.put(i,i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", map.size()); } }
输出为5000,是线程安全的
ConcurrentHashMap-demo
@Slf4j @ThreadSafe public class ConcurrentHashMapExample { //请求总数 public static int clientTotal = 5000; //同时并发执行的线程数 public static int threadTotal = 200; //HashMap是线程不安全的 private static Map<Integer,Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static void update(int i) { map.put(i,i); } public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //定义线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //定义信号量 final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); //定义计数器闭锁 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal); for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) { final int count = i; executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); update(count); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception",e); } countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); log.info("size:{}", map.size()); } }
输出为5000,是线程安全的