本篇博客将主要对 mybatis 整体介绍,包括 mybatis 的项目结构,执行的主要流程,初始化流程,API 等各模块进行简单的串联,让你能够对 mybatis 有一个整体的把握。另外在 mybatis 源码的阅读过程中,如果不想写 demo 可以直接使用项目中的单元测试;
一、mybatis 结构介绍
mybatis的主要功能和使用 demo,在网上已经有很多了我就不再啰嗦了,同时 官方文档 也非常的详细;另外 mybatis 中使用了多种设计模式,包括建造者、动态代理、策略、装饰器模式等,在查看源码的时候,最好先对这些设计模式有一定的了解;
其中 mybatis 的模块结构如下:
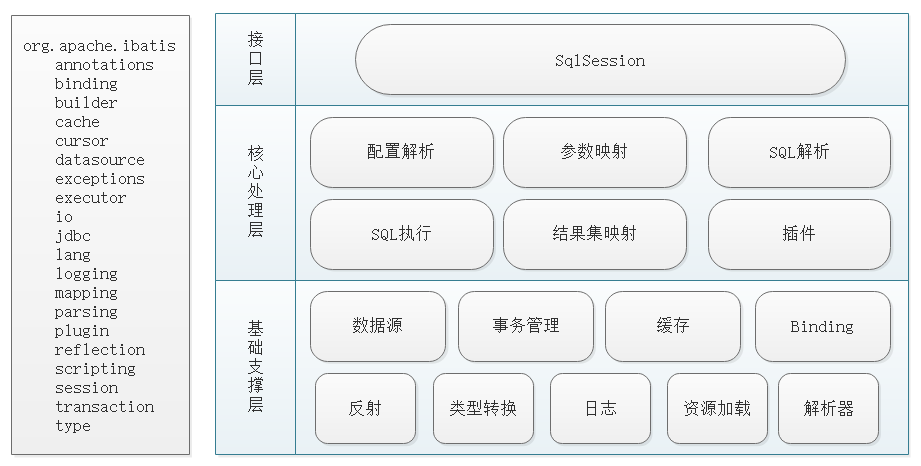
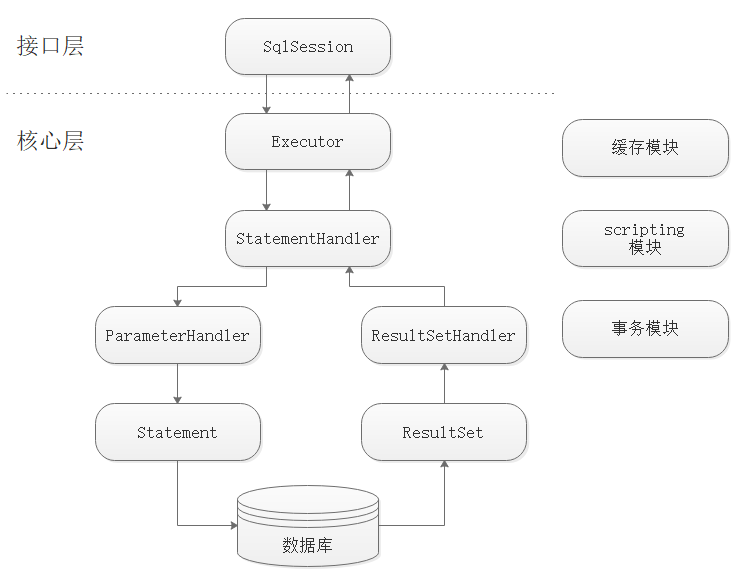
mybatis 的执行流程如下:
- 首先通过 Java API 或者 XML 配置完成初始化,最终所有的配置都在 Configuration 类中维护;
- 然后通过 SqlSessionFactory 得到 SqlSession,这里 SqlSession 就是 mybatis 的顶层 API 了,主要通过他完成数据库的增删改查等操作;
- 然后 SqlSession 将具体的操作委托给 Executor 执行,Executor 就是 mybatis 的调度核心了,主要职责有 SQL 语句生成、一二级缓存维护和事务的相关操作;
- 然后 Executor 将数据库相关的操作委托给 StatementHandler,StatementHandler 中完成了 mybatis 最核心的工作,包括参数绑定,指定 SQL 语句,结果集映射等;
具体过程如图所示:
二、初始化
mybatis 中包含了很多的配置项,具体每一项的讲解 官网 也很详细,其结构大致如下:(另外正如上面说的 mybatis 的配置项最后都由 Configuration 类维护,这其实就是外观模式)
configuration(配置)
properties(属性)
settings(设置)
typeAliases(类型别名)
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
objectFactory(对象工厂)
plugins(插件)
environments(环境配置)
environment(环境变量)
transactionManager(事务管理器)
dataSource(数据源)
mappers(映射器)
1. Java API 初始化
Java API 初始化的方式虽然不常用,但是相较于 XML 的方式可以更清楚的看到 Configuration 的构成,其示例如下:
PooledDataSource dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriver("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=GMT");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.addMapper(UserMapper.class);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
2. XML 配置初始化
相交于 Java API 的方式,XML 配置初始化,必然会多出 XML 的解析部分;代码如下:
String resource = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/MapperConfig.xml";
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
下面是一个相对完整的配置示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="org/apache/ibatis/databases/blog/blog-derby.properties"/>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
...
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Author"/>
<typeAlias alias="Blog" type="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Blog"/>
...
</typeAliases>
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler javaType="String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" handler="org.apache.ibatis.builder.CustomStringTypeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
<objectFactory type="org.apache.ibatis.builder.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="objectFactoryProperty" value="100"/>
</objectFactory>
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="org.apache.ibatis.builder.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="pluginProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<!--<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/apache/ibatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/apache/ibatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
...
</mappers>
</configuration>
其解析的流程如下:
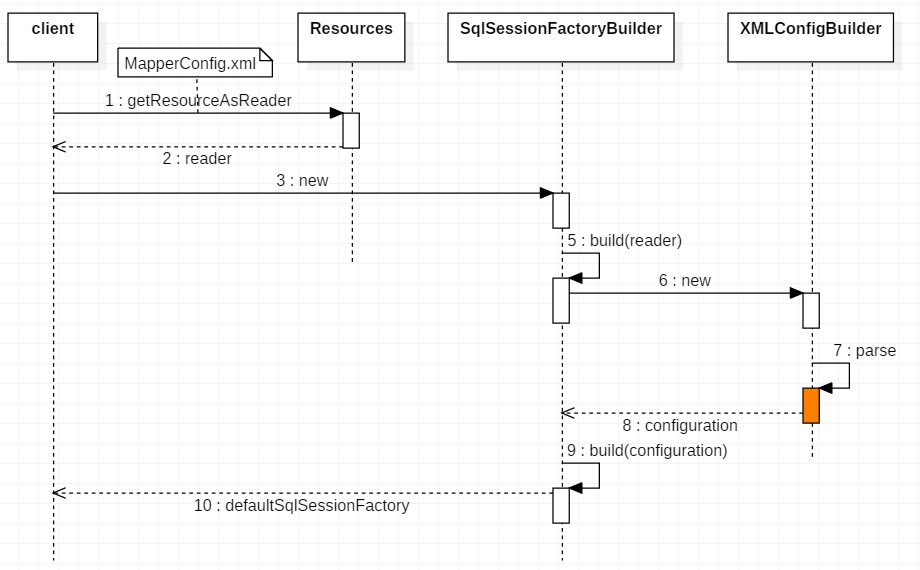
主要代码如下:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) { }
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
从上面的代码和流程图中可以看到,XML 初始化的主要流程被封装到了 XMLConfigBuilder 当中;主要的代码逻辑如下:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); }
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
三、SqlSession 使用方式
1. 直接指定 MappedStatement
try (SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession()) {
Author author = session.selectOne("org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.mappers.AuthorMapper.selectAuthor", new Author(101));
}
这种方式通过 namespace + sqlId 的方式直接指定 MappedStatement;这种方式因为直接编写字符串和强类型转换,既不安全也稍显麻烦,所以现在已经不推荐使用了;
@Override
public <T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
Cursor<T> cursor = executor.queryCursor(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds);
registerCursor(cursor);
return cursor;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
2. 动态代理 Mapper 的方式
try (SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession()) {
AuthorMapper mapper = session.getMapper(AuthorMapper.class);
Author author = mapper.selectAuthor(500);
}
这种方式不经避免了以上的问题,同时也能够使用注解的方式编写 sql,而且可以使用 IDE 提示;现在一般都推荐使用这种方式;但是其最终也是调用了上面的接口;
首先在初始化的时候通过 bindMapperForNamespace,注册对应的 Mapper(要求namespace和Mapper的全限定名保持一致);
// XMLMapperBuilder
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { //ignore, bound type is not required }
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
// MapperRegistry
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); }
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); // 添加代理工厂
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
使用的时候,通过 class 类名获取 MapperProxyFactory 代理工厂,制造一个新的 Mapper 代理(注意这里时每次都要生成一个代理类,因为其中包含了 SqlSession,而 SqlSession 是线程不安全的所以不能缓存,但是我觉得这里任然是可以优化的,有兴趣你可以自己尝试一下);
try (SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession()) {
AuthorMapper mapper = session.getMapper(AuthorMapper.class); // 代理类
}
// MapperRegistry
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); }
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); // 创建代理对象
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// MapperProxyFactory
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
// MapperProxy
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // 从Object中继承的方法
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) { // 有默认实现的接口方法
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); // 然后由 MapperMethod 执行,这里使用策略模式,后面还会详细讲解
}
总结
-
SqlSession 是线程不安全的,所以在示例代码中每次使用都会将其关闭?
在 mybatis 中还有一个类 SqlSessionManager 里面有一个 ThreadLocal 用来管理 SqlSession,在 Spring 中也同样是用 SqlSessionHolder 来管理的,所以并不会每次都创建一个新的 SqlSession;
-
以上内容只是大致将了 mybatis 的主要结构,后面的章节还会分模块进行讲解;
另外本文主要参考了《MyBatis技术内幕》,有兴趣的可以自行查看;