前几天由于出行计划没有更博QwQ
(其实是因为调试死活调不出来了TAT我好菜啊)
伸展树
伸展树(英语:Splay Tree)是一种二叉查找树,它能在O(log n)内完成插入、查找和删除操作。它是由丹尼尔·斯立特(Daniel Sleator)和罗伯特·塔扬在1985年发明的[1]。
在伸展树上的一般操作都基于伸展操作:假设想要对一个二叉查找树执行一系列的查找操作,为了使整个查找时间更小,被查频率高的那些条目就应当经常处于靠近树根的位置。于是想到设计一个简单方法, 在每次查找之后对树进行调整,把被查找的条目搬移到离树根近一些的地方。伸展树应运而生。伸展树是一种自调整形式的二叉查找树,它会沿着从某个节点到树根之间的路径,通过一系列的旋转把这个节点搬移到树根去。
它的优势在于不需要记录用于平衡树的冗余信息。
优点
缺点
伸展树最显著的缺点是它有可能会变成一条链。这种情况可能发生在以非降顺序访问n个元素之后。然而均摊的最坏情况是对数级的——O(log n)
以上摘自中文Wikipedia
永远不要用单旋代替双旋...单旋那叫Spaly,Splay中的势能分析在单旋时会失效,复杂度不对的...(警告某整天单旋的ryf)
Rotate操作:
在离散数学中,树旋转(英语:Tree rotation)是在二叉树中的一种子树调整操作, 每一次旋转并不影响对该二叉树进行中序遍历的结果. 树旋转通常应用于需要调整树的局部平衡性的场合。
然后上几张图来作一下左旋/右旋的说明:

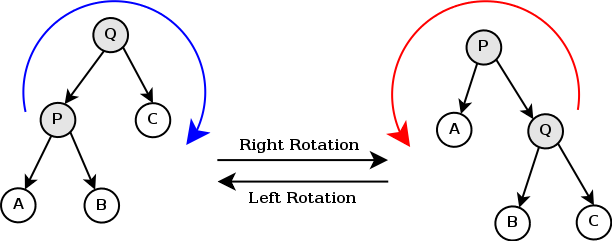
(第一张是动图不知道cnblogs能不能很好地滋磁GIF)
我们可以将左旋理解为将根旋转为右子节点的左子树,右旋为将根旋转为左子节点的右子树(往哪旋根就变成哪边的子树)
附C++袋马实现(左右合并,k=0为左旋,k=1为右旋)

#define lch chd[0] #define rch chd[1] #define kch chd[k] #define xch chd[k^1] void Rotate(Node* root,int k){ Node* tmp=root->xch; if(root->prt==NULL) this->root=tmp; else if(root->prt->lch==root) root->prt->lch=tmp; else root->prt->rch=tmp; tmp->prt=root->prt; root->xch=tmp->kch; if(root->xch!=NULL) root->xch->prt=root; tmp->kch=root; root->prt=tmp; }
注:Node的定义:

struct Node{ int k; Node* prt; Node* chd[2]; Node(const int& key){ this->k=key; this->prt=NULL; this->lch=NULL; this->rch=NULL; } inline int size(){ return this==NULL?0:this->s; } inline int key(){ return this==NULL?0:this->k; } inline int Pos(){ return this==this->prt->lch; } };
这样定义可以直接使用new与空指针NULL而且不必在每次都判空
还可以防止delete野指针造成RE
然后是在前面我为了方便而使用的宏定义:

1 #define lch chd[0] 2 #define rch chd[1] 3 #define kch chd[k] 4 #define xch chd[k^1]
如果要维护子树大小还要记得旋转之后先维护原根(代码中的root)再维护新根(代码中的tmp)
Splay操作:
Splay(伸展)操作是Splay Tree的核心,作用是将一个指定的结点旋转到根的位置.
这时可分三种情况:
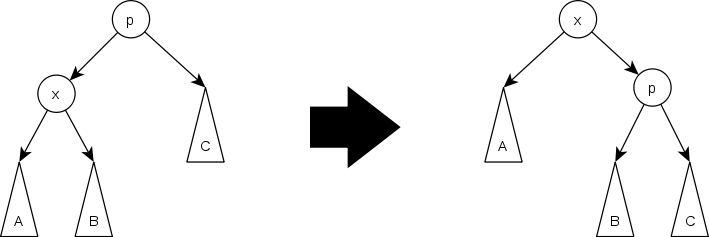
I.要伸展的结点的父节点就是根
这时直接一次单旋解决(Zig Step)
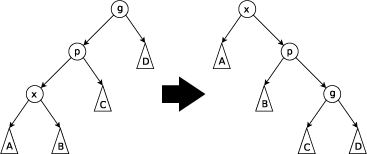
II.要伸展的结点的父节点不是根且要伸展的结点/该结点的父节点/该节点的祖父结点成一条直线
这时要先旋转祖父结点再旋转父节点且旋转方向相同(Zig-zig Step)
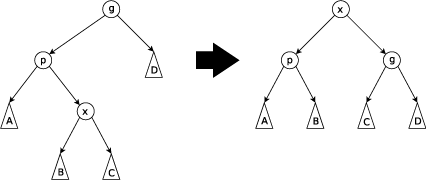
III.要伸展的结点的父节点不是根且要伸展的结点/该结点的父结点/该结点的祖父结点不在一条直线上
这时要先旋转父节点再反向旋转祖父结点(Zig-zag Step).需要注意的是旋转父节点后要伸展的结点的祖父结点变成了父结点.
重复上面的情况直至要伸展的结点伸展至根.
实际应用时伸展函数有时候会有两个参数:要伸展的结点指针和根的父节点指针.这样可以控制结点不一定要伸展到整棵树的根而是一个子树的根.后面Insert和Delete操作中会用到.
然后是代码实现.这里将三种情况进行了适当合并,感性理解一下就好

1 void Splay(Node* root,Node* prt=NULL){ 2 while(root->prt!=prt){ 3 int k=root->Pos(); 4 if(root->prt->prt==prt){ 5 this->Rotate(root->prt,k); 6 } 7 else{ 8 int d=root->prt->Pos(); 9 this->Rotate(k==d?root->prt->prt:root->prt,k); 10 this->Rotate(root->prt,d); 11 } 12 } 13 }
Insert操作:
这个操作有多种写法,对于最朴素的Splay可以先按照普通二叉树的方法插入结点,然后将插入的结点伸展到根.
如果题目要求需要维护子树大小来求第K大/小的值与某数的排名的话可以用双参Splay操作与K大/排名操作配合进行,先查找该值前驱伸展到根,然后查找该值后继伸展到根的右子树,然后直接将右子树的左儿子上新建一个结点.
第一种写法的代码是我从Wikipedia上摘录的,其中将模板部分替换为了int并将下划线命名规则改为大驼峰:

1 void Insert( const int &key ) { 2 Node *z = root; 3 Node *p = 0; 4 5 while( z ) { 6 p = z; 7 if( key<z->key ) z = z->lch; 8 else z = z->rch; 9 } 10 11 z = new Node( key ); 12 z->prt = p; 13 14 if( !p ) root = z; 15 else if( z->key<p->key ) p->lch = z; 16 else p->rch = z; 17 18 Splay( z ); 19 }
第二种写法的代码如下:

1 void Insert(const int& key){ 2 int pos=this->Rank(key)-1; 3 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos)); 4 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos+1),this->root); 5 Node* tmp=new Node(key); 6 this->root->rch->lch=tmp; 7 tmp->prt=this->root->rch; 8 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 9 this->root->Maintain(); 10 }
注:Maintain()函数的作用为维护子树大小信息,Kth()为求K大函数,Rank()为求排名函数,定义见后续.
Delete操作:
Delete操作同样有多种写法,首先对于无附加信息的普通Splay:
首先查找到要删除的结点,然后伸展到根,并从它的右子树中查找值最小的结点并用它把待删除的结点替换掉.注意维护这两个结点周边结点的指针信息.代码如下,摘自Wikipedia:

1 Node* Find( const T &key ) { 2 Node *z = root; 3 while( z ) { 4 if(key<z->key()) 5 z=z->lch; 6 else if(z->key<key) 7 z=z->rch; 8 else return z; 9 } 10 return NULL; 11 } 12 void Delete( const int &key ) { 13 Node *z = Find( key ); 14 if( !z ) return; 15 16 Splay( z ); 17 18 if( !z->lch ) Replace( z, z->rch ); 19 else if( !z->rch ) Replace( z, z->lch ); 20 else { 21 Node *y = SubtreeMinimum( z->rch ); 22 if( y->prt != z ) { 23 Replace( y, y->rch ); 24 y->rch = z->rch; 25 y->rch->prt = y; 26 } 27 Replace( z, y ); 28 y->lch = z->lch; 29 y->lch->prt = y; 30 } 31 32 delete z; 33 } 34 Node* subtreeMinimum( Node *u ) { 35 while( u->lch ) u = u->lch; 36 return u; 37 }
注:Wikipedia中使用了两个辅助函数,一个是Find()用于查找,一个是SubtreeMinimum()用于查找子树最小值.这两个函数也摘录在上面的代码中了.
对于维护了子树大小附加信息的Splay则与Insert类似,不同的是一个是新建结点一个是切断连接并删除罢了
代码如下:

1 void Delete(const int& key){ 2 int pos=this->Rank(key); 3 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos-1)); 4 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos+1),root); 5 delete this->root->rch->lch; 6 this->root->rch->lch=NULL; 7 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 8 this->root->Maintain(); 9 }
以上即为伸展树的几种基本操作.如果我们维护了子树大小的话还可以计算第K大/小的值与某数的排名,代码如下,具体原理不再详述.

1 int Rank(const int& key){ 2 Node* root=this->root; 3 int rank=1; 4 while(root!=NULL){ 5 if(root->key()<key){ 6 rank+=root->lch->size()+1; 7 root=root->rch; 8 } 9 else 10 root=root->lch; 11 } 12 return rank; 13 } 14 15 void Insert(const int& key){ 16 int pos=this->Rank(key)-1; 17 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos)); 18 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos+1),this->root); 19 Node* tmp=new Node(key); 20 this->root->rch->lch=tmp; 21 tmp->prt=this->root->rch; 22 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 23 this->root->Maintain(); 24 }
通过这两个函数还可求某数的前驱与后继的值,代码如下:

1 inline int Predecessor(const int& key){ 2 return this->Kth(this->Rank(key)-1)->key(); 3 } 4 5 inline int Successor(const int& key){ 6 return this->Kth(this->Rank(key+1))->key(); 7 }
对于Insert/Delete操作的第二种写法需要在进行所有操作前新建两个结点,值分别为INF与-INF来保证不会访问空指针
最后附上封装好的完整代码,维护了子树大小,可作为"普通平衡树"的模板.

1 #define lch chd[0] 2 #define rch chd[1] 3 #define kch chd[k] 4 #define xch chd[k^1] 5 6 const int INF=0x7FFFFFFF; 7 8 class SplayTree{ 9 private: 10 struct Node{ 11 int k; 12 int s; 13 Node* prt; 14 Node* chd[2]; 15 Node(const int& key){ 16 this->k=key; 17 this->s=1; 18 this->prt=NULL; 19 this->lch=NULL; 20 this->rch=NULL; 21 } 22 inline int size(){ 23 return this==NULL?0:this->s; 24 } 25 inline int key(){ 26 return this==NULL?0:this->k; 27 } 28 inline void Maintain(){ 29 if(this!=NULL) 30 this->s=this->lch->size()+this->rch->size()+1; 31 } 32 inline int Pos(){ 33 return this==this->prt->lch; 34 } 35 }*root; 36 37 void Rotate(Node* root,int k){ 38 Node* tmp=root->xch; 39 if(root->prt==NULL) 40 this->root=tmp; 41 else if(root->prt->lch==root) 42 root->prt->lch=tmp; 43 else 44 root->prt->rch=tmp; 45 tmp->prt=root->prt; 46 root->xch=tmp->kch; 47 if(root->xch!=NULL) 48 root->xch->prt=root; 49 tmp->kch=root; 50 root->prt=tmp; 51 root->Maintain(); 52 tmp->Maintain(); 53 } 54 55 void Splay(Node* root,Node* prt=NULL){ 56 while(root->prt!=prt){ 57 int k=root->Pos(); 58 if(root->prt->prt==prt){ 59 this->Rotate(root->prt,k); 60 } 61 else{ 62 int d=root->prt->Pos(); 63 this->Rotate(k==d?root->prt->prt:root->prt,k); 64 this->Rotate(root->prt,d); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 public: 69 Node* Kth(int pos){ 70 Node* root=this->root; 71 while(root!=NULL){ 72 int k=root->lch->size()+1; 73 if(pos<k) 74 root=root->lch; 75 else if(pos==k) 76 return root; 77 else{ 78 pos-=k; 79 root=root->rch; 80 } 81 } 82 return NULL; 83 } 84 85 int Rank(const int& key){ 86 Node* root=this->root; 87 int rank=1; 88 while(root!=NULL){ 89 if(root->key()<key){ 90 rank+=root->lch->size()+1; 91 root=root->rch; 92 } 93 else 94 root=root->lch; 95 } 96 return rank; 97 } 98 99 void Insert(const int& key){ 100 int pos=this->Rank(key)-1; 101 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos)); 102 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos+1),this->root); 103 Node* tmp=new Node(key); 104 this->root->rch->lch=tmp; 105 tmp->prt=this->root->rch; 106 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 107 this->root->Maintain(); 108 } 109 110 void Delete(const int& key){ 111 int pos=this->Rank(key); 112 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos-1)); 113 this->Splay(this->Kth(pos+1),root); 114 delete this->root->rch->lch; 115 this->root->rch->lch=NULL; 116 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 117 this->root->Maintain(); 118 } 119 120 inline int Predecessor(const int& key){ 121 return this->Kth(this->Rank(key)-1)->key(); 122 } 123 124 inline int Successor(const int& key){ 125 return this->Kth(this->Rank(key+1))->key(); 126 } 127 128 SplayTree(){ 129 this->root=new Node(-INF); 130 this->root->rch=new Node(INF); 131 this->root->rch->prt=this->root; 132 this->root->rch->Maintain(); 133 this->root->Maintain(); 134 } 135 };
然后是图包时间QwQ

