局部加权线性回归
【转载时请注明来源】:http://www.cnblogs.com/runner-ljt/
Ljt
作为一个初学者,水平有限,欢迎交流指正。
线性回归容易出现过拟合或欠拟合的问题。
局部加权线性回归是一种非参数学习方法,在对新样本进行预测时,会根据新的权值,重新训练样本数据得到新的参数值,每一次预测的参数值是不相同的。
权值函数:
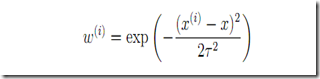
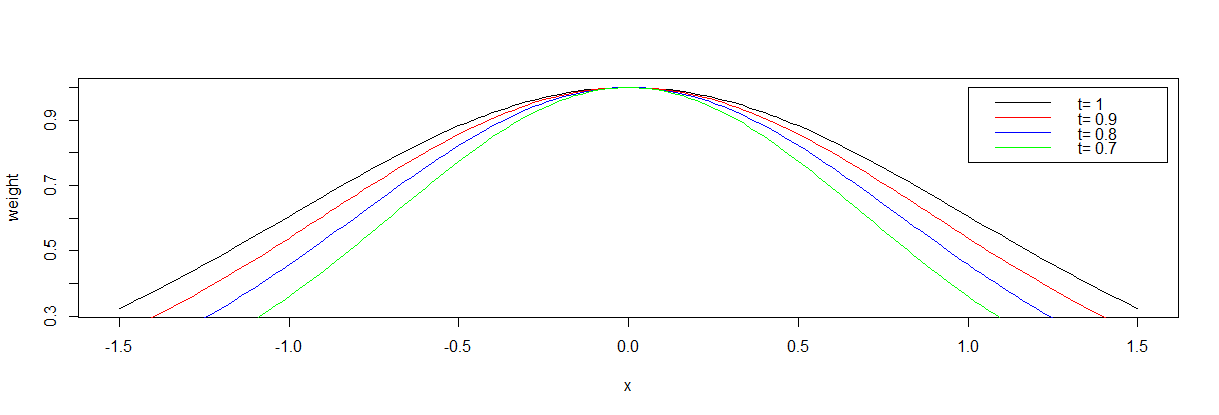
t用来控制权值的变化速率(建议对于不同的样本,先通过调整t值确定合适的t)
不同t值下的权值函数图像:
局部加权线性回归R实现:
#Locally Weighted Linear Regression 局部加权回归(非参数学习方法)
##x为数据矩阵(mxn m:样本数 n:特征数 );y观测值(mx1);xp为需要预测的样本特征,t权重函数的权值变化速率
#error终止条件,相邻两次搜索结果的幅度;
#step为设定的固定步长;maxiter最大迭代次数,alpha,beta为回溯下降法的参数
LWLRegression<-function(x,y,xp,t,error,maxiter,stepmethod=T,step=0.001,alpha=0.25,beta=0.8)
{
w<-exp(-0.5*(x-xp)^2./t^2) #权重函数,w(i)表示第i个样本点的权重,t控制权重的变化速率
m<-nrow(x)
x<-cbind(matrix(1,m,1),x)
n<-ncol(x)
theta<-matrix(0,n,1) #theta初始值都设置为0
iter<-0
newerror<-1
while((newerror>error)|(iter<maxiter)){
iter<-iter+1
h<-x%*%theta
des<-t(t(w*(h-y))%*%x) #梯度
#回溯下降法求步长t
if(stepmethod==T){
step=1
new_theta<-theta-step*des
new_h<-x%*%new_theta
costfunction<-t(w*(h-y))%*%(h-y) #(最小二乘损失函数)局部加权线性回归损失函数
new_costfunction<-t(w*(new_h-y))%*%(new_h-y)
#回溯下降法求步长step
while(new_costfunction>costfunction-alpha*step*sum(des*des)){
step<-step*beta
new_theta<-theta-step*des
new_h<-x%*%new_theta
new_costfunction<-t(w*(new_h-y))%*%(new_h-y)
}
newerror<-t(theta-new_theta)%*%(theta-new_theta)
theta<-new_theta
}
#直接设置固定步长
if(stepmethod==F){
new_theta<-theta-step*des
newerror<-t(theta-new_theta)%*%(theta-new_theta)
theta<-new_theta
}
}
xp<-cbind(1,xp)
yp<-xp%*%theta
#costfunction<-t(x%*%theta-y)%*%(x%*%theta-y)
#result<-list(yp,theta,iter,costfunction)
#names(result)<-c('拟合值','系数','迭代次数','误差')
#result
yp
}
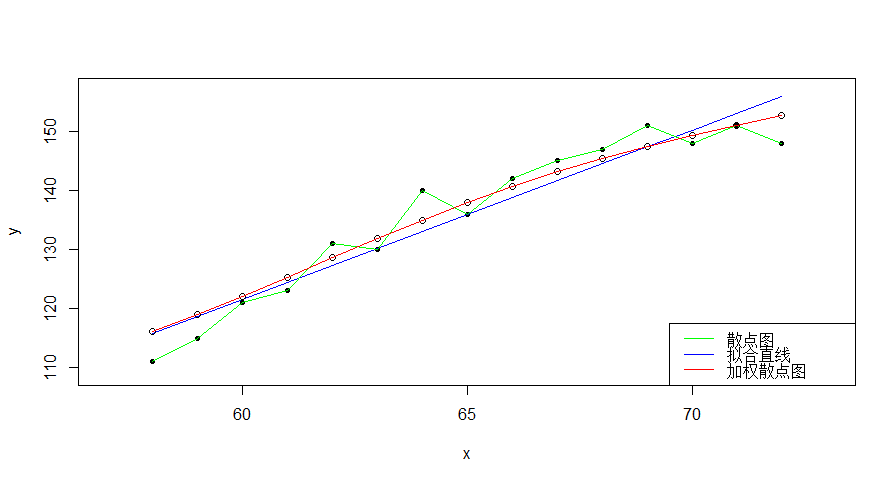
运用局部线性加权回归预测每个样本点x对于的y值,连接各预测值后得到一条平滑曲线,反映出y与x之间的非线性关系。
> t(x)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8] [,9] [,10] [,11] [,12] [,13] [,14] [,15]
[1,] 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72
> t(y)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8] [,9] [,10] [,11] [,12] [,13] [,14] [,15]
[1,] 111 115 121 123 131 130 140 136 142 145 147 151 148 151 148
>
> lm(y~x)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-50.245 2.864
> yy<--50.245+2.864*x
> t(yy)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8] [,9] [,10] [,11] [,12] [,13] [,14] [,15]
[1,] 115.867 118.731 121.595 124.459 127.323 130.187 133.051 135.915 138.779 141.643 144.507 147.371 150.235 153.099 155.963
>
> g<-apply(x,1,function(xp){LWLRegression(x,y,xp,3,1e-7,100000,stepmethod=F,step=0.00001,alpha=0.25,beta=0.8)})
>
> t(g)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8] [,9] [,10] [,11] [,12] [,13] [,14]
[1,] 116.093 119.0384 122.1318 125.3421 128.6115 131.862 135.009 137.9771 140.7136 143.194 145.4244 147.4373 149.2831 151.018
[,15]
[1,] 152.693
>
> plot(x,y,pch=20,xlim=c(57,73),ylim=c(109,157))
> lines(x,y,col='green')
> lines(x,yy,col='blue')
> points(x,g,pch=21)
> lines(x,g,col='red')
> legend("bottomright",legend=c('散点图','拟合直线','加权散点图'),lwd=1,col=c('green','blue','red'))
>