在C++中没有直接对应的split函数,字符串分割可借助以下方法实现:
1、借助strtok函数
函数原型:char * strtok (char *str, char * delim);
函数功能:以delim为分隔符分割字符串str
参数说明:str:要分隔的字符串;delim:分隔符
返回值:从str开头开始的一个个被分割的字符串。当没有被分割时则返回null
代码1:直接使用strtok函数分割char*类型的字符串
代码2:借助strtok分割string类型的字符串,将结果保存在vector<string>中
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char s[] = "my name is lmm";
char *p;
const char *delim = " ";
p = strtok(s, delim);
while(p) {
cout << p << endl;
p = strtok(NULL, delim);
}
return 0;
}
思路:先将整个string字符串转换为char*类型,分割后得到char*类型的子字符串,将子字符串转换为string类型,并存入结果数组中。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<string> split(const string& str, const string& delim) {
vector<string> res;
if("" == str) return res;
//先将要切割的字符串从string类型转换为char*类型
char * strs = new char[str.length() + 1] ; //不要忘了
strcpy(strs, str.c_str());
char * d = new char[delim.length() + 1];
strcpy(d, delim.c_str());
char *p = strtok(strs, d);
while(p) {
string s = p; //分割得到的字符串转换为string类型
res.push_back(s); //存入结果数组
p = strtok(NULL, d);
}
return res;
}
void test1() { //空字符串
cout << "******test1****** "<<endl;
string s = "";
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
void test2() { //只有一个字符串
cout << "******test2****** " <<endl;
string s = "my";
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
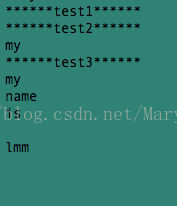
void test3() { //正常字符串
cout << "******test3****** "<<endl;
string s = "my name is lmm ";//连续多个空格,空格会被过滤掉
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
int main() {
test1();
test2();
test3();
return 0;
}
注意:test3中连续多个空格出现,空格都会被过滤掉
2、借助于string类的find和substr函数
1)find函数
函数原型:size_t find(const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
功能说明:从pos位置开始查找子字符串str第一次出现的位置
参数说明:str为要查找的子字符串,pos从为初始查找位置
返回值:找到的话返回子字符串第一次出现的位置,否则返回string::npos
2)substr函数
函数原型:string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t n = npos) const;
功能说明:获取从指定的起始位置开始,长度为n的子字符串
参数说明:pos为起始位置,n获取的1字符串长度
返回值:子字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
string reverse_one_word(string str) {
for(int i = 0; i < str.length()/2; i ++) {
char tmp;
tmp = str[i];
str[i] = str[ str.length() - i - 1 ];
str[ str.length() - i - 1 ] = tmp;
}
return str;
}
vector<string> split(const string& str,const string& delim) { //将分割后的子字符串存储在vector中
vector<string> res;
if("" == str) return res;
string strs = str + delim; //*****扩展字符串以方便检索最后一个分隔出的字符串
size_t pos;
size_t size = strs.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
pos = strs.find(delim, i); //pos为分隔符第一次出现的位置,从i到pos之前的字符串是分隔出来的字符串
if( pos < size) { //如果查找到,如果没有查找到分隔符,pos为string::npos
string s = strs.substr(i, pos - i);//*****从i开始长度为pos-i的子字符串
res.push_back(s);//两个连续空格之间切割出的字符串为空字符串,这里没有判断s是否为空,所以最后的结果中有空字符的输出,
i = pos + delim.size() - 1;
}
}
return res;
}
void test1() { //空字符串
cout << "******test1****** "<<endl;
string s = "";
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
void test2() { //只有一个字符串
cout << "******test2****** " <<endl;
string s = "my";
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
void test3() { //正常字符串
cout << "******test3****** "<<endl;
string s = "my name is lmm ";
std::vector<string> res = split(s, " ");
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i)
{
cout << res[i] <<endl;
}
}
int main() {
test1();
test2();
test3();
return 0;
}
注意:test3中的多个空格未被过滤掉,也就是说两个空格分隔符之间的空子串也被存进了结果数组中。要想避免这个问题可以在分隔出子字符串s时,判断一下若为空(两个分隔符相邻,中间的子串为空),则不加入字符数组即可去掉。