A.String Master
(O(n^3))跑跑跑,相当与(LCS)加一维,然后考场上似乎内存炸了,突发奇想改了(short)A掉了,妙啊
B.Tourist Attractions
考虑只枚举(2-3)这样的边,然后对答案的贡献就是,(u所连接点的个数-1) * (v所连接点的个数-1)然后再减去一个重复计算的部分,就是同时连接了(u)和(v)的点做的贡献
像这样
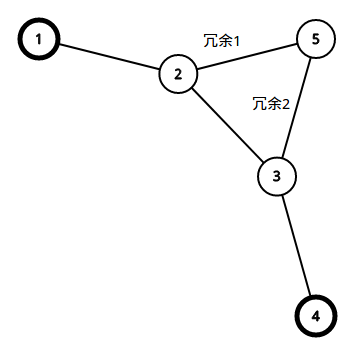
5显然做了两次贡献
((d_u - 1) * (d_v - 1) - son[u]cap son[v])
得到了70分的好成绩
然后用(bitset)维护一下取交集的操作就okk了
注意题目中较小的数据范围
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
for(; ch > '9' || ch < '0'; ch = getchar()) if(ch == '-') w = -1;
for(; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar()) x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
return x * w;
}
const int ss = 2333;
bitset<1501> b[ss];
int d[ss];
long long dp[ss][ss], ans;
char s[ss][ss];
signed main(){
freopen("tourist.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("tourist.out", "w", stdout);
int n = read();
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dp[1][i] = 1;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(register int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(s[i][j] == '1') d[i]++;
for(register int t = 2; t <= 4; t++)
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(register int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(s[i][j] == '1') dp[t][i] += dp[t - 1][j];
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans += dp[4][i];
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans -= d[i] * d[i] * 2;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(register int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(s[i][j] == '1') b[i][j] = 1, ans++;
}
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(register int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++){
if(b[i][j]) ans -= (b[i] & b[j]).count() * 2;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
C.Walk
对于每一个值,只有可能和自己的子集连边,然后不得不复习一下如何求一个数的所有子集
signed main(){
int n = read();
for(register int i = n; i; i = (i - 1) & n)
cout << i << endl;
}