1.1 查询语句
1.1.1 select
select 用于从数据看查询数据。语法
select field1,filed2,.. . from tablename [where condition]
1 -- 查询所有员工的名字和雇员号 2 select empno,ename from emp; 3 4 -- 查询所有员工的雇员号、姓名、岗位 5 select empno,ename,job from emp; 6 7 -- 字段的别名 as 8 select ename as "姓名" from emp; 9 select ename as "姓名",job as "岗位" from emp; 10 11 -- 别名一定要用双引号,不能用单引号 12 select ename "姓名",job "岗位" from emp; 13 -- 双引号可以省略 14 select ename 姓名 from emp; 15 16 -- 表的别名 17 select emp.ename,emp.job from emp; 18 select e.ename,e.job from emp e;
* 是通配符表示查询所有字段。如果要查特定的字段时,不要使用*,影响查询效率。
1.1.2 distinct 去重
把重复性的记录去掉,只保留一条。
select empno,ename,job,mgr,hiredate,sal,comm,deptno from emp; -- * 通配符表示所有字段 select * from emp;
修饰多字段时,多个字段的值都不一样才保留。
1.1.3 where 子句
where 表示查询的条件。
[1] =,!= ,<>,<,>,<=,>= 关系运算符
<> 表示不等于
1 -- where 子句 2 3 -- 把部分10的雇员查询出来 4 select * 5 from emp 6 where deptno = 10; 7 8 -- 把名称为smith的雇员 9 select e.* 10 from emp e 11 where e.ename = 'SMITH'; 12 13 -- 查询底薪大于等于1000的员工 14 select e.* 15 from emp e 16 where e.sal >= 1000; 17 18 select e.* 19 from emp e 20 where e.sal <> 800
any/som/all(list)
any/some(list) 满足list列表中的任意一个条件
all(list) 满足list列表的中所有条件
1 -- any some all 2 3 -- 查询薪资大于1000或者薪资大于800的雇员 4 select e.* 5 from emp e 6 where e.sal > some(1000,800); 7 8 -- 查询薪资大于1000 9 select e.* 10 from emp e 11 where e.sal > all(1000,800);
[2] null
null 在sql中表示的是不确定 => 可以认为没有值(一些情况下)
1 -- null/not null 2 -- 查询没有津贴的雇员 3 select e.* 4 from emp e 5 where e.comm is null 6 7 select e.* 8 from emp e 9 where e.comm is not null
【3】betweem x and y
表示一个值位于【x,y】区间,x与Y一般都是数字
-- between x and y -- 查询薪资在1000-5000之间的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.sal between 1000 and 5000 -- 查询薪资在(3000,5000]之间的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.sal between 3000.01 and 5000
【4】in/not in list
表示字段值是否在list列表中
1 -- in/not in(list) 2 -- 查询部分号是10和20的员工 3 select e.* 4 from emp e 5 where e.deptno in(10,20); 6 7 select e.* 8 from emp e 9 where e.deptno not in(10,20); 10 11 -- 查询薪资是1000,2000,5000的员工 12 select e.* 13 from emp e 14 where e.sal in (1000,2000,5000);
【5】模糊查询
like 关键字 用于模糊查询中
%:表示任意字符出现多次(含0次),
_:表示任意字符出现1次。
escape(‘x’)表示指定的转义字符为x,一般指定为
-- 查询名字是c开头的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.ename like 'c%'; -- 查询名字中第二个字母是M的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.ename like '_M%' -- 查询名字中含有M的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.ename like '%M%'; -- 查询名字中含有%的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.ename like '%\%%' escape('');
1.2 复杂查询(and /or)
where 后面的条件可以跟多个and或者or连接
and:且、并且
or:或、或者
1 -- 查询部门10且薪资大于等2000的雇员 2 select e.* 3 from emp e 4 where e.deptno = 10 and e.sal >= 2000; 5 6 -- 查询名字中含M且薪资大于1000的雇员 7 select e.* 8 from emp e 9 where e.ename like '%M%' and e.sal > 1000 10 11 -- 查询部门在10或20的雇员 12 select e.* 13 from emp e 14 where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 20
where 中and、or的执行效率问题
-- 思考:查询条件的顺序对查询速度是否有影响? /* 分析: and 表示且,条件越多,检索的数据量越来越少 or 表示或,条件越多,检索的数据量越来越多 where 条件的执行顺序从后向前 */ -- 优化后的sql select e.* from emp e where e.sal>=2000 and e.deptno = 10 -- 结论 -- AND: 把检索结果较少的条件放到后面 -- 查部门10或30的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 30;
综合案例
1 --使用in查询部门名称为 SALES 和 RESEARCH 的雇员姓名、工资、部门编号 2 -- 思考:部门名称位于dept,雇员信息位于emp表 3 select e.ename,e.sal,e.deptno 4 from emp e 5 where e.deptno in 6 ( 7 select d.deptno 8 from dept d 9 where d.dname = 'SALES' or d.dname = 'RESEARCH' 10 );
1.3 计算字段
我们经常需要把数据库中检索出来的信息进行再加工,允许的操作+、-、*、/。通过四个运算得到新的字段(计算字段)。
计算字段在数据表中不存在。
-- 查询出每个雇员的月薪(收入) select e.ename,e.sal+e.comm as "收入",e.deptno from emp e
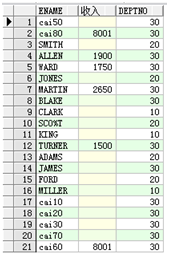
注意:很多记录中的comm是null,表示不确定的值,经常四则运算后的值也不确定。
当遇到字段时null时,可以通过nvl函数把null转化便于运算的类型。
-- nvl函数优化 select e.ename,e.sal+nvl(e.comm,0) "收入",e.deptno from emp e