1.1 File类
file类在java中表示文件或目录(带路径)
1.1.1 File常用属性和方法
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 给定路径创建File对象 4 // File file = new File("D:"+File.separator+"javatest"+File.separator+"a.txt"); 5 File file = new File("d:\javatest\b.mp3"); 6 System.out.println(file); 7 8 // 文件基本属性 9 System.out.println(file.canExecute()); 10 System.out.println(file.canRead()); 11 System.out.println(file.canWrite()); 12 13 // 文件的创建、删除 14 if(!file.exists()) { 15 16 boolean r; 17 try { 18 r = file.createNewFile(); 19 if(r) { 20 System.out.println("文件创建成功"); 21 } 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 // 删除文件 28 file.delete(); 29 }
创建文件时会抛出检查时IOException。
1.1.12File的路径相关
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\a"); 4 // File file = new File("a.txt"); 5 6 // 获取file的绝对路径 7 System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); 8 // 获取file的创建时的路径字符串 9 System.out.println(file.getPath()); 10 // 获取文件或者目录的名字 11 System.out.println(file.getName()); 12 // 获取文件或者目录的父目录 13 System.out.println(file.getParent()); 14 15 }
注意:如果file是相对路径,相对路径的当前路径是工程目录(java17)
1.1.13目录的创建
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\c\d\e"); 4 5 if(!file.exists()) { 6 boolean r; 7 8 try { 9 // 一次只能创建一个目录 10 // r = file.mkdir(); 11 r = file.mkdirs(); 12 if(r) { 13 System.out.println("目录创建成功"); 14 } 15 } catch (Exception e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 19 } 20 }
1.1.14目录的遍历
list():返回一个file表示的目录中的子目录或者文件,字符串数组类型
listFiles():返回一个file表示的目录中的子目录或者文件,File数组类型
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 需求:遍历d:javatest目录 4 // list() 5 File file = new File("d:\javatest"); 6 7 8 /* 9 String[] list = file.list(); 10 11 for (String str : list) { 12 System.out.print(str); 13 File f = new File(file.getPath()+"\"+str); 14 if(f.isDirectory()) { 15 System.out.println(" 目录"); 16 }else { 17 System.out.println(" 文件"); 18 } 19 }*/ 20 21 22 // listFiles(); 23 File[] listFiles = file.listFiles(); 24 for (File f : listFiles) { 25 System.out.print(f.getName()); 26 if(f.isDirectory()) { 27 System.out.println(" 目录"); 28 }else { 29 System.out.println(" 文件"); 30 } 31 } 32 }
1.2 IO流
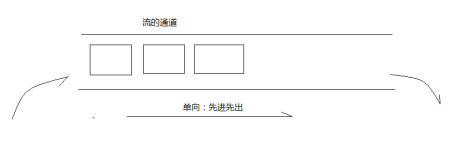
1.2.1 流
流(stream):流是一连串流动的数据(字节、字符),以先进先出的方式发送的信息的通道中
1.2.2 输入流和输出流
输入流
数据从源数据源流入程序的过程称为输入流。可以理解为从源数据源读取数据到程序的过程
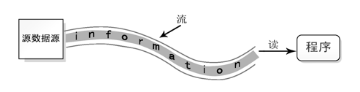
输出流
数据从程序流出到目的地的过程称为输出流。可以理解为把数据从程序写入目的地的过程

数据源一般指提供数据的原始媒介,一般常见有文件、数据库、云端、其他硬件等能提供数据的媒介。
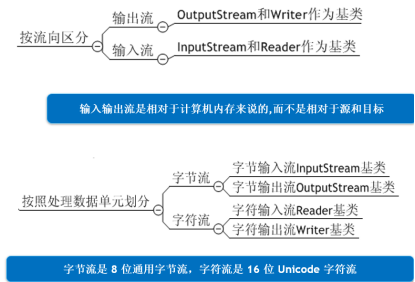
1.2.13流的分类
按照流向分为输入流和输出流
按照处理单元分为字节流和字符流
按照功能分为节点流和转换流,处理流。
1.3 InputStream/OutputStream
InputStream 是所有字节输入流的抽象父类,提供了
read 读取一个字节
read(byte[] buf) 读取一定量的字节到缓冲区数组 buf中。
OutputStream 是所有字节输出流的抽象父类,提供了
write() 写入一个字节
write(byte[] buf) 写入一定量的字节到输出流
FileInputStream 文件字节输入流,专门用于从文件中读取字节到程序内存中。
FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流,专门用于从内存中写入字节到文件中。
需求:从文件读取一个字节
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 需求:读取一个文件中的一个字节 4 File file = new File("d:\javatest\a.txt"); 5 6 // 【1】创建管道 7 FileInputStream in = null; 8 9 try { 10 in = new FileInputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】从管道读取一个字节 13 /* 14 int t; 15 t = in.read(); 16 t = in.read(); 17 t = in.read(); 18 t = in.read(); 19 */ 20 // System.out.println(t); 21 22 // 循环读取一个字节 23 int t; 24 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 25 while( (t=in.read()) != -1 ) { 26 sb.append((char)t); 27 } 28 29 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 30 31 32 33 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } catch(IOException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 // 【3】关闭流管道 40 try { 41 in.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 }
一次读取多个字节
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 需求:一次读取多个字节 4 File file = new File("d:\javatest\a.txt"); 5 6 // 【1】创建管道 7 FileInputStream in = null; 8 9 try { 10 in = new FileInputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】从管道读取多个字节到缓冲区 13 /* 14 byte[] buf = new byte[5]; 15 int len; 16 len = in.read(buf); 17 len = in.read(buf); 18 len = in.read(buf); 19 len = in.read(buf); 20 21 for(byte b:buf) { 22 System.out.print((char)b+" "); 23 } 24 System.out.println(len); 25 */ 26 27 // 通过循环读取文件 28 byte[] buf = new byte[5]; 29 int len; 30 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 31 while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1 ) { 32 // 读取的内容是原始二进制流,需要根据编码的字符集解码成对于字符 33 String str = new String(buf,0,len); 34 sb.append(str); 35 } 36 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 37 38 39 40 41 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } catch(IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 47 // 【3】关闭流管道 48 try { 49 in.close(); 50 } catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } 53 }
需求:按照指定编码写入文件
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 File file = new File("d:\javatest\c.txt"); 5 6 FileOutputStream out = null; 7 8 try { 9 // 【1】创建输出流管道 10 out = new FileOutputStream(file); 11 12 // 【2】写入数据到管道中 13 // 一次写入一个字节 14 /* 15 out.write(97); 16 out.write(98); 17 out.write(99); 18 */ 19 20 // 一次写入多个字节 21 String str = "hello world"; 22 // gbk 23 /* 24 byte[] buf = str.getBytes(); 25 out.write(buf); 26 */ 27 28 byte[] buf = str.getBytes("UTF-8"); 29 out.write(buf); 30 31 System.out.println("写入完成!"); 32 33 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } catch (IOException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 // 【3】关闭流 40 try { 41 out.close(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 }
注意:
[1]字符串写入文件时一定会存在编码问题
[2]使用utf8编码写入文件时,如果不含中文时,win系统会对文件的编码造成误判。
[3] 通过字节流写入文件时,向管道写入一个字节,该字节立即写入文件中。
总结
InputStream/OutputStream 用于字节的读写。主要用于读取二进制文件(图片、音频、视频),也可以读取文件性文件。
需求:请把d:\javatest\logo.png 复制到工程目录中,并显示复制进度。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { 2 3 4 File oriFile = new File("d:\javatest\logo.jpg"); 5 File toFile = new File("logo.jpg"); 6 7 long totalLen = oriFile.length(); // 文件大小 8 long cpyedLen = 0; // 已复制完成的大小 9 float progress = 0.0f; 10 11 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(oriFile); 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(toFile); 13 14 // 一次读取1kb 15 byte[] buf = new byte[512]; 16 int len; 17 while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1) { 18 out.write(buf, 0, len); 19 cpyedLen += len; 20 progress = cpyedLen*1.0f/totalLen; 21 System.out.println(progress); 22 23 24 } 25 26 in.close(); 27 out.close(); 28 29 System.out.println("复制完成!"); 30 31 }
思考:用字节流来读取文本性文件时,按字节读容易造成乱码。此时,能不能按字符来读取。
1.4 Reader/Writer
Reader 是字符输入流的抽象父类,提供了
read 一次读取一个字符
read(char[] cbuf) 一次读取多个字符到字符缓冲区cbuf,返回长度表示读取的字符个数。
Writer 是字符输出流的抽象父类,提供了
write
write(char[] cbuf)
write(string)
FileReader 文件字符输入流,专门用于读取默认字符编码文本性文件。
FileWriter 文件字符输出流,专门用于写入默认字符编码的文本性文件。为了提高效率,FileWriter内部存在一个字节缓冲区,用于对待写入的字符进行统一编码到字节缓冲区,一定要在关闭流之前,调用flush方法刷新缓冲区。
需求:一次读取一个字符/多个字符到cbuf
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\d.txt"); 4 5 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 6 7 // 【1】一次读取一个字符 8 /* 9 int c; 10 c = reader.read(); 11 c = reader.read(); 12 c = reader.read(); 13 c = reader.read(); 14 c = reader.read(); 15 System.out.println((char)c); 16 */ 17 18 // 【2】一次读取多个字符到cbuf中 19 /* 20 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 21 int len; 22 len = reader.read(cbuf); 23 len = reader.read(cbuf); 24 len = reader.read(cbuf); 25 len = reader.read(cbuf); 26 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cbuf)); 27 System.out.println(len); 28 */ 29 30 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 31 int len; 32 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 33 while( (len=reader.read(cbuf)) != -1 ) { 34 sb.append(cbuf,0,len); 35 } 36 37 System.out.println(sb); 38 }
需求:写入字符到文件中
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 4 File file = new File("d:\javatest\f.txt"); 5 6 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); 7 8 // 【1】一次写入一个字符 9 /*writer.write('中'); 10 writer.write('国');*/ 11 12 // 【2】一次写入多个字符 13 /*char[] cbuf = {'h','e','l','l','o','中','国'}; 14 writer.write(cbuf);*/ 15 16 // 【3】一次写入一个字符串 17 String str = "hello你好"; 18 writer.write(str); 19 20 21 // 刷新字节缓冲区 22 writer.flush(); 23 24 // 关闭流通道 25 writer.close(); 26 27 System.out.println("写入完成"); 28 }
思考:如何把字符串以utf8或者其他编码写入文件?
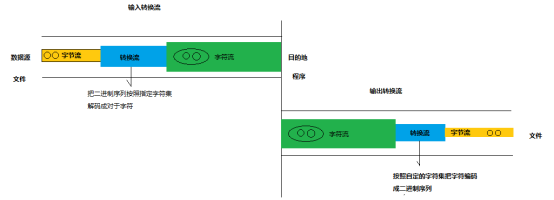
1.5 转换流
InputStreamReader 继承于Reader,是字节流通向字符流的桥梁,可以把字节流按照指定编码 解码 成字符流。
OutputStreamWriter 继承于Writer,是字符流通向字节流的桥梁,可以把字符流按照指定的编码 编码 成字节流。
1.5.1 转换流工作原理
需求:按utf8字符集写入文件
1 /** 2 * 把一个字符串以utf8编码写入文件 3 */ 4 public class Test01 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 6 7 8 String str = "hello中国"; 9 File file = new File("d:\javatest\g.txt"); 10 11 // 【1】创建管道 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 13 OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "utf8"); 14 15 // 【2】写入管道 16 writer.write(str); 17 18 // 【3】刷新缓冲区 19 writer.flush(); 20 21 // 【4】关闭管道 22 out.close(); 23 writer.close(); 24 25 System.out.println("写入完成"); 26 } 27 }
需求:读取utf8文件
/** * 读取utf8编码的文本文件 */ public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:\javatest\g.txt"); // 【1】建立管道 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "UTF-8"); char[] cbuf = new char[2]; int len; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while( (len=reader.read(cbuf))!=-1 ) { sb.append(cbuf, 0, len); } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } }
注意:
[1]win平台默认的utf8编码的文本性文件带有BOM,java转换流写入的utf8文件不带BOM。所以用java读取手动创建的utf8文件会出现一点乱码(?hello中国,?是bom导致的)
[2] 一句话:用字符集编码,一定用字符集解码!!
FileReader = InputStreamReader + GBK
1 package cn.sxt07.outputstreamwriter; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileReader; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 8 9 /** 10 * 读取一个gbk编码的文本性文件 11 */ 12 public class Test02 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 14 15 16 File file = new File("d:\javatest\f.txt"); 17 18 // 【1】建立管道 19 /* 20 * FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); 21 * InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "GBK"); 22 */ 23 24 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 25 26 char[] cbuf = new char[2]; 27 int len; 28 29 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 30 while( (len=reader.read(cbuf))!=-1 ) { 31 sb.append(cbuf, 0, len); 32 } 33 34 reader.close(); 35 36 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 37 } 38 }
1.6 BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
BufferedReader 继承于Reader,提供了
read
read(char[] cbuf)
readLine() 用于读取一行文本,实现对文本的高效读取。
BufferedReader 初始化时需要一个reader,本质上BufferedReader在reader的基础上增加readLine()的功能。
BufferedWriter继承于Writer,提供了
write
write(char[] cbuf)
write(string)
newline() 写入一个行分隔符。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 // 按行读取gbk文本性文件 4 5 File file = new File("d:\javatest\i.txt"); 6 7 // 【1】创建管道 8 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 9 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 10 11 // 【2】读取一行 12 /* 13 String line = br.readLine(); 14 line = br.readLine(); 15 line = br.readLine(); 16 line = br.readLine(); 17 */ 18 19 String line; 20 while( (line=br.readLine()) != null) { 21 System.out.println(line); 22 } 23 }
需求:以gbk编码写入一首诗到文件
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\j.txt"); 4 5 // 【1】创建gbk管道 6 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); 7 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 8 9 // 【2】写入一行 10 bw.write("窗前明月光,"); 11 bw.newLine(); 12 13 bw.write("疑似地上霜。"); 14 15 // for win 16 // bw.write(" "); 17 18 // for unix/linux/mac 19 // bw.write(" "); 20 21 bw.write("举头望明月,"); 22 bw.newLine(); 23 24 // 【3】flush 25 bw.flush(); 26 27 // 【4】关闭管道 28 bw.close(); 29 writer.close(); 30 }
需求:以utf8编码高效写入文件
1 /** 2 * 以utf8写入一首诗 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test02 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 9 File file = new File("d:\javatest\j-utf8.txt"); 10 11 // 【1】创建utf8管道 12 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 13 OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "UTF-8"); 14 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 15 16 // 【2】写入一行 17 bw.write("窗前明月光,"); 18 bw.newLine(); 19 20 bw.write("疑似地上霜。"); 21 22 // for win 23 bw.write(" "); 24 25 // for unix/linux/mac 26 // bw.write(" "); 27 28 bw.write("举头望明月,"); 29 bw.newLine(); 30 31 // 【3】flush 32 bw.flush(); 33 34 // 【4】关闭管道 35 bw.close(); 36 writer.close(); 37 } 38 }
1.7 标准输入输出流
1.7.1 标准输入流
源数据源是标准输入设备(键盘、鼠标、触摸屏)等输入设备。在java中用System.in 得到一个InputStream字节输入流。
需求:在控制台输入一句话,然后原样输出
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 // 需求:输入一句话,然原样输出 3 InputStream in = System.in; 4 5 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 6 int len; 7 // buf中包含回车和换行 8 len = in.read(buf); 9 10 String str = new String(buf, 0, len); 11 // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf)); 12 System.out.println(str); 13 }
注意:
[1] 标准输入流以字节流流入内存,如果在控制台中输入字符,字符以默认编码(win简体:gbk)编码成字节进入标准输入流。
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 // 需求:从控制台高效读取一行数据。把一首诗写入文件。 3 4 InputStream in = System.in; 5 InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "GBK"); 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 7 8 File file = new File("d:\javatest\k.txt"); 9 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file); 10 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 11 12 String end = "bye"; 13 while(true) { 14 String line = br.readLine(); 15 if(line.equals(end)) { 16 break; 17 } 18 19 bw.write(line); 20 // bw.newLine(); 21 } 22 23 bw.flush(); 24 25 bw.close(); 26 writer.close(); 27 28 }
1.7.2 标准输出流(PrintStream)
数据目的地是标准输出设备(显示器)等输出设备。在java中用System.out得到一个PrintStream 字节输出流(字节打印流)。提供了更强大的
println
打印方法用于打印各种数据类型。
需求:读取文件,显示到标准输出设备
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\k.txt"); 4 5 FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); 6 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 7 8 PrintStream ps = System.out; 9 10 String line; 11 while( (line=br.readLine())!=null ) { 12 ps.println(line); 13 } 14 }
PrintStream 打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码(可以指定编码)转换为字节。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String str = "hello中国"; byte[] buf = str.getBytes("utf-8"); PrintStream ps = System.out; ps.write(buf); }
1.8 Scanner(C)
通过scanner扫描文件、字节流等
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 // 扫描平台默认编码的文件 4 /*File file = new File("d:\javatest\j.txt"); 5 Scanner sc = new Scanner(file); 6 */ 7 8 // 扫描指定编码的文件 9 Scanner sc = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(new File("d:\javatest\j-utf8.txt")), "UTF-8"); 10 11 String line; 12 while (sc.hasNextLine()) { 13 line = sc.nextLine(); 14 System.out.println(line); 15 } 16 17 }
1.10 序列化
把内存中的对象永久保存到硬盘的过程称为对象序列化,也叫做持久化。
把硬盘持久化的内存恢复的内存的过程称为对象反序列化。
1.10.1 Serializable
类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化,并抛出异常
Exception in thread "main" java.io.NotSerializableException: cn.sxt05.serializable.Student at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject0(ObjectOutputStream.java:1184) at java.io.ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(ObjectOutputStream.java:348) at cn.sxt05.serializable.Test01.main(Test01.java:22)
Serializable接口没有方法或字段,仅用于标识可序列化的语义
public class Student implements Serializable{
1.10.2 序列化对象
ObjectOutputStream 继承于OutputStream,专门用于把对象序列化到本地。提供了
writeXXX
writeObject() 用于写入一个对象
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 Student stu = new Student("001", "大狗", 20, Gender.男); 4 5 /** 6 * 方案1:取stu所有的属性,通过特定的字符串(-),把各个属性值连接起来 7 * 001-大狗-20-男 8 */ 9 10 File file = new File("d:\javatest\l.txt"); 11 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file); 12 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); 13 14 oos.writeObject(stu); 15 16 oos.close(); 17 out.close(); 18 }
1.10.3 反序列化对象
ObjectInputStream 继承于InputStream ,专门用于把本地持久化内容反序列化到内存,提供了
readXXX
readObject() 用于读取一个序列化内容并返回一个对象。
public class Student implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -1003763572517930507L;
1.10.5 transient
开发过程中,如果想忽略某些字段不让其序列化时,可以使用transient修饰。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { File file = new File("d:\javatest\l.txt"); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in); Student student = (Student) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(student.getId()); System.out.println(student.getName()); System.out.println(student.getAge()); System.out.println(student.getGender()); ois.close(); in.close(); }
1.10.4 序列化版本
当序列化完成后,后期升级程序中的类(Student),此时再反序列化时会出现异常。
Exception in thread "main" java.io.InvalidClassException: cn.sxt05.serializable.Student; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = -6288733824962181189, local class serialVersionUID = 1690603786167234505 at java.io.ObjectStreamClass.initNonProxy(ObjectStreamClass.java:687) at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readNonProxyDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1876) at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readClassDesc(ObjectInputStream.java:1745) at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readOrdinaryObject(ObjectInputStream.java:2033) at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject0(ObjectInputStream.java:1567) at java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject(ObjectInputStream.java:427) at cn.sxt05.serializable.Test02.main(Test02.java:16)
异常原因:序列化流的serialVersionUID和升级后类的版本不匹配。
解决方案:给Student类加序列化版本号,有两种方式
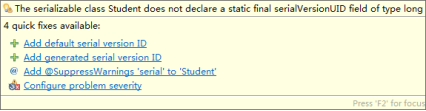
1 public class Student implements Serializable { 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 7222966748321328300L; 4 5 private String id; 6 private transient String name; 7 private transient int age; 8 private Gender gender; 9 private String phone;
1.11 DataInputStream/DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream 继承OutputStream,专门用于把基本java数据类型写入输出流。提供了writeXXX 写入基本java数据类型。
DataInputStream 继承于InputStream,允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。
DataInputStream/DataOutputStream 特别适合读取/写入在网络传输过程中的数据流。
写入基本java数据类型
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 3 File file = new File("d:\javatest\n.txt"); 4 FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream(file); 5 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out); 6 7 dos.writeInt(10); 8 dos.writeUTF("hello中国"); 9 10 dos.close(); 11 out.close(); 12 13 System.out.println("写入完成"); 14 15 }
读取基本java数据类型
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("d:\javatest\n.txt"); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in); int a = dis.readInt(); String str = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(a); System.out.println(str); }
注意:
以什么顺序写入基本java数据类型,就以什么顺序读取基本java数据类型。