①BZOJ1123 BLO(割点)
若选择的点是割点,则通过删除他的边能获得的每个子树的子树大小(siz)都与((n-siz))构成答案;所有割出的子树大小和为(sum),((n-sum-1))和(sum+1)又能构成答案;最后还有该点和其他所有点构成答案((n-1))
若该点不是割点,删除并不会影响图的连通性,所以答案为(2*(n-1))
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
struct edge {
int to, next;
}e[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], edge_cnt;
inline void add(int from,int to)
{
e[++edge_cnt] = { to,head[from] };
head[from] = edge_cnt;
}
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], num;
ll ans[maxn], siz[maxn];
bool cut[maxn];
int n, m;
void tarjan(int from)
{
dfn[from] = low[from] = ++num; siz[from] = 1;
ans[from] = 0;
int flag = 0;
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = head[from]; i != -1; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (!dfn[to])
{
tarjan(to);
siz[from] += siz[to];
low[from] = min(low[from], low[to]);
if (low[to] >= dfn[from])
{
flag++;
ans[from] += siz[to] * (n - siz[to]);
sum += siz[to];
if (from != 1 || flag > 1)
cut[from] = 1;
}
}
else
low[from] = min(low[from], dfn[to]);
}
if (cut[from])
ans[from] += (n - 1) + (n - sum - 1) * (sum + 1);
else
ans[from] = 2 * (n - 1);
}
int main()
{
fastio;
cin >> n >> m;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
while (m--)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x == y)continue;
add(x, y), add(y, x);
}
num = 0;
tarjan(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
②Mr. Young's Picture Permutations(线性dp)
dp[a][b][c][d][e]表示从第一行到第五行分别的a、b、c、d、e人的合法状态集合的大小,每次转移可以这样理解:
将上一状态所有已排好人的身高全部++,然后在你需要转移的位置(选取的行的末尾)插入一个大小为1的人也合法。
(因为行人数从1到5逐行不升)
状态转移方程:太多了看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll dp[31][31][31][31][31];
int main()
{
fastio;
int k;
while (cin >> k, k)
{
int s[6] = { 0 };
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)cin >> s[i];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0][0][0][0] = 1;
for (int a = 0; a <= s[1]; a++)
for (int b = 0; b <= min(a, s[2]); b++)
for (int c = 0; c <= min(b, s[3]); c++)
for (int d = 0; d <= min(c, s[4]); d++)
for (int e = 0; e <= min(d, s[5]); e++)
{
ll& x = dp[a][b][c][d][e];
if (a && a - 1 >= b) x += dp[a - 1][b][c][d][e];
if (b && b - 1 >= c) x += dp[a][b - 1][c][d][e];
if (c && c - 1 >= d) x += dp[a][b][c - 1][d][e];
if (d && d - 1 >= e) x += dp[a][b][c][d - 1][e];
if (e) x += dp[a][b][c][d][e - 1];
}
cout << dp[s[1]][s[2]][s[3]][s[4]][s[5]] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
③LCIS(线性dp)
以dp[i][j]并不能表示以a[i]和b[j]结尾的两串的最长LCIS,因为这里为了避免重复转移(如果根据(LCS)转移方程当a[i]!=b[j]时(dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j],dp[i][j-1])),当(a[i]=2,b[j1]=b[j2]=2)时,会在a[i]==b[j]的转移中重复转移。因此转移只能dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]。之前得到的最长dp不一定能转移到dp[n][n].
因此dp[i][j]表示以a1ai和b1bj可以构成的(以bj为结尾的LCIS)的长度。
只有a[i]==b[j]时才需要从前面找一个合法状态+1取max,合法状态可以记录为val,每次新加入b[j]时当b[j]<a[i]更新val。
对样例dp数组打表: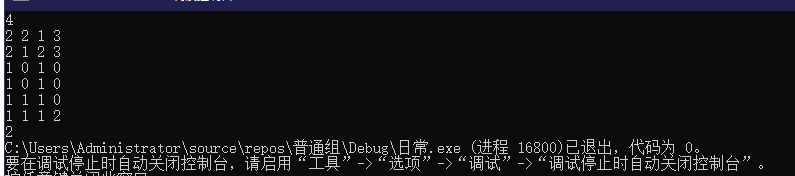
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int dp[3005][3005];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n + 1), b(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> b[i];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int val = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[i] == b[j])dp[i][j] = val + 1;
else dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];//为什么不能写max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]),因为当a[i]=2,b[j1]=b[j2]=2时,会重复转移
if (b[j] < a[i])val = max(val, dp[i - 1][j]);
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
④LUOGU p1006传纸条(线性dp)
当路径不重合时:dp[a][b][c][d] = max(max(dp[a - 1][b][c - 1][d], dp[a - 1][b][c][d - 1]), max(dp[a][b - 1][c - 1][d], dp[a][b - 1][c][d - 1]))+ v[a][b] + v[c][d];
当(a==c&&b==d)时只需要将v[a][b]加一次即可,这个重合状态会向下转移,不影响后续的不重合取数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int dp[55][55][55][55];
int v[55][55];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> v[i][j];
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++)
for(int b=1;b<=m;b++)
for(int c=1;c<=n;c++)
for (int d = 1; d <= m; d++)
{
dp[a][b][c][d] = max(max(dp[a - 1][b][c - 1][d], dp[a - 1][b][c][d - 1]), max(dp[a][b - 1][c - 1][d], dp[a][b - 1][c][d - 1]));
dp[a][b][c][d] += v[a][b] + v[c][d];
if (a == c && b == d)dp[a][b][c][d] -= v[a][b];
}
cout << dp[n][m - 1][n - 1][m];
return 0;
}
⑤Mobile Service(线性DP)
如果设计状态dp[i][a][b][c],复杂度为(N*L^3),显然是会T的。
通过观察可以发现:每次只需移动1人,只需要在状态中记录不动的2个人的位置,另一个人的位置就是上一个请求的位置。
状态转移即:
dp[i][a][b] = min(dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[last][p], dp[i][a][b]);
dp[i][a][last] = min(dp[i][a][last], dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[b][p]);
dp[i][last][b] = min(dp[i][last][b], dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[a][p]);
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL);
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int dp[1010][205][205];
int c[205][205];
int main()
{
fastio;
int L, n;
cin >> L >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= L; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= L; j++)
cin >> c[i][j];
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof(dp));
dp[0][1][2] = dp[0][2][1] = 0;
int last = 3;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int p;
cin >> p;
for (int a = 1; a <= 200; a++)
{
for (int b = 1; b <= 200; b++)
{
if (a == b || a == last || b == last)continue;
dp[i][a][b] = min(dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[last][p], dp[i][a][b]);
dp[i][a][last] = min(dp[i][a][last], dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[b][p]);
dp[i][last][b] = min(dp[i][last][b], dp[i - 1][a][b] + c[a][p]);
}
}
last = p;
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int a = 1; a <= 200; a++)
for (int b = 1; b <= 200; b++)
ans = min(ans, min(dp[n][a][b], min(dp[n][a][last], dp[n][last][b])));
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
⑥AcWing395 冗余路径
将图进行v-dcc缩点,答案即缩点后(度为1的点的数量/2)上取整
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int head[maxn], edge_cnt;
struct edge {
int to, next;
}e[maxn << 1];
inline void add(int from, int to)
{
e[++edge_cnt] = { to,head[from] };
head[from] = edge_cnt;
}
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], num;
int c[maxn], dcc;
bool bridge[maxn << 1];
stack<int>s;
void tarjan(int from, int in_edge)
{
dfn[from] = low[from] = ++num;
s.push(from);
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (!dfn[to])
{
tarjan(to, i);
low[from] = min(low[from], low[to]);
if (low[to] > dfn[from])
bridge[i] = bridge[i ^ 1] = 1;
}
else if (i != (in_edge ^ 1))
low[from] = min(low[from], dfn[to]);
//用反向边更新追溯值
}
if (dfn[from] == low[from])
{
++dcc;
while (s.top() != from)
{
c[s.top()] = dcc;
s.pop();
}
c[s.top()] = dcc;
s.pop();
}
}
vector<int>G[maxn];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
edge_cnt = 1;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
while (m--)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);
add(y, x);
}
dcc = 0;
tarjan(1, -1);
for (int i = 2; i <= edge_cnt; i++)//遍历每一条边,正反都存
{
int x = e[i].to, y = e[i ^ 1].to;
if (c[x] == c[y])continue;
G[c[x]].push_back(c[y]);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= dcc; i++)
{
//cout << i << " " << G[i].size() << endl;
if (G[i].size()==1)
ans++;
}
cout << (ans + 1) / 2;
return 0;
}
⑦AcWing1183 电力
求出割点的同时记录能割出多少个dcc,答案=最开始的双连通分量数量+ (min(flag + (from != root)) - 1);
对于每个点from,flag为其dfn[from]>=low[to]的数量。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
int head[maxn], edge_cnt;
struct edge {
int to, next;
}e[maxn << 1];
inline void add(int from, int to)
{
e[++edge_cnt] = { to,head[from] };
head[from] = edge_cnt;
}
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], root, num, ans, tot;
bool cut[maxn];
void tarjan(int from)
{
//cout << from << endl;
dfn[from] = low[from] = ++num;
int flag = 0;
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (!dfn[to])
{
tarjan(to);
low[from] = min(low[from], low[to]);
if (low[to] >= dfn[from])
{
flag++;
if (from != root || flag > 1)
cut[from] = 1;
}
}
else low[from] = min(low[from], dfn[to]);
//用反向边更新追溯值
}
ans = max(ans, flag + (from != root));
}
int main()
{
fastio;
int n, m;
while (cin >> n >> m, n || m)
{
edge_cnt = 1;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
memset(dfn, 0, sizeof(dfn));
ans = tot = num = 0;
while (m--)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x++, y++;
add(x, y);
add(y, x);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!dfn[i])
{
tot++;
root = i;
tarjan(i);
}
cout<< tot + ans - 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
CF600E Lomsat gelral(dsu on tree模版)
题意:
有一棵 (n) 个结点的以 (1) 号结点为根的有根树。
每个结点都有一个颜色,颜色是以编号表示的, (i) 号结点的颜色编号为 (c_i)
如果一种颜色在以 (x) 为根的子树内出现次数最多,称其在以 (x) 为根的子树中占主导地位。显然,同一子树中可能有多种颜色占主导地位。
你的任务是对于每一个(i∈[1,n]),求出以 (i) 为根的子树中,占主导地位的颜色的编号和。
(n≤10^5,c_i≤n)
看上去暴力统计肯定会T。。。
用和轻重链剖分一样方法统计出重儿子,然后去暴力算答案,对于一个节点i:
暴力统计所有子树的贡献
若其为父节点的重儿子,则不需要清空他的贡献;
若其不是重儿子,则清空所有贡献
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
struct edge{
int to, next;
}e[maxn << 1];
int edge_cnt = 0, head[maxn];
inline void add(int from, int to)
{
e[++edge_cnt] = { to,head[from] };
head[from] = edge_cnt;
}
ll col[maxn], ans[maxn], cnt[maxn];
int siz[maxn], son[maxn];
void getson(int from, int fa)//统计重儿子
{
int MAX = 0;
siz[from] = 1;
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (to == fa)continue;
getson(to, from);
siz[from] += siz[to];
if (siz[to] > MAX)
MAX = siz[to], son[from] = to;
}
}
int Son;
ll sum = 0, MAX = 0;
void add(int from,int fa,int flag)//暴力统计答案
{
ll &tot = cnt[col[from]];
tot += flag;
if (tot > MAX)MAX = tot, sum = col[from];
else if (tot == MAX)sum += col[from];
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (to == fa || to == Son)continue;
add(to, from, flag);
}
}
void dfs(int from, int fa, int opt)//dsu on tree
{
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to;
if (to == fa)continue;
if (to != son[from])dfs(to, from, 0);//先去计算轻儿子的答案
}
if (son[from])dfs(son[from], from, 1), Son = son[from];//再去计算重儿子的答案
//计算完之后:
add(from, fa, 1), Son = 0;//由于重儿子的答案不会被删除,只需要统计from轻儿子的答案
ans[from] = sum;//计入答案
if (!opt)add(from, fa, -1), sum = 0, MAX = 0;//如果这个点不是其父节点的重儿子,则要暴力清空答案
}
int main()
{
fastio;
int n;
cin >> n;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> col[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);
add(y, x);
}
getson(1, -1);
dfs(1, 0, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
校oj Teacher Ma专场 H: 闪电五连鞭
最优方案肯定要每次取n-1个,可能有a[i]比较大,需要特判
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 5e4 + 10;
ll inf = 1e17 + 7;
int main()
{
fastio;
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<ll>a(n + 1);
ll MAX = 0;
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
sum += a[i];
MAX = max(MAX, a[i]);
}
sum = (sum + n - 2) / (n - 1);
cout << max(sum, MAX);
return 0;
}
校oj Teacher Ma专场 I: 啪的一下,很快的哈
分层图最短路,就直接开个K维嗯转移就没了
这种dij大概不需要记录遍历过的点,毕竟每次贪心取得都是最小的距离,贪心之后不会再被其他的点更新
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int maxn = 5e4 + 10;
ll inf = 1e17 + 7;
struct edge {
ll to, cost, next;
}e[maxn<<1];
int edge_cnt = 0, head[maxn];
void add(int from, int to, ll cost)
{
e[++edge_cnt] = { to,cost,head[from] };
head[from] = edge_cnt;
}
int S, T, cnt = 0;
struct node {
ll cost;
int from;
int cnt;
friend bool operator <(node a, node b){
return a.cost > b.cost;
}
};
priority_queue<node>q;
ll dis[maxn][11];
int pre[maxn];
ll fee[maxn];
int n, m, K;
void dij(int n)
{
while (!q.empty())q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= K; j++)
dis[i][j] = inf;
dis[S][0] = 0;
q.push({ 0,S,0 });
while (!q.empty())
{
int from = q.top().from, cnt = q.top().cnt;
q.pop();
for (int i = head[from]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
int to = e[i].to, cost = e[i].cost;
if (dis[to][cnt] > dis[from][cnt] + cost)
{
dis[to][cnt] = dis[from][cnt] + cost;
q.push({ dis[to][cnt],to,cnt });
}
if (cnt < K && dis[to][cnt + 1]>dis[from][cnt])
{
dis[to][cnt + 1] = dis[from][cnt];
q.push({ dis[to][cnt + 1] ,to,cnt + 1 });
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
fastio;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
cin >> n >> m >> K;
cin >> S >> T;
while (m--)
{
ll x, y, cost;
cin >> x >> y >> cost;
add(x, y, cost), add(y, x, cost);
}
dij(n);
ll ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i <= K; i++)
ans = min(ans, dis[T][i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}