定义:
正则表达式是对字符串操作的一种逻辑公式,用事先定义好的一些特定字符、以及特定字符的组合,组成一个‘规则字符串’,‘规则字符串’用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑
正则表达式非python独有,在python中,re模块实现正则表达式
使用在线正则表达式测试样例:
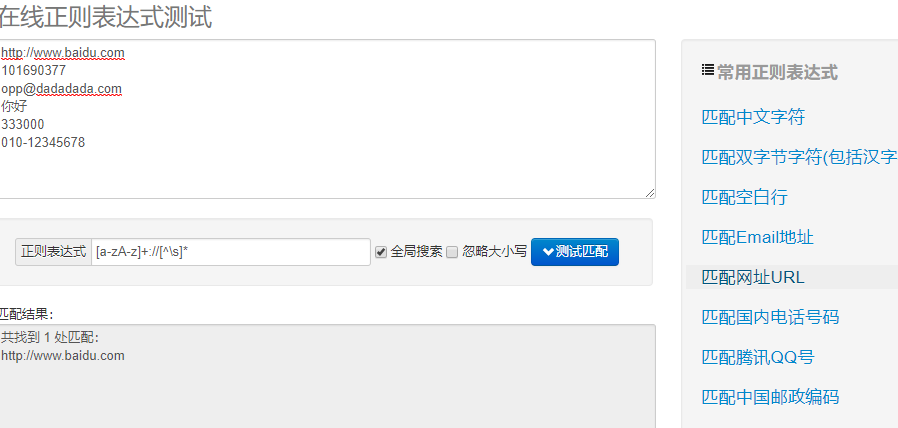
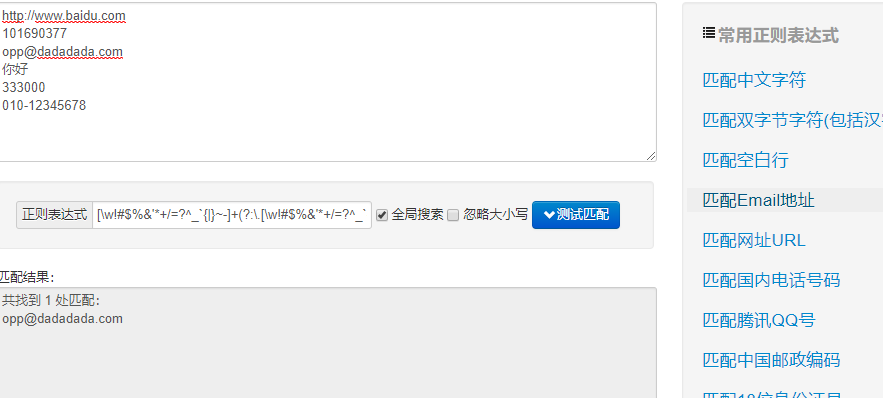
import re #常规匹配 content = 'hello 123 4567 world_this is a re demo' result = re.match('^hellosdddsd{4}sw{10}.*demo',content) print(result)
输出结果:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 38), match='hello 123 4567 world_this is a re demo'>
#泛匹配
content = 'hello 123 4567 world_this is a re demo'
result = re.match('^hello.*demo$',content)
print(result)
#匹配目标 content = 'hello 1234567 world_this is a re demo' result = re.match('^hellos(d+)sworld.*demo$',content) print(result) print(result.group(1))
输出结果为:1234567
#贪婪匹配 content = 'hello 1234567 world_this is a re demo' result = re.match('^hello.*(d+).*demo$',content) print(result) print(result.group(1))
输出结果为:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 37), match='hello 1234567 world_this is a re demo'>
7
可以看出group(1)只匹配到7
.*会尽可能多的进行匹配,这就是贪婪匹配
content = 'hello 1234567 world_this is a re demo'
result = re.match('^hello.*?(d+).*demo$',content)
print(result)
print(result.group(1))
输出结果为:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 37), match='hello 1234567 world_this is a re demo'>
1234567
在.*后面加上一?,就变为非贪婪匹配
匹配模式:re.S
转义:
想要匹配特殊字符,如^和$,在特殊字符前面加
小结:
尽量使用泛匹配,使用括号得到匹配目标,尽量使用非贪婪匹配,有换行符就用re.S匹配模式
以上就是正则表达式中最常用的一些方式
上面用match方法进行了演示,但是match方法有些时候不方便,因为它会从第一个字符开始匹配,如果第一个匹配不到,就会返回None下面介绍一些常用的匹配方法
re.search:
扫描整个字符串并返回第一个成功的匹配
import re
content = 'extra strings hello 1234567 wold_this is a demo'
result1 = re.match('hello.*?(d+).*?demo$',content)
result2 = re.search('hello.*?(d+).*?demo$',content)
print(result1)
print(result2)
输出结果为:
None
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(14, 47), match='hello 1234567 wold_this is a demo'>
小结:为匹配方便,能用search就不用match
search匹配练习:
1、匹配 齐秦 往事随风
import re
html = '''
<div id="songs-list">
<h2 class ="title">经典老歌</h2>
<p class=Introduction>
经典老歌列表
</p>
<url id="list" class ="list-group">
<li data-view="2">一路上有你</li>
<li data-view="7">
<a href="2/mp3" singer="任贤齐" >沧海一声笑</a>
</li>
<li data-view="4" class = "active">
<a href="3/mp3" singer="齐秦">往事随风</a>
</li>
<li data-view="6" ><a href="4/mp3" singer="beyond">光辉岁月</a></li>
<li data-view="5" ><a href="5/mp3" singer="陈慧琳">记事本</a></li>
<li data-view = "5">
<a href="6/mp3" singer="邓丽君"><i class = "fa fa-user"></li>但愿人长久</a>
</li>
</url>
</div>
'''
response = re.search('<li.*?active">.*?<a.*?singer="(w+)">(w+)</a>',html,re.S)
if response:
print(response)
print(response.group(1),response.group(2))
输出结果为:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(127, 313), match='<li data-view="2">一路上有你</li>
<li data-view=">
齐秦 往事随风
2、将匹配模式re.S去掉(.就不能匹配换行符了)
import re
html = '''
<div id="songs-list">
<h2 class ="title">经典老歌</h2>
<p class=Introduction>
经典老歌列表
</p>
<url id="list" class ="list-group">
<li data-view="2">一路上有你</li>
<li data-view="7">
<a href="2/mp3" singer="任贤齐" >沧海一声笑</a>
</li>
<li data-view="4" class = "active">
<a href="3/mp3" singer="齐秦">往事随风</a>
</li>
<li data-view="6" ><a href="4/mp3" singer="beyond">光辉岁月</a></li>
<li data-view="5" ><a href="5/mp3" singer="陈慧琳">记事本</a></li>
<li data-view = "5">
<a href="6/mp3" singer="邓丽君"><i class = "fa fa-user"></li>但愿人长久</a>
</li>
</url>
</div>
'''
response = re.search('<li.*?<a.*?singer="(w+)">(w+)</a>',html)
if response:
print(response)
print(response.group(1),response.group(2))
输出结果为:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(328, 387), match='<li data-view="6" ><a href="4/mp3" singer="beyond>
beyond 光辉岁月
re.findall:
搜索字符串,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串
import re
html = '''
<div id="songs-list">
<h2 class ="title">经典老歌</h2>
<p class=Introduction>
经典老歌列表
</p>
<url id="list" class ="list-group">
<li data-view="2">一路上有你</li>
<li data-view="7">
<a href="2/mp3" singer="任贤齐">沧海一声笑</a>
</li>
<li data-view="4" class = "active">
<a href="3/mp3" singer="齐秦">往事随风</a>
</li>
<li data-view="6" ><a href="4/mp3" singer="beyond">光辉岁月</a></li>
<li data-view="5" ><a href="5/mp3" singer="陈慧琳">记事本</a></li>
<li data-view = "5">
<a href="6/mp3" singer="邓丽君"><i class = "fa fa-user"></li>但愿人长久</a>
</li>
</url>
</div>
'''
response = re.findall('<li.*?href="(.*?)".*?singer="(.*?)">(.*?)</a>',html,re.S)
# if response:
# print(response)
print(response)
输出结果为:
[('2/mp3', '任贤齐', '沧海一声笑'), ('3/mp3', '齐秦', '往事随风'), ('4/mp3', 'beyond', '光辉岁月'), ('5/mp3', '陈慧琳', '记事本'), ('6/mp3', '邓丽君', '<i class = "fa fa-user"></li>但愿人长久')]
输出结果为一个列表形式,列表中的每一个元素是元组形式
re.sub:
替换字符串中每一个匹配的子串后返回替换后的字符串
第一个参数:正则表达式
第二个参数:要替换成的目标字符串
第三个参数:原字符串
#将字符串中的数字替换为空字符
import re content = "extre hllo 12345 nihao" result = re.sub("d+",'',content) print(result) 输出结果为: extre hllo nihao
如果要替换的字符串中有原来的字符串怎么办?用分组的形式,如:
import re
content = "extre hllo 12345 nihao"
result = re.sub("(d+)",r'1 8910',content)
print(result)
输出结果为:
extre hllo 12345 8910 nihao
###不要忘记加r
re.compile:
将正则表达式编译为正则表达式对象,以便于复用该匹配模式
import re
content = "hello ,world ,I love Python"
pattern = re.compile("hello.*?Python",re.S)
result = re.search(pattern,content)
print(result)
输出结果为:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 27), match='hello ,world ,I love Python'>
实战练习:
爬去豆瓣读书首页所有书籍信息(书名,作者等等)
豆瓣读书:
https://book.douban.com/