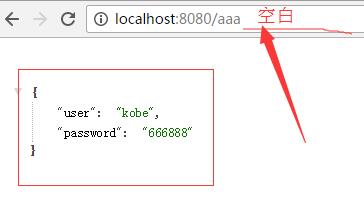
获取GET请求内容
由于GET请求直接被嵌入路径中,URL是完整的请求路径,包括了?后面的部分,因此可以手动解析后面的内容作为GET请求的参数
HTML部分:一个最基本的表单提交
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <form action="http://localhost:8080/aaa" method="GET"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user"><br> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
创建一个服务器:
const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
const util = require('util')
http.createServer( (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=utf-8'})
res.end(util.inspect(url.parse(req.url, true)))
/*
url.parse(urlString[, parseQueryString])
urlString: 要解析的URL字符串
parseQueryString: 为true,则返回一个对象;为false,则返回一个未解析的字符串。默认为false
*/
}).listen(8080)
查看页面返回结果:
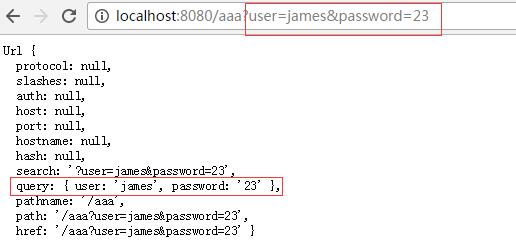
在此基础之上,我们也可以获取URL的参数
const http = require('http')
const url = require('url')
http.createServer( (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset=utf-8'})
// 解析URL参数
let params = url.parse(req.url, true).query
res.write(`用户名:${params.user}`)
res.write(`
`)
res.write(`密码:${params.password}`)
res.end()
}).listen(8080)
查看返回结果:

获取POST请求内容
POST请求的内容全部都在请求体中,http.ServerRequest并没有一个属性内容为请求体,原因是等待请求体传输可能是一件耗时的工作,比如上传文件。
很多时候我们可能并不需要理会请求体的内容,恶意的POST请求会大大消耗服务器的资源,所以Node.js默认是不会解析请求体的,当你需要的时候,需要手动来做
HTML部分:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <form action="http://localhost:8080/aaa" method="POST"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user"><br> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>
创建服务器:
const http = require('http')
const querystring = require('querystring')
const util = require('util')
http.createServer( (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain; charset: utf-8'})
let str = '' // 用于暂存请求体的信息
// 通过req的data事件监听函数,每当接受到请求体的数据,就累加到str变量里面
req.on('data', function (chunk) {
str += chunk
})
// 在end事件触发后,通过querystring.parse将str解析为真正的POST请求格式,然后向客户端返回
req.on('end', function () {
str = querystring.parse( str )
/*
querystring.parse(str[, sep[, eq[, options]]]) 该方法用于将一个查询字符串解析成Javascript对象
*/
res.end( util.inspect(str) )
})
}).listen(8080)
查看返回结果: