1、ES6模块系统
1-1、export 导出
(1)、单独导出
// a.ts export let a = 1;
(2)、批量导出
// a.ts let b = 2; let c = 3; export { b, c };
(3)、导出接口
// a.ts export interface Info { name: string; age: number; }
(4)、导出函数
// a.ts export function f() { console.log('function f'); }
(5)、导出时 起别名
// a.ts function g() { console.log('function g'); } export { g as G }
(6)、默认导出,无需函数名
// a.ts export default function() { console.log('default function'); }
(7)、导出常量
// b.ts export const str = 'hello';
(8)、引入外部模块,重新导出
// a.ts export { str as hello } from './b';
1-2、import 导入
(1)、批量导入
import { a, b, c } from './a';
console.log('a, b, c: ', a, b, c); // a, b, c: 1 2 3
(2)、导入接口
import { Info } from './a';
let jim: Info = {
name: 'Jim Green',
age: 12
}
console.log('jim', jim); // jim { name: 'Jim Green', age: 12 }
(3)、导入时 起别名
import { f as foo } from './a';
foo(); // function f
(4)、导入模块中的所有成员,绑定在All上
import * as All from './a'; console.log(All.G()); // function g console.log(All.g()); // 类型“typeof import("e:/study/ts-demo/es6/a")”上不存在属性“g”
(5)、不加 {},导入默认
import myFunction from './a'; myFunction(); // default function
2、CommonJS 模块系统
2-1、exports 导出
(1)、module.exports 整体导出
// a-node.ts let a = { x: 2, y: 3 }; module.exports = a;
(2)、exports 导出多个变量
// b-node.ts exports.c = 3; exports.d = 4;
2-2、require 导入
let a1 = require('./a-node');
let b1 = require('./b-node');
console.log(a1); // {x: 2, y: 3}
console.log(b1); // {c: 3, d: 4}
3、export = 和 import = require()
当一个模块使用 ES6模块导出,CommonJS模块导入时,就会出现模块不兼容的情况
let a2 = require('../es6/a.ts');
a2(); // Uncaught TypeError: a2 is not a function
理论上,调用a2 方法其实就是调用 a.ts 中 export.default 默认导出的那个方法,但是此处报错了。这里有两个解决方法:
(1)、调用 default 方法(不推荐)
let a2 = require('../es6/a.ts');
a2.default(); // default function
(2)、export = 语法
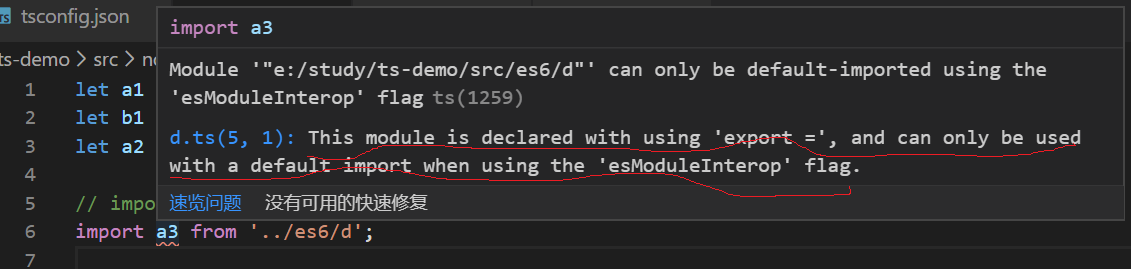
export = 语法定义一个模块的导出对象,它可以是类、接口、命名空间、函数或枚举
若要导入一个 export = 的模块时,必须使用 ts 提供的特定语法 import module = require('module')
// d.ts // export 会被编译成 CommonJS中的 module.exports,同时,意味着这个模块中不能再有其它的导出 export = function () { console.log('hello world'); }
import a3 = require('../es6/d');
a3(); // hello world
很多库使用了 CommonJS 的导出方式,如 module.exports=a,这样会导致使用ES的方式导入时失败,如 import a from 'X'。因为ES会默认访问 a 的 default 属性。TypeScript 为了兼容,引入了 esModuleInterop 选项,在编辑时自动添加default属性。
当开启 tsconfig.json 中的 esModuleInterop 选项时,可以使用 ES6模块的导入语法
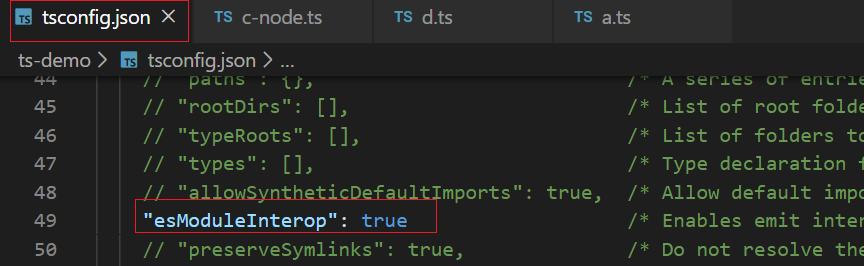
import a3 from '../es6/d'; a3(); // hello world
如果关闭该选项,使用 ES6模块语法导入时则会报错