前言:不断学习就是程序员的宿命
此题对应力扣题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/
一、LRU介绍
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的数据予以淘汰。
二、设计思想
1、所谓缓存,必须要有读+写操作,按照命中率的思路考虑,写操作+读操作时间复杂度都需要为O(1)
2、特性要求
a.必须要有顺序之分,区分最近使用的和很久没有使用的数据排序
b.读和写操作一次搞定
c.如果容量满了要删除最不常用的数据,每次新访问的还要把新的数据插入到队头
综上所述:查找快、插入快、删除快、且还要先后排序----?什么样的数据结构可以满足这个问题呢?且时间复杂度为O(1)完成操作,你觉得什么样的数据结构合适呢?
答案:LRU的算法核心就是哈希链表(哈希可以保证时间复杂度为O(1)、链表可以保证插入和删除快)
本质就是:HashMap+DoubleLinkedList,时间复杂度是O(1),哈希表+双向链表的结合体
三、LRU实操
1、封装双向链表节点Node作为数据载体
可参考JDK源码:AQS抽象队列同步器内部Node(封装Thread等信息)、HashMap内部节点Node
class Node<K, V> { K key; V value; Node<K, V> prev; Node<K, V> next; public Node() { this.prev = this.next = null; } public Node(K key, V value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.prev = this.next = null; } }
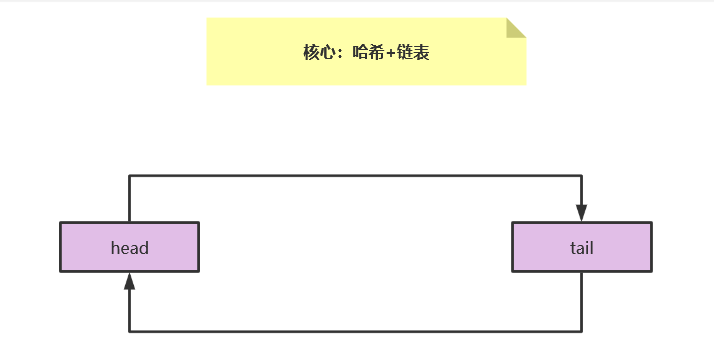
2、双向链表构造方法
class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> { Node<K, V> head;//头节点 Node<K, V> tail;//尾节点 public DoubleLinkedList() { //头尾哨兵节点 this.head = new Node<K, V>(); this.tail = new Node<K, V>(); this.head.next = this.tail; this.tail.prev = this.head; } }
执行完成构造方法以后此时双向链表结构如下:
3、双向链表添加节点方法
class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> { Node<K, V> head;//头节点 Node<K, V> tail;//尾节点 public DoubleLinkedList() { //头尾哨兵节点 this.head = new Node<K, V>(); this.tail = new Node<K, V>(); this.head.next = this.tail; this.tail.prev = this.head; } /** * 添加节点 */ public void add(Node<K, V> node) { node.next = head.next; node.prev = head; head.next.prev = node; head.next = node; } }
执行添加节点操作如下:
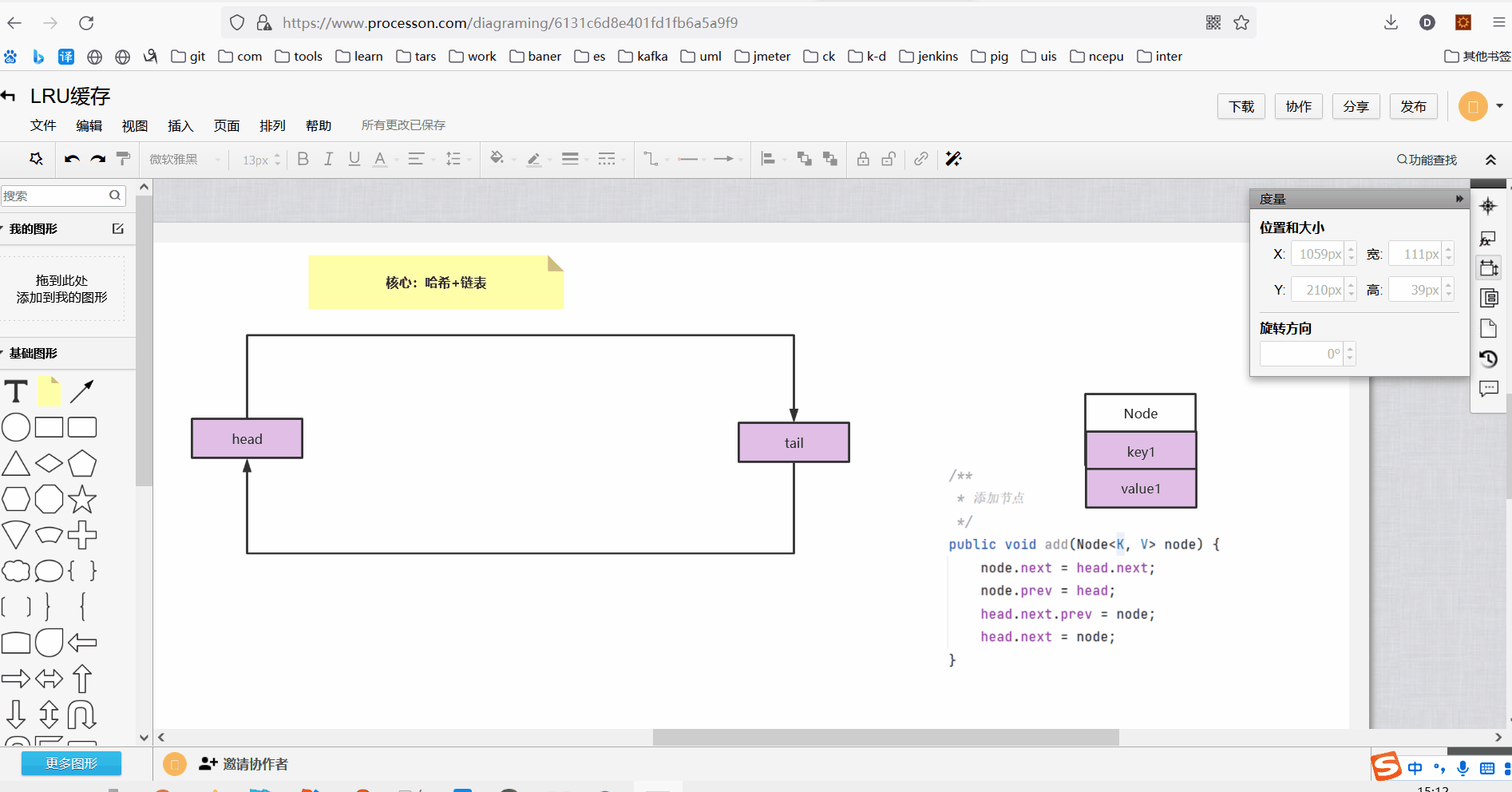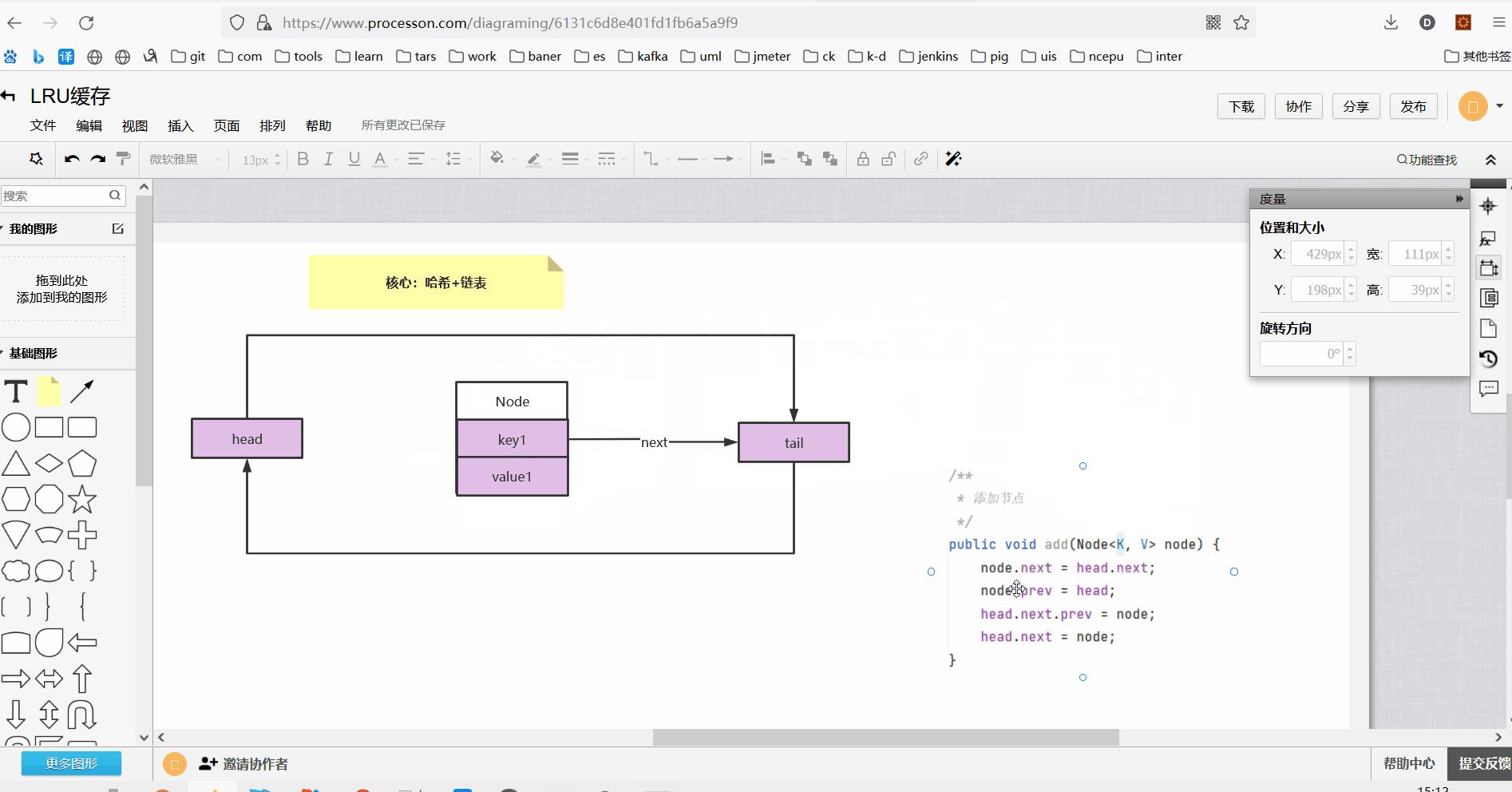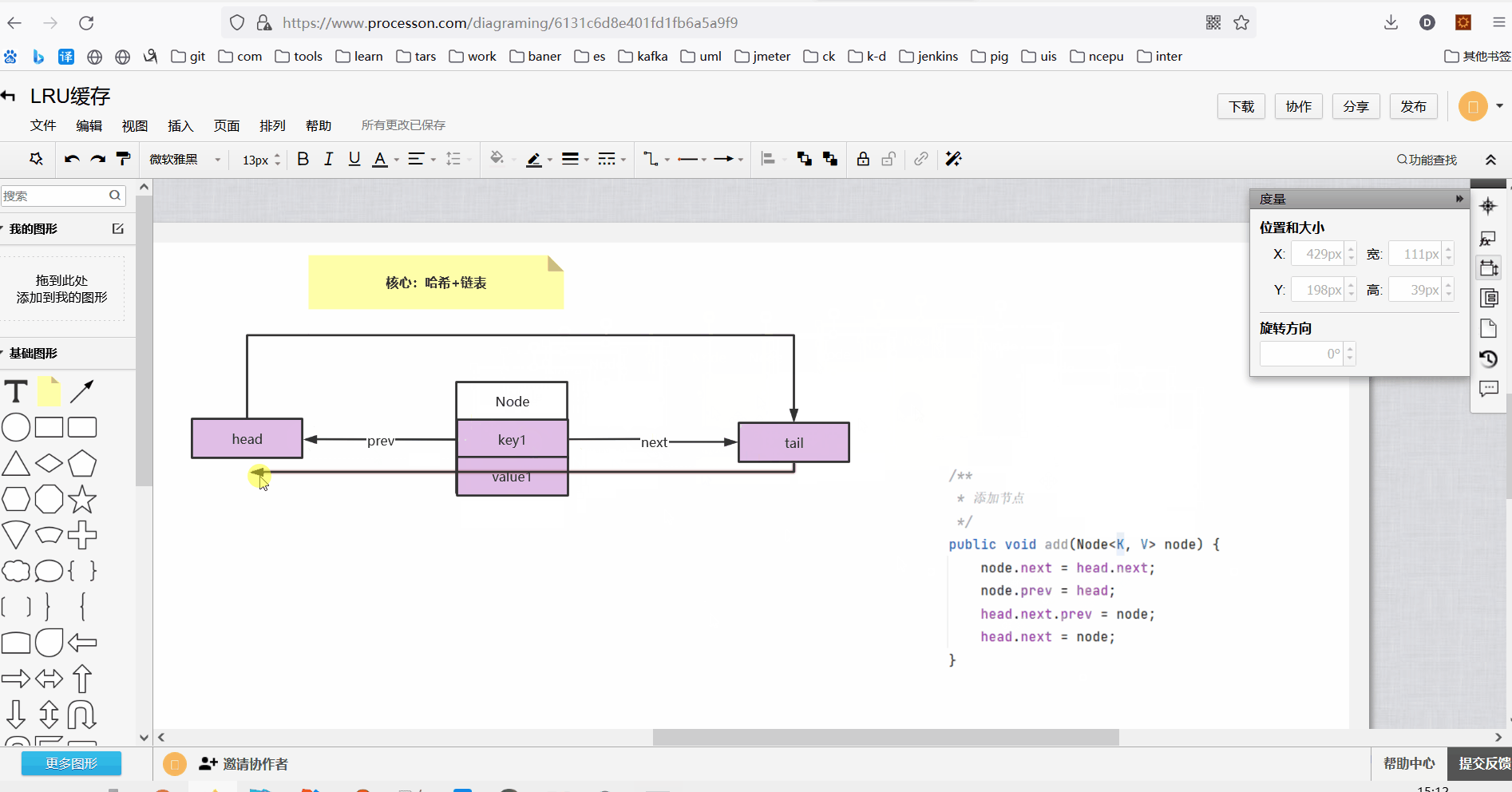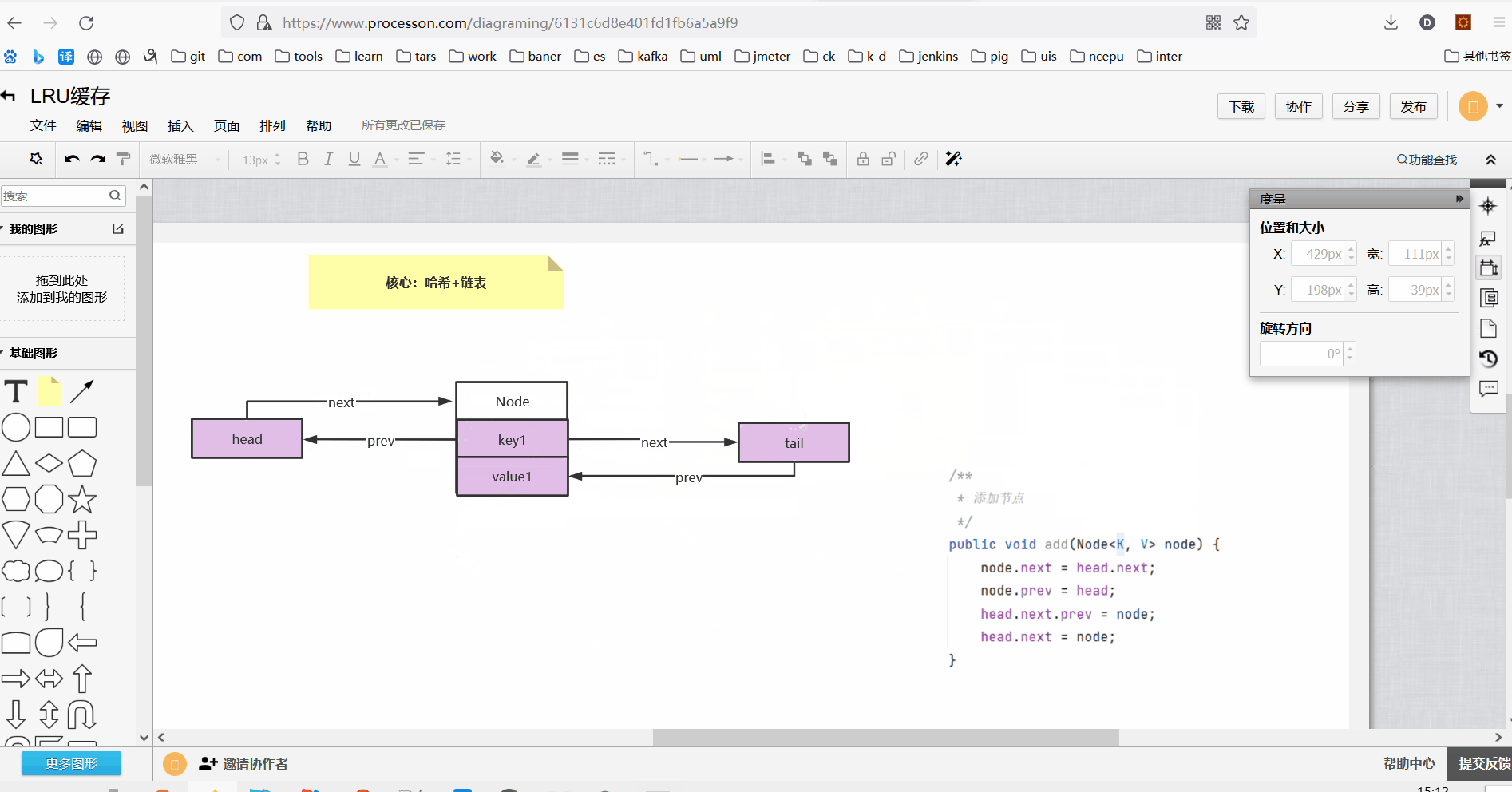
执行完添加方法以后此时双向链表结构如下:
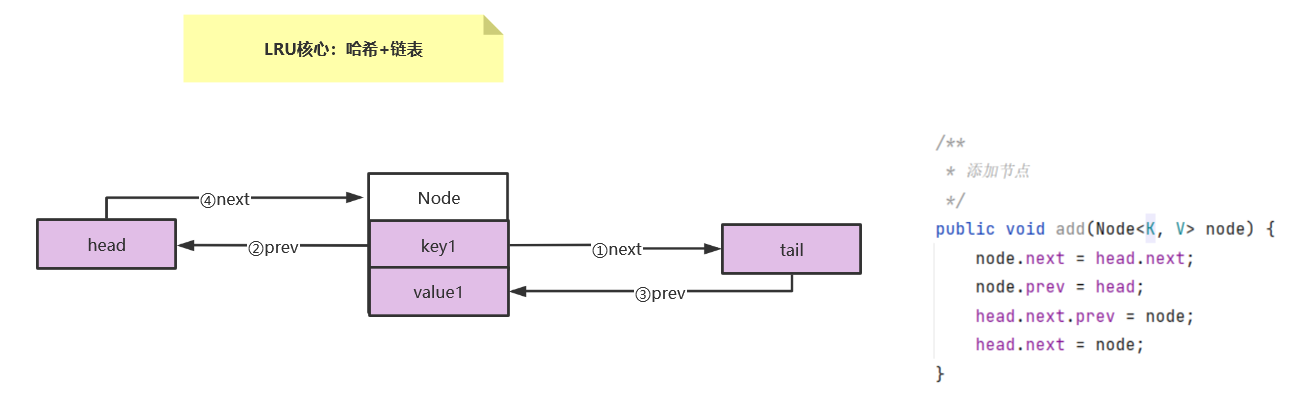
4、双向链表删除节点
/** * 删除节点 */ public void remove(Node<K, V> node) { node.next.prev = node.prev; node.prev.next = node.next; node.prev = null; node.next = null; }
删除节点操作如下:

5、获取最后一个结点
/** * 获取最后一个节点 * 将来用作最久不使用的数据 * @return */ public Node<K, V> getLast() { return this.tail.prev; }
6、完整代码
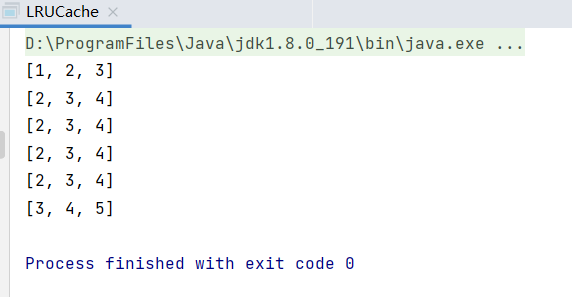
public class LRUCache { //容量 private int capacity; //map用于查找 时间复杂度O(1) private Map<Integer, Node<Integer, Integer>> map; //双向链表 private DoubleLinkedList<Integer, Integer> doubleLinkedList; //构造 public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; this.map = new HashMap<>(); this.doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList<>(); } public Integer get(int key) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { //查找对应元素 时间复杂度O(1) Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key); //使用一次就删除 this.doubleLinkedList.remove(node); //重新放在头结点位置(认为是最近使用的) this.doubleLinkedList.add(node); return node.value; } return -1; } public void put(int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { //如果存在则进行更新 Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key); node.value = value; map.put(key, node); //更新完成以后放至头结点位置,认为是最近使用的 this.doubleLinkedList.remove(node); this.doubleLinkedList.add(node); } else { //如果不存在则进行判断容量是否达上限 if (map.size() == this.capacity) { //最后一个节点即最近最少使用的 Node<Integer, Integer> lastNode = this.doubleLinkedList.getLast(); map.remove(lastNode.key); //删除最近最少使用的 doubleLinkedList.remove(lastNode); } Node<Integer, Integer> node = new Node<>(); node.key = key; node.value = value; map.put(key, node); //添加至头结点位置,认为是最近刚刚使用的 this.doubleLinkedList.add(node); } } //map负责查找,构建一个虚拟的双向链表,里面为一个个Node,作为数据载体 //双向链表节点 class Node<K, V> { K key; V value; Node<K, V> prev; Node<K, V> next; public Node() { this.prev = this.next = null; } public Node(K key, V value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.prev = this.next = null; } } class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> { Node<K, V> head;//头节点 Node<K, V> tail;//尾节点 public DoubleLinkedList() { //头尾哨兵节点 this.head = new Node<K, V>(); this.tail = new Node<K, V>(); this.head.next = this.tail; this.tail.prev = this.head; } /** * 添加节点 */ public void add(Node<K, V> node) { node.next = head.next; node.prev = head; head.next.prev = node; head.next = node; } /** * 删除节点 */ public void remove(Node<K, V> node) { node.next.prev = node.prev; node.prev.next = node.next; node.prev = null; node.next = null; } /** * 获取最后一个节点 * 将来用作最久不使用的数据 * * @return */ public Node<K, V> getLast() { return this.tail.prev; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(3); lruCache.put(1,1); lruCache.put(2,2); lruCache.put(3,3); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); lruCache.put(4,4); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); lruCache.put(3,1); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); lruCache.put(3,1); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); lruCache.put(3,1); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); lruCache.put(5,1); System.out.println(lruCache.map.keySet()); } }
验证结果如下: