一. 关于测试的补充
1.MiniTest报告程序
为了让 Rails 应用的测试适时显示红色和绿色,我建议你在测试辅助文件中加入以下内容:
(1).打开文件:test/test_helper.rb
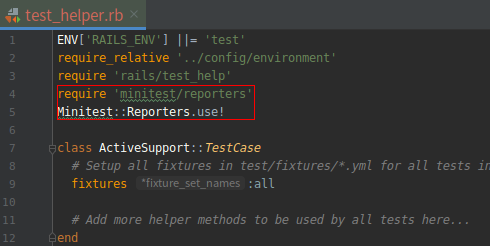
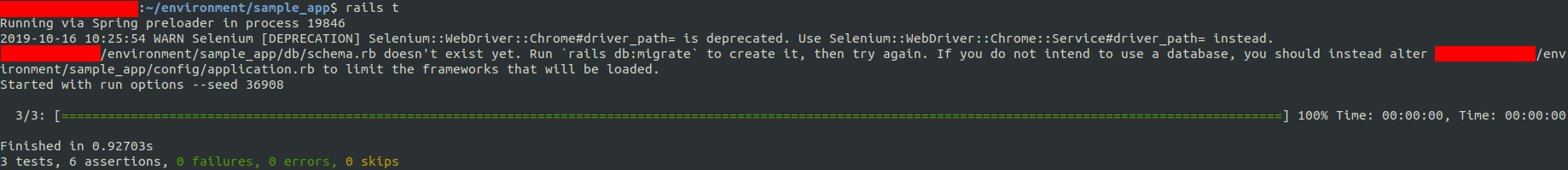
修改之后,再测试时的样子将会是:
2.使用Guard自动测试
使用 rails test 命令有一点很烦人, 总是要切换到命令行然后手动运行测试。为了避免这种不便, 我们可以使用 Guard 自动运行测试。Guard 会监视文件系统的变动, 假如你修改了 static_pages_controller_test.rb文件, 那么 Guard 只会运行这个文件中的测试。而且, 我们还可以配置 Guard,让它在 home.html.erb 文件被修改后,也自动运行 static_pages_controller_test.rb 文件中的测试。项目文件中的 Gemfile 已经包含了 guard gem,所以我们只需初始化即可:
$ bundle exec guard init
注:然后,编辑生成的 Guardfile 文件,让 Guard 在集成测试和视图发生变化后运行正确的测试,如下代码所示。为了尽量提高灵活性,我建议使用这里的 Guardfile :railstutorial.org/guardfile。注意,默认的 Guardfile 在 Cloud9 IDE 中可能不起作用,请参照前一段给出的网址里的第一行注释。

# A sample Guardfile # More info at https://github.com/guard/guard#readme ## Uncomment and set this to only include directories you want to watch # directories %w(app lib config test spec features) # .select{|d| Dir.exists?(d) ? d : UI.warning("Directory #{d} does not exist")} ## Note: if you are using the `directories` clause above and you are not ## watching the project directory ('.'), then you will want to move ## the Guardfile to a watched dir and symlink it back, e.g. # # $ mkdir config # $ mv Guardfile config/ # $ ln -s config/Guardfile . # # and, you'll have to watch "config/Guardfile" instead of "Guardfile" guard :minitest, spring: "bin/rails test", all_on_start: false do # with Minitest::Unit watch(%r{^test/(.*)/?test_(.*).rb$}) watch(%r{^lib/(.*/)?([^/]+).rb$}) { |m| "test/#{m[1]}test_#{m[2]}.rb" } watch(%r{^test/test_helper.rb$}) { 'test' } watch("config/routes.rb") { intergration_test } watch(%r[^app/models/(.*?).rb$]) do |matches| "test/models/#{matches[1]}_test.rb" end watch(%r{^app/controllers/(.*?)_controller.rb$}) do |matches| resource_tests(matches[1]) end watch(%r{^app/views/([^/]*?)/.*.html.erb$}) do |matches| ["test/controllers/#{matches[1]}_controller_test.rb"] + integration_tests(matches[1]) end watch(%r{^app/helpers/(.*?)_helper.rb$}) do |matches| integration_tests(matches[1]) end watch('app/views/layouts/application.html.erb') do 'test/integration/site_layout_test.rb' end watch('app/helpers/sessions_helper.rb') do integration_tests << 'test/helpers/sessions_helper_test.rb' end watch('app/controllers/sessions_controller.rb') do ['test/controllers/sessions_controller_test.rb', 'test/integration/users_login_test.rb'] end watch('app/controllers/account_activations_controller.rb') do 'test/integration/users_signup_test.rb' end watch(%r{app/views/users/*}) do resource_tests('users') + ['test/integration/microposts_interface_test.rb'] end end # Returns the integration tests corresponding to the given resource. def integration_tests(resource = :all) if resource == :all Dir["test/integration/*"] else Dir["test/integration/#{resource}_*.rb"] end end # Returns the controller tests corresponding to the given resource. def controller_test(resource) "test/controllers/#{resource}_controller_test.rb" end # Returns all tests for the given resource. def resource_tests(resource) integration_tests(resource) << controller_test(resource) end
下面这行代码会让 Guard 使用 Rails 提供的 Spring 服务器,从而减少加载时间,而且启动时不运行整个测试组件。
guard :minitest, spring: "bin/rails test", all_on_start: false do
使用 Guard 时,为了避免 Spring 和 Git 发生冲突,应该把 spring/ 目录添加到 .gitignore 文件中,让 Git 忽略它
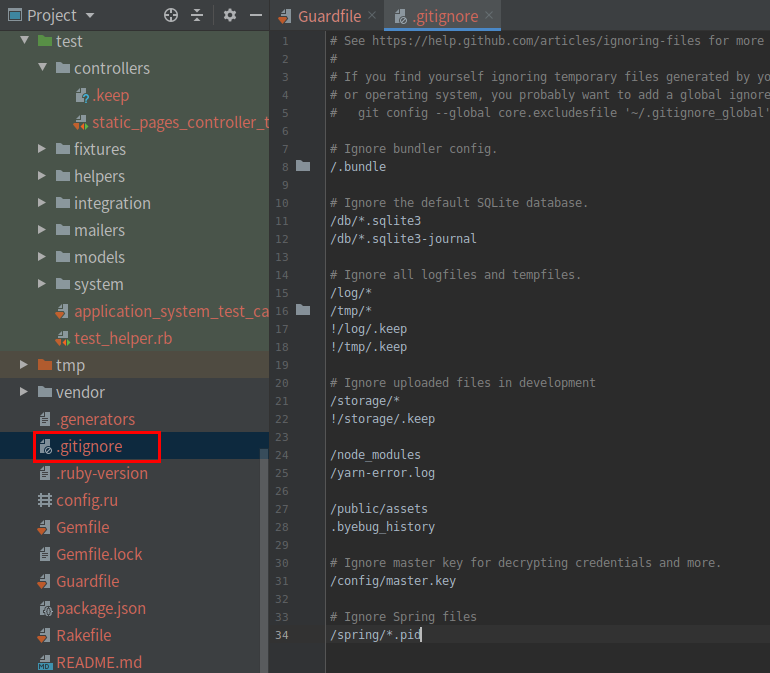
配置好 Guard 之后,应该打开一个新终端窗口(与启动 Rails 服务器的做法一样),在其中执行下述命令(若想退出 Guard,按 Ctrl-D 键):
$ bundle exec guard
注:自己试试吧
。。。
测试已经差不多,等会整点别的
