一. 数组
1.定义一个数组
games = ["英雄联盟", "绝地求生", "钢铁雄心"] puts games
2.数组的循环
games.each do |geam| puts "玩《#{geam}》" end games.each_with_index do |game, index| puts "我喜欢的第:#{index+1}个游戏是:#{game}" end
注:相当于Python中的enumerate(枚举)方法遍历数组中的元素及其下标
3.数组的连接
puts games.join("|")
注:数组数据的拼接方法,大部分语言都有且都为join
4.判断是否是一个数组
if games.respond_to?("each") puts "true" end if games.respond_to?("each_with_index") puts "true" end
5.Ruby数组中的方法
请参看:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-array.html
二. 备注
备注的使用: 1. 一行备注 # :井号备注 2. 多行备注 "=begin...=end" 3. 之后全备注 __END__
三. Ruby的操作符
请参看:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-operator.html
1.值得注意的:
(1). Ruby 三元运算符
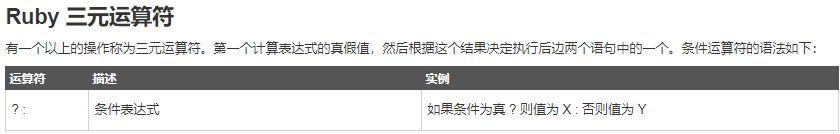
a = 1...10 puts a.size >= 9? "是" : "否"
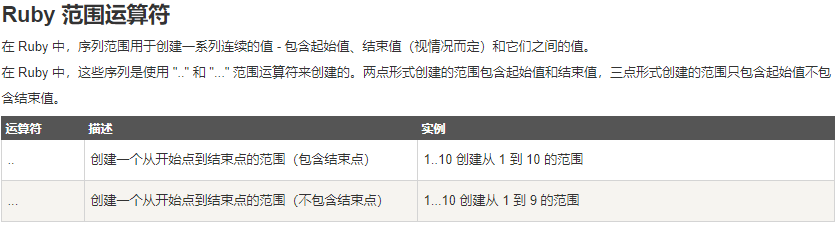
(2). Ruby 范围运算符
(3). Ruby defined? 运算符


用法 1 defined? variable # 如果 variable 已经初始化,则为 True 例如: foo = 42 defined? foo # => "local-variable" defined? $_ # => "global-variable" defined? bar # => nil(未定义) 用法 2 defined? method_call # 如果方法已经定义,则为 True 例如: defined? puts # => "method" defined? puts(bar) # => nil(在这里 bar 未定义) defined? unpack # => nil(在这里未定义) 用法 3 # 如果存在可被 super 用户调用的方法,则为 True defined? super 例如: defined? super # => "super"(如果可被调用) defined? super # => nil(如果不可被调用) 用法 4 defined? yield # 如果已传递代码块,则为 True 例如: defined? yield # => "yield"(如果已传递块) defined? yield # => nil(如果未传递块)
(4). Ruby 点运算符 "." 和双冒号运算符 "::"


实例1: MR_COUNT = 0 # 定义在主 Object 类上的常量 module Foo MR_COUNT = 0 ::MR_COUNT = 1 # 设置全局计数为 1 MR_COUNT = 2 # 设置局部计数为 2 end puts MR_COUNT # 这是全局常量 puts Foo::MR_COUNT # 这是 "Foo" 的局部常量 实例2: CONST = ' out there' class Inside_one CONST = proc {' in there'} def where_is_my_CONST ::CONST + ' inside one' end end class Inside_two CONST = ' inside two' def where_is_my_CONST CONST end end puts Inside_one.new.where_is_my_CONST puts Inside_two.new.where_is_my_CONST puts Object::CONST + Inside_two::CONST puts Inside_two::CONST + CONST puts Inside_one::CONST puts Inside_one::CONST.call + Inside_two::CONST
四. Ruby中的字符串
请参看:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-string.html
1.值得注意的:
(1). Ruby中的%Q与%q
desc1 = %Q{Ruby 的字符串可以使用 '' 和 ""。}
desc2 = %q|Ruby 的字符串可以使用 '' 和 ""。|
puts desc1
puts desc2
%Q:用于替代双引号的字符串. 当你需要在字符串里放入很多引号时候, 可以直接用下面方法而不需要在引号前逐个添加反斜杠 (")
%q:%q与%Q类似,但表示单引号,其实在双引号中' ' 不需要转义的
(2). +,<<,*
+:字符连接 # 常用 <<:字符带入 # 没见过 *:字符循环 # python中有但没用过
a = "我爱你" b = "亲爱的姑娘" puts a+b puts a<<b puts a puts a*3 输出结果: 我爱你亲爱的姑娘 我爱你亲爱的姑娘 我爱你亲爱的姑娘 我爱你亲爱的姑娘我爱你亲爱的姑娘我爱你亲爱的姑娘
(3). 单引号 '' 和双引号 "" 的区别
str = "流影之主 劫" str1 = '刀锋之影 泰隆' query = "#{40+10+50}" query1 = '#{40+10+50}' puts str puts str1 puts query puts query1 输出结果: 流影之主 劫 刀锋之影 泰隆 100 #{40+10+50}
注:Ruby中的大部分关于string的方法与Python中的方法大体相同,可放心使用
