JsonPath
在xml的使用过程中,对于xml的解析我们知道可以使用xpath的方式,随意的获取到我们想要的属性值。那么在使用json时,我们能不能实现同样的操作呢?
答案就是 json-path
基础介绍
跟 XPath 类似,JsonPath 通过路径来检索JSON,对语法格式如下
语法
| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| $ | 表示json的根节点,表示根节点下的所有数据 |
| . | 表示子节点,如 $.store 表示根节点下的store节点下的所有数据 |
| .. | 可实现递归搜索,如 $..title 表示搜索json中所有key为title属性的值 |
| * | 可表示某一层节点,如 $.*.book 表示根节点下所有节点的book节点数据 |
| @ | 在表达式中使用,表示当前节点对象 |
| [' |
如 $..['author'] 表示所有节点中author节点的值 |
| [ |
如 $..['0'] 表示所有节点中下标为0的节点的值 |
| [start:end] | 如 $..book[2] 取json中book数组的第3个值 |
| [?( |
过滤器表达式,表达式结果必须是boolean |
过滤器表达式
通常的表达式格式为:[?(@.age > 18)]
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| == | 等于符号,但数字1不等于字符1(note that 1 is not equal to ‘1’) |
| != | 不等于符号 |
| < | 小于符号 |
| <= | 小于等于符号 |
| > | 大于符号 |
| >= | 大于等于符号 |
| =~ | 判断是否符合正则表达式,例如[?(@.name =~ /foo.*?/i)] |
| in | 所属符号,例如[?(@.size in [‘S’, ‘M’])] |
| nin | 排除符号 |
| size | size of left (array or string) should match right |
| empty | 判空符号 |
示例
{
"store": {
"book": [
{
"category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Herman Melville",
"title": "Moby Dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
},
"expensive": 10
}
在线测试:http://jsonpath.herokuapp.com/?path=$.store.book%5B*%5D.author
| JsonPath表达式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| $.store.book[*].author | 获取json中store下book下的所有author值 |
| $..author | 获取所有的 author 的值 |
| $.store.book.* | 获取json中store下book下的所有值 |
| $.store..price | 获取json中store下所有price的值 |
| $..book[2] | 获取json中book数组的第3个值 |
| $..book[-2] | 倒数的第二本书 |
| $..book[0,1] | 前两本书 |
| $..book[:2] | 从索引0(包括)到索引2(排除)的所有图书 |
| $..book[1:2] | 从索引1(包括)到索引2(排除)的所有图书 |
| $..book[-2:] | 获取json中book数组的最后两个值 |
| $..book[2:] | 获取json中book数组的第3个到最后一个的区间值 |
| $..book[?(@.title)] | 获取json中book数组中包含title的所有节点 |
| $.store.book[?(@.price < 10)] | 获取json中book数组中price<10的所有值 |
| $..book[?(@.price <= $['expensive'])] | 获取json中book数组中price<=$['expensive']结果的所有值 |
| $..book[?(@.author =~ /.*REES/i)] | 获取json中book数组中的作者以REES结尾的所有值(REES不区分大小写) |
| $..* | 逐层列出json中的所有值,层级由外到内 |
| $..book.length() | 获取json中book数组的长度 |
使用
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
特别说明:下文中使用的 JSON_DATA 变量的值都为上面所示的json范例
使用静态方法直接读
List<String> authors = JsonPath.read(JSON_DATA, "$.store.book[*].author");
如果需要多次读,那么这种方法不够理想,因为每次都会重新解析一次json数据
一次解析,多次使用
我们可以先将json数据一次解析,然后多次使用,提升性能。json-path提供了如ReadContext ,DocumentContext等类,我们可以随意使用,其关系如下:
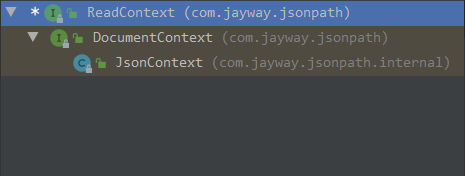
DocumentContext documentContext = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA);
// 或者
ReadContext ctx = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA);
List<String> author = ctx.read("$.store.book[?(@.isbn)].author");
类型转换
在java中使用JsonPath时,当我们知道我们读取过后的返回值是什么类型时,JsonPath会尝试将其转换为我们想要的类型
// 结果为 "Nigel Rees" ,如果我们强制转换为List那么会抛出 java.lang.ClassCastException 异常
List<String> list = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[0].author")
// 正常
String author = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[0].author")
我们在解析相应的json是可以设置解析过后的值自动转换为对应的类型的。默认情况下,MappingProvider SPI提供了一个简单的对象映射器。
String JSON_DATA = "{"date_as_long" : 1411455611975}";
Date date = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$['date_as_long']", Date.class);
// 2014-09-23 15:00:11
如果我们需要转换为更加具体的对象,如一个POJO等,就需要我们配置更加详细的json解析器JacksonMappingProvider 或 GsonMappingProvider
Book book = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[0]", Book.class);
Configuration conf = Configuration.builder().mappingProvider(new JacksonMappingProvider()).build();
TypeRef<List<String>> typeRef = new TypeRef<List<String>>(){};
List<String> titles = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[*].title", typeRef);
过滤
根据路径过滤
List<Map<String, Object>> books = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[?(@.price < 10)]");
// [{"category":"reference","author":"Nigel Rees","title":"Sayings of the Century","price":8.95},{"category":"fiction","author":"Herman Melville","title":"Moby Dick","isbn":"0-553-21311-3","price":8.99}]
根据过滤器过滤
Filter cheapFictionFilter = Filter.filter(Criteria.where("category").is("fiction").and("price").lte(10D));
List<Map<String, Object>> books = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA).read("$.store.book[?]", cheapFictionFilter);
// [{"category":"fiction","author":"Herman Melville","title":"Moby Dick","isbn":"0-553-21311-3","price":8.99}]
// 使用and或者or连接多个条件
Filter fooOrBar = filter(
where("foo").exists(true)).or(where("bar").exists(true)
);
Filter fooAndBar = filter(
where("foo").exists(true)).and(where("bar").exists(true)
);
自定义过滤器
ReadContext reader = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA);
Predicate booksWithIsbn = new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean apply(PredicateContext context) {
return context.item(Map.class).containsKey("isbn");
}
};
reader.read("$.store.book[?].isbn", List.class, booksWithIsbn);
// ["0-553-21311-3","0-395-19395-8"]
注意:在自定义过滤器中,context.item(Map.class) 这句话。这句中的Map.class是根据预定的结果类型定义的,如果返回的是String类型值,那就改为String.class
返回值
在JsonPath中,我们可以通过配置来指定本次读取时是返回相应的值,还是返回符合结果路径
Configuration configuration = Configuration.builder().options(Option.AS_PATH_LIST).build();
List<String> pathList = JsonPath.using(configuration).parse(JSON_DATA).read("$..author");
// ["$['store']['book'][0]['author']","$['store']['book'][1]['author']","$['store']['book'][2]['author']","$['store']['book'][3]['author']"]
Option.AS_PATH_LIST 表示返回路径,同时,该类还有其他几个参数:
- DEFAULT_PATH_LEAF_TO_NULL:对应路径的节点不存在时,返回null
[
{
"name" : "john",
"gender" : "male"
},
{
"name" : "ben"
}
]
Configuration conf = Configuration.defaultConfiguration();
// 正常
String gender0 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[0]['gender']");
// 异常 PathNotFoundException thrown
String gender1 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[1]['gender']");
Configuration conf2 = conf.addOptions(Option.DEFAULT_PATH_LEAF_TO_NULL);
// 正常
String gender0 = JsonPath.using(conf2).parse(json).read("$[0]['gender']");
// 正常 (返回 null)
String gender1 = JsonPath.using(conf2).parse(json).read("$[1]['gender']");
- ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST:始终将结果包装在List中
Configuration conf = Configuration.defaultConfiguration();
// 正常
List<String> genders0 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[0]['gender']");
// 异常 PathNotFoundException thrown
List<String> genders1 = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(json).read("$[1]['gender']");
- SUPPRESS_EXCEPTIONS :确保不会从路径评估传播异常
如果选项ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST存在,将返回一个空列表
如果选项ALWAYS_RETURN_LIST不存在返回null
操作key
有时,我们解析一个json并不是为了将其解析出来,用于其他。而是我们需要将json解析出来,然后去修改或者删除其中的key。比如对一个json格式数据进行某些字段的脱敏处理。这是我们就需要用到其提供的 .set() 和 .put() 方法,同时还有 .delete()、.add() ...
这些方法的实现都在 JsonContext 中,其继承关系如图:

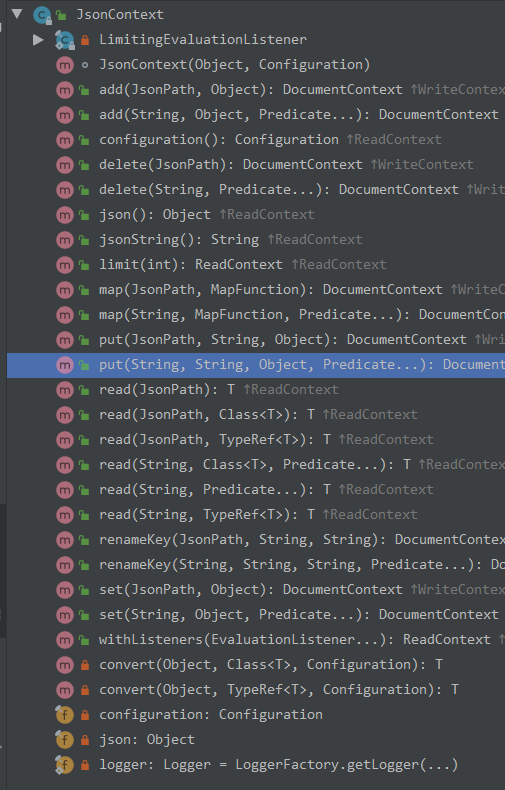
使用
要想对json进行增删改,我们首先要提高一个路径,用来让JsonPath可以找到对应的key或者是节点。
先解析
// 首先解析json为文档
DocumentContext documentContext = JsonPath.parse(JSON_DATA);
根据提供的路径直接修改
- 路径直接定义到具体的值
// 将所有书籍的作者修改为dimples
JsonPath p = JsonPath.compile("$.store.book[*].author");
documentContext.set(p, "dimples");
- 路径定义到节点
此时不能直接使用set()方法,因为此时返回的不是具体值的列表,而是所有book子节点的列表。此时使用put方法为佳,如下,就实现了与上面代码一样的效果
JsonPath p = JsonPath.compile("$.*.book");
documentContext.put(p, author, "dimples");
- 不替换所有key
在上面的两种写法中,我们会替换book节点下的所有节点的author的值,那么我们怎么实现根据我们的需要修改值呢?
- 过滤器表达式
// 修改 author 值为 Nigel Rees 的元素的值
JsonPath p = JsonPath.compile(StrUtil.format("$..[?(@.author == 'Nigel Rees')]");
documentContext.put(p, author, "dimples");
- 使用过滤器
DocumentContext documentContext = JsonPath.parse(DATA);
filter = Filter.filter(Criteria.where("author ").is("Nigel Rees"));
// 替换
documentContext.put("$..[?]","author","dimples",filter);
其中 ? 代表过滤器的占位符,如果没有 ? ,那么配置filter将无效。
也可以使用set方法,原理类似
根据值条件获取路径,然后修改
Configuration conf = Configuration.builder().options(Option.AS_PATH_LIST).build();
Filter filter = Filter.filter(Criteria.where("author").contains("Nigel Rees");
// 获取满足条件值的路径
List<String> path = JsonPath.using(conf).parse(JSON_DATA).read("$..[?]", filter);
// 替换 (此处举例,不做遍历,只获取第一个)
documentContext.set(path.get(0), "dimples");
也可以使用put方法,原理类似
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42452045/article/details/92768660
https://blog.csdn.net/Dream_Weave/article/details/106421388
FastJson - json-path
alibaba-json-path 官方参考:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONPath