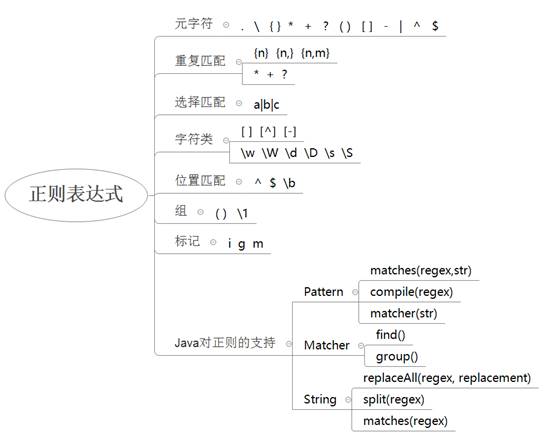
1.1 正则表达式
1.2 简介
Regular Expression 正则表达式 常简称为: regex、正则
正则表达式是一整套约束字符串的语法规则,独立于任何编程语言
正则表达式 方便、灵活、功能强大,多部分编程语言都对正则表达式提供了支持
我们通常把正则作为一个工具,进行字符串的 校验、获取、替换等操作
1.2 普通字符和元字符
正则表达式中,所有字符分为两类:普通字符和元字符(具有特殊含义的字符)
主要普通字符:小写字母、大写字母、数字、下划线、部分特殊符号、非西文字符等
主要元字符:. { } * + ? ( ) [ ] - | ^ $
. 表示任意一个字符(除了换行符)
转移符,用来改变其他字符的含义,
如:
元字符 把元字符转义为普通字符,如. 把元字符 . 转义为普通字符的 .
普通字符 把普通字符转义为含有特殊含义的字符,如 换行符, 回车符, 制表符
2 java对正则的支持
2.1 Pattern类
Java提供了java.util.regex.Pattern 类来创建正则表达式对象
public static boolean matches(regex, str) // 用来判断str是否匹配regex,或者说用来判断str是否符合regex的要求
import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class RegexTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String regex = "abc";// 要求字符串为"abc" String str = "abc"; boolean match = Pattern.matches(regex, str); System.out.println(match);//输出true } }
2.1.1 元字符的用法
易错点:
1 Java代码中的 \ 只表示正则中的
2 表示换行符,即使用和n这两个字符组合在一起表示一个换行字符
public static void main(String[] args) { /* String regex = ".";// .在正则中标识任意字符,要求str="任意字符" String str = "a"; boolean match = Pattern.matches(regex, str); System.out.println(match);//输出 true */ String regex = "\.";// 相当于正则中的.,要求str="." String str = "a"; boolean match = Pattern.matches(regex, str); System.out.println(match);//输出 false }
2.1.2 重复匹配
(x表示一个字符,或者一个字符类,或者一个组等)
x{n} x连续出现n次
x{n,} x至少连续出现n次
x{n,m} x至少连续出现n次,至多连续出现m次
x* x连续出现0次或多次,等同于x{0,}
x+ x至少连续出现1次,等同于x{1,}
x? x出现0次或1次,等同于x{0,1}
/* String regex = "a{3}";// 要求a连续出现3次,str="aaa"
String str = "a";//false
*/
/* String regex = "a{3,6}";// 要求a至少连续出现3次,str="aaa.."
String str = "aaaaa";//true
*/
String regex = "a?";
String str = "a";//true
boolean match = Pattern.matches(regex, str);
System.out.println(match);2.1.3 选择匹配
使用 | 实现选择匹配,即多个选项中任选一个
a|b|c 匹配a或者b或者c
red|blue|green 匹配red或者blue或者green
/* String regex = "a|b|c";// str="a" "b" "c" String str = "b";//true */ String regex = "red|blue|green";// str= "red"或"blue"或"green" String str = "blue";//true boolean match = Pattern.matches(regex, str); System.out.println(match);
2.1.4 字符类
匹配候选字符的任意一个
[ ] [abc] 匹配abc中任意一个字符,类似 a|b|c
[^ ] [^abc] 匹配非abc的任意一个字符
[ - ] [0-9]、[a-z]、[a-zA-Z] 匹配范围内的任意一个字符
注意:字符类中的元字符(除外),会被自动转义为普通字符,比如 [.] 等同于 [.]
w 代表一个单词字符,类似于[a-zA-Z0-9_],有的语言中也可以匹配中文
W 代表一个非单词字符,类似于[^a-zA-Z0-9_]
d 代表一个数字字符,等同于[0-9]
D 代表一个非数字字符,等同于[^0-9]
s 代表一个空白字符
S 代表一个非空白字符
// String regex = "hello[abc]";// str="helloa" "hellob" "helloc"
// String regex = "[0-9]";// str="0" "1"..."9"
2.2 Matcher类
Java还提供了 java.util.regex.Matcher 匹配器类,用来支持复杂的正则操作
Matcher matcher = Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(str);
boolean find = matcher.find();// 查找str中是否有下一个匹配regex的子字符串
String group = matcher.group();// 返回当前和regex匹配的子字符串
//典型用法
while (matcher.find()) {
String substr = matcher.group();
// ...
}
贪婪匹配:在重复匹配时,默认会匹配尽可能多的字符
非贪婪匹配:在重复匹配后面加上?问号,会匹配尽可能少的字符(并不严格)
public static void main(String[] args) { // String regex = "ab";// 要求str的子字符串substr="ab" // String str = "xabxxabmmabx"; //打印出一个字符串里面的所有的qq邮箱 String regex = "[1-9][0-9]{4,}@qq.com";// qq邮箱的正则表达式写法 String str = "xx12345@qq.comabc123456@qq.commm1234567@qq.com"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str); while (matcher.find()) { String group = matcher.group(); System.out.println(group); } }
输出:
12345@qq.com
123456@qq.com
1234567@qq.com2.2.1 贪婪匹配和非贪婪匹配
贪婪匹配:在重复匹配时,默认会匹配尽可能多的字符。这也是正则中默认的匹配模式。
非贪婪匹配:在重复匹配后面加上?问号,会匹配尽可能少的字符(并不严格)
注意下面三处代码的不同
1.
String regex = "[1-9][0-9]{4,}";// qq邮箱的正则表达式写法
String str = "xx012345@qq.comabc0123456@qq.commm1234567@qq.com";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
while (matcher.find()) {
String group = matcher.group();
System.out.println(group);
}
输出:
12345
123456
12345672.
String regex = "[1-9][0-9]{4,}?";// qq邮箱的正则表达式写法
String str = "xx012345@qq.comabc0123456@qq.commm1234567@qq.com";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
while (matcher.find()) {
String group = matcher.group();
System.out.println(group);
}
输出:
12345
12345
123453.
String regex = "[1-9][0-9]{4,}@qq.com";// qq邮箱的正则表达式写法
String str = "xx012345@qq.comabc0123456@qq.commm1234567@qq.com";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
while (matcher.find()) {
String group = matcher.group();
System.out.println(group);
}
输出:
12345@qq.com
123456@qq.com
1234567@qq.com2.3 String支持正则操作的方法
由于正则表达式和字符串如此相关,Java就为 java.lang.String 字符串类提供了若干可以直接进行正则操作的方法。
这里有个小技巧,String的方法中参数为regex的都是支持正则的。
//使用replacement替换全部匹配regex的子字符串
String newStr = str.replaceAll(regex, replacement);
String[] newStrs = str.split(regex);//使用regex作为分隔符切分str
boolean match = str.matches(regex);// 等同于Pattern.matches(regex, str)
String str="0123456789";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("[0-9]", "*"));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
String str2="apple12orange84745banana666hello";
String[] parts = str2.split("[0-9]+");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(parts));输出:
**********
--------------------------------------
[apple, orange, banana, hello]