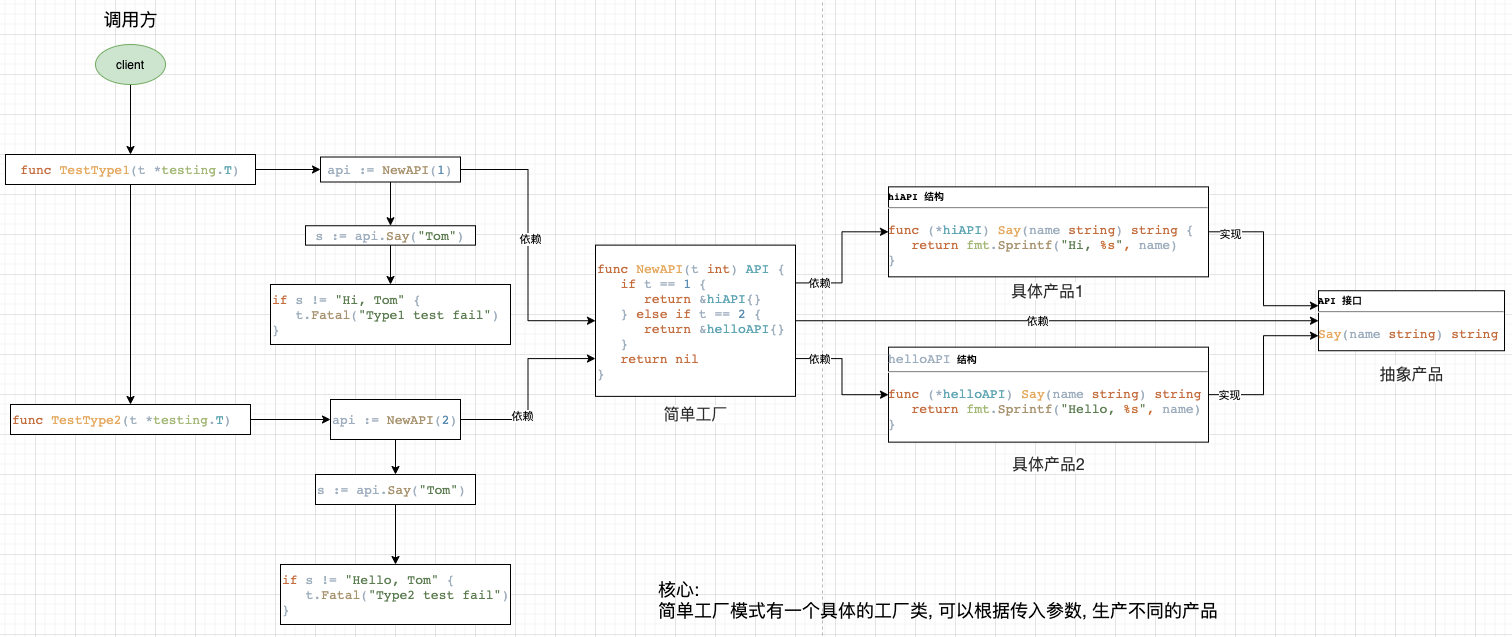
简单工厂模式
go 语言没有构造函数一说,所以一般会定义函数来初始化相关类。
函数返回接口时就是简单工厂模式,也就是说Golang的一般推荐做法就是简单工厂。
simple.go代码
package simplefactory
import "fmt"
//API is interface
type API interface {
Say(name string) string
}
//NewAPI return Api instance by type
func NewAPI(t int) API {
if t == 1 {
return &hiAPI{}
} else if t == 2 {
return &helloAPI{}
}
return nil
}
//hiAPI is one of API implement
type hiAPI struct{}
//Say hi to name
func (*hiAPI) Say(name string) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hi, %s", name)
}
//HelloAPI is another API implement
type helloAPI struct{}
//Say hello to name
func (*helloAPI) Say(name string) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hello, %s", name)
}
simple_test.go代码
package simplefactory
import "testing"
//TestType1 test get hiapi with factory
func TestType1(t *testing.T) {
api := NewAPI(1)
s := api.Say("Tom")
if s != "Hi, Tom" {
t.Fatal("Type1 test fail")
}
}
func TestType2(t *testing.T) {
api := NewAPI(2)
s := api.Say("Tom")
if s != "Hello, Tom" {
t.Fatal("Type2 test fail")
}
}
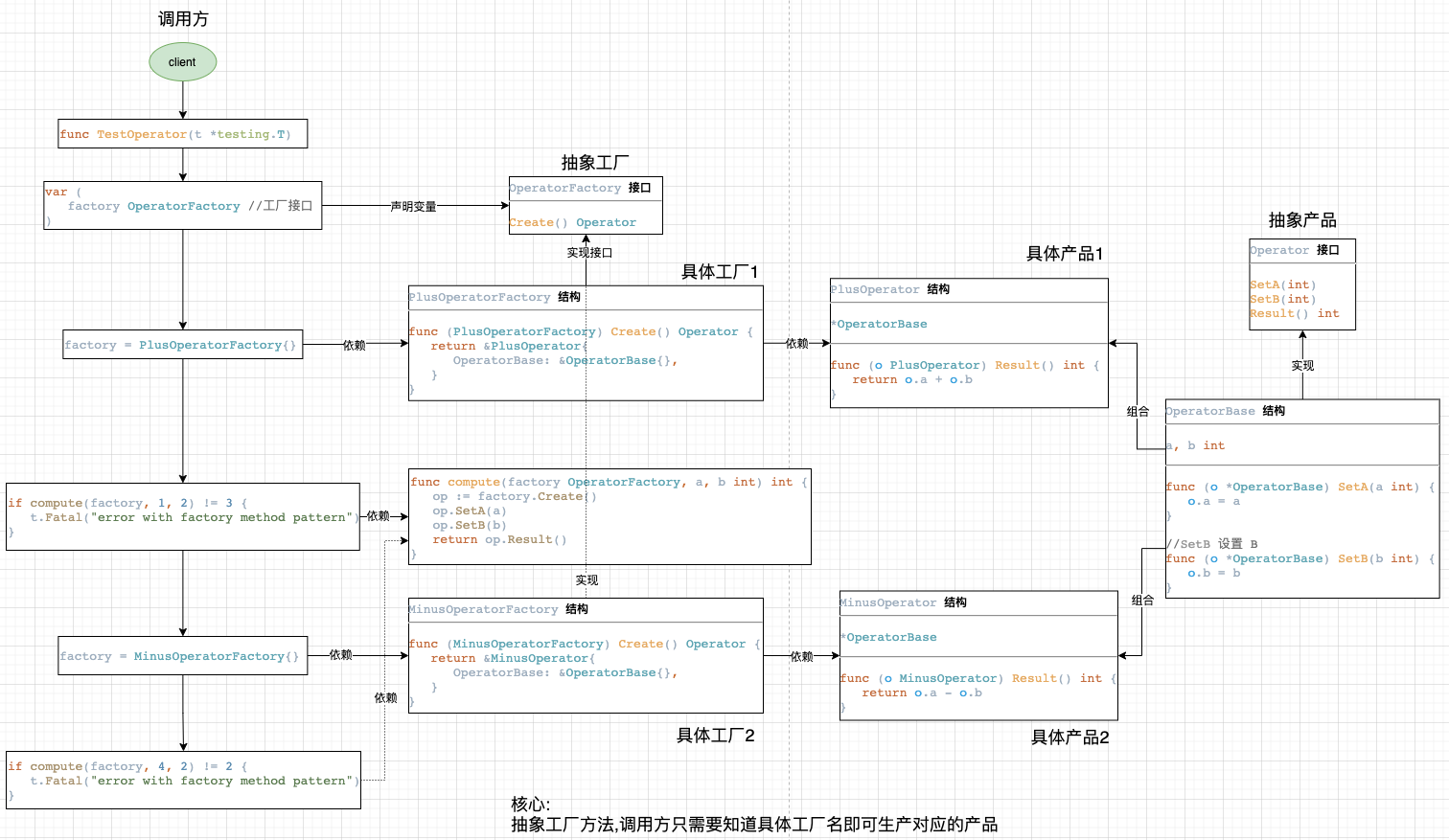
工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式使用子类的方式延迟生成对象到子类中实现。
Go中不存在继承 所以使用匿名组合来实现
factorymethod.go
package factorymethod
//Operator 是被封装的实际类接口
type Operator interface {
SetA(int)
SetB(int)
Result() int
}
//OperatorFactory 是工厂接口
type OperatorFactory interface {
Create() Operator
}
//OperatorBase 是Operator 接口实现的基类,封装公用方法
type OperatorBase struct {
a, b int
}
//SetA 设置 A
func (o *OperatorBase) SetA(a int) {
o.a = a
}
//SetB 设置 B
func (o *OperatorBase) SetB(b int) {
o.b = b
}
//PlusOperatorFactory 是 PlusOperator 的工厂类
type PlusOperatorFactory struct{}
func (PlusOperatorFactory) Create() Operator {
return &PlusOperator{
OperatorBase: &OperatorBase{},
}
}
//PlusOperator Operator 的实际加法实现
type PlusOperator struct {
*OperatorBase
}
//Result 获取结果
func (o PlusOperator) Result() int {
return o.a + o.b
}
//MinusOperatorFactory 是 MinusOperator 的工厂类
type MinusOperatorFactory struct{}
func (MinusOperatorFactory) Create() Operator {
return &MinusOperator{
OperatorBase: &OperatorBase{},
}
}
//MinusOperator Operator 的实际减法实现
type MinusOperator struct {
*OperatorBase
}
//Result 获取结果
func (o MinusOperator) Result() int {
return o.a - o.b
}
factorymethod_test.go
package factorymethod
import "testing"
func compute(factory OperatorFactory, a, b int) int {
op := factory.Create()
op.SetA(a)
op.SetB(b)
return op.Result()
}
func TestOperator(t *testing.T) {
var (
factory OperatorFactory
)
factory = PlusOperatorFactory{}
if compute(factory, 1, 2) != 3 {
t.Fatal("error with factory method pattern")
}
factory = MinusOperatorFactory{}
if compute(factory, 4, 2) != 2 {
t.Fatal("error with factory method pattern")
}
}
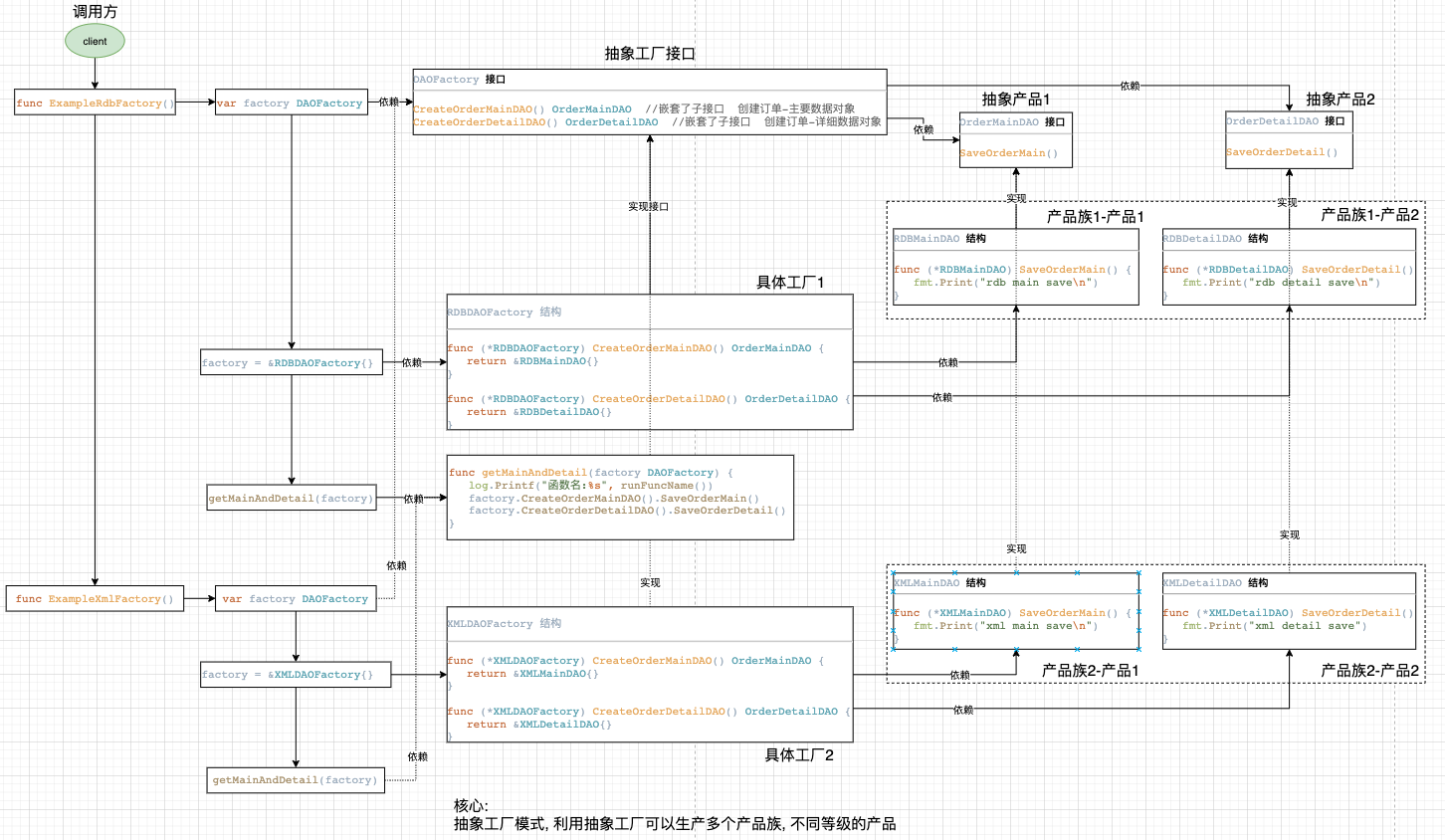
抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式用于生成产品族的工厂,所生成的对象是有关联的。
如果抽象工厂退化成生成的对象无关联则成为工厂函数模式。
比如本例子中使用RDB和XML存储订单信息,抽象工厂分别能生成相关的主订单信息和订单详情信息。
如果业务逻辑中需要替换使用的时候只需要改动工厂函数相关的类就能替换使用不同的存储方式了。
abstractfactory.go
package abstractfactory
import "fmt"
//OrderMainDAO 为订单主记录
type OrderMainDAO interface {
SaveOrderMain()
}
//OrderDetailDAO 为订单详情纪录
type OrderDetailDAO interface {
SaveOrderDetail()
}
//DAOFactory DAO 抽象模式工厂接口
type DAOFactory interface {
CreateOrderMainDAO() OrderMainDAO
CreateOrderDetailDAO() OrderDetailDAO
}
//RDBMainDAP 为关系型数据库的OrderMainDAO实现
type RDBMainDAO struct{}
//SaveOrderMain ...
func (*RDBMainDAO) SaveOrderMain() {
fmt.Print("rdb main save
")
}
//RDBDetailDAO 为关系型数据库的OrderDetailDAO实现
type RDBDetailDAO struct{}
// SaveOrderDetail ...
func (*RDBDetailDAO) SaveOrderDetail() {
fmt.Print("rdb detail save
")
}
//RDBDAOFactory 是RDB 抽象工厂实现
type RDBDAOFactory struct{}
func (*RDBDAOFactory) CreateOrderMainDAO() OrderMainDAO {
return &RDBMainDAO{}
}
func (*RDBDAOFactory) CreateOrderDetailDAO() OrderDetailDAO {
return &RDBDetailDAO{}
}
//XMLMainDAO XML存储
type XMLMainDAO struct{}
//SaveOrderMain ...
func (*XMLMainDAO) SaveOrderMain() {
fmt.Print("xml main save
")
}
//XMLDetailDAO XML存储
type XMLDetailDAO struct{}
// SaveOrderDetail ...
func (*XMLDetailDAO) SaveOrderDetail() {
fmt.Print("xml detail save")
}
//XMLDAOFactory 是RDB 抽象工厂实现
type XMLDAOFactory struct{}
func (*XMLDAOFactory) CreateOrderMainDAO() OrderMainDAO {
return &XMLMainDAO{}
}
func (*XMLDAOFactory) CreateOrderDetailDAO() OrderDetailDAO {
return &XMLDetailDAO{}
}
abstractfactory_test.go
package abstractfactory
func getMainAndDetail(factory DAOFactory) {
factory.CreateOrderMainDAO().SaveOrderMain()
factory.CreateOrderDetailDAO().SaveOrderDetail()
}
func ExampleRdbFactory() {
var factory DAOFactory
factory = &RDBDAOFactory{}
getMainAndDetail(factory)
// Output:
// rdb main save
// rdb detail save
}
func ExampleXmlFactory() {
var factory DAOFactory
factory = &XMLDAOFactory{}
getMainAndDetail(factory)
// Output:
// xml main save
// xml detail save
}
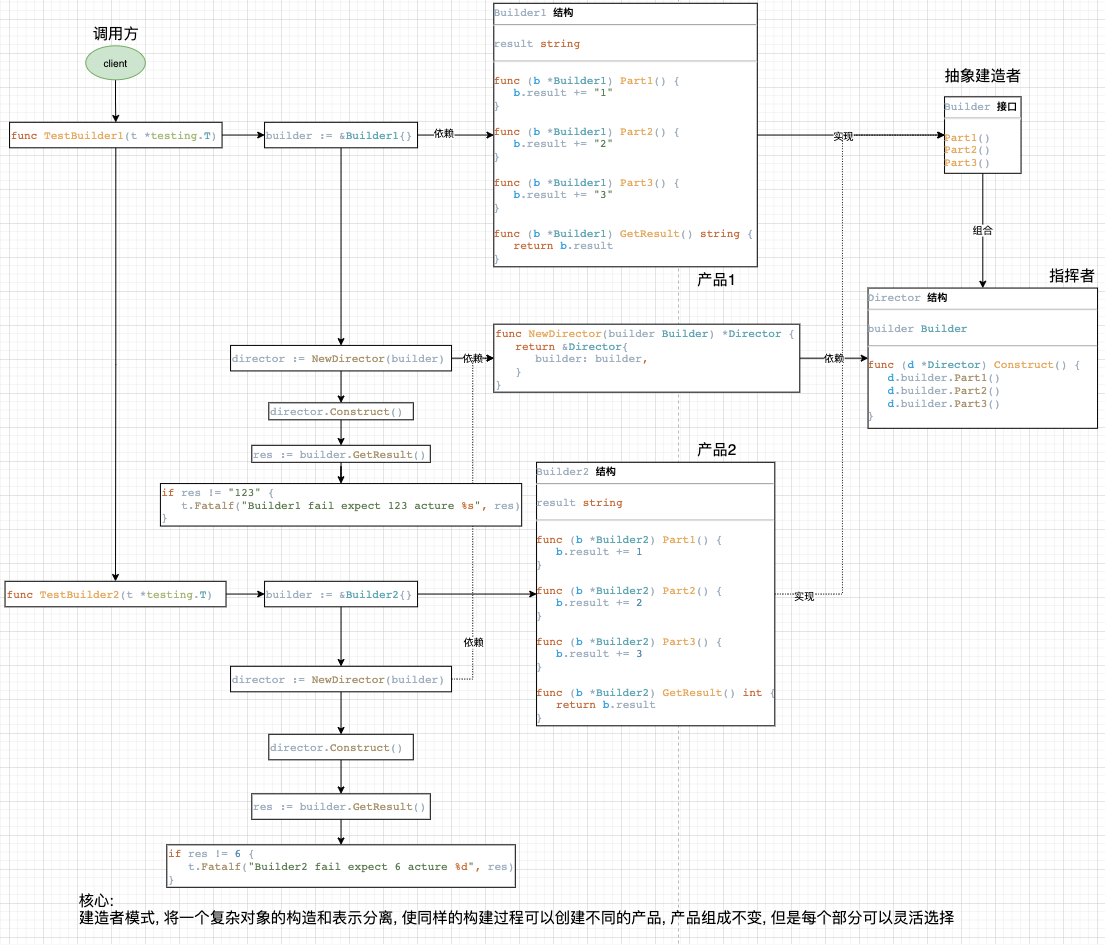
创建者模式
builder.go
package builder
//Builder 是生成器接口
type Builder interface {
Part1()
Part2()
Part3()
}
type Director struct {
builder Builder
}
// NewDirector ...
func NewDirector(builder Builder) *Director {
return &Director{
builder: builder,
}
}
//Construct Product
func (d *Director) Construct() {
d.builder.Part1()
d.builder.Part2()
d.builder.Part3()
}
type Builder1 struct {
result string
}
func (b *Builder1) Part1() {
b.result += "1"
}
func (b *Builder1) Part2() {
b.result += "2"
}
func (b *Builder1) Part3() {
b.result += "3"
}
func (b *Builder1) GetResult() string {
return b.result
}
type Builder2 struct {
result int
}
func (b *Builder2) Part1() {
b.result += 1
}
func (b *Builder2) Part2() {
b.result += 2
}
func (b *Builder2) Part3() {
b.result += 3
}
func (b *Builder2) GetResult() int {
return b.result
}
builder_test.go
package builder
import "testing"
func TestBuilder1(t *testing.T) {
builder := &Builder1{}
director := NewDirector(builder)
director.Construct()
res := builder.GetResult()
if res != "123" {
t.Fatalf("Builder1 fail expect 123 acture %s", res)
}
}
func TestBuilder2(t *testing.T) {
builder := &Builder2{}
director := NewDirector(builder)
director.Construct()
res := builder.GetResult()
if res != 6 {
t.Fatalf("Builder2 fail expect 6 acture %d", res)
}
}
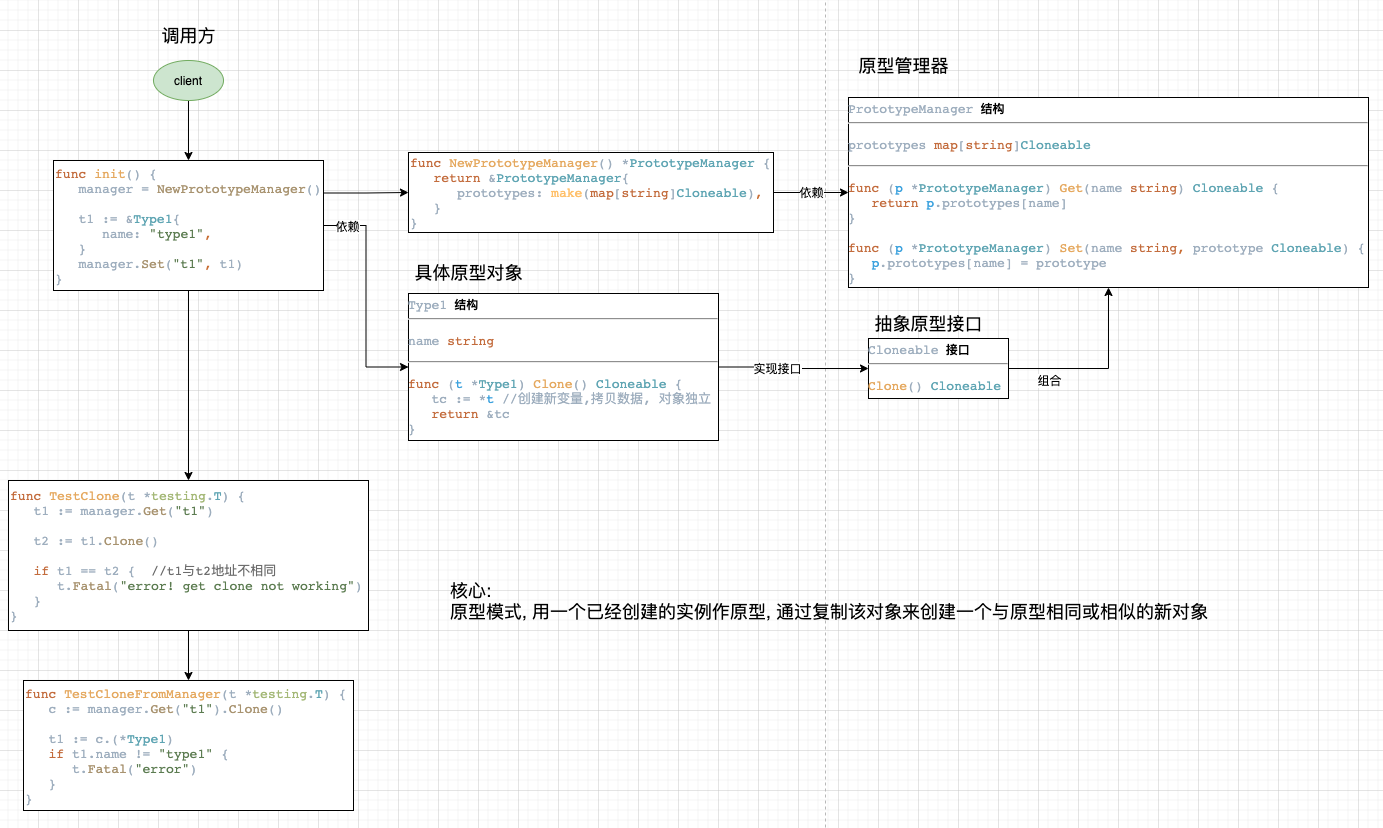
原型模式
原型模式使对象能复制自身,并且暴露到接口中,使客户端面向接口编程时,不知道接口实际对象的情况下生成新的对象。
原型模式配合原型管理器使用,使得客户端在不知道具体类的情况下,通过接口管理器得到新的实例,并且包含部分预设定配置。
package prototype
//Cloneable 是原型对象需要实现的接口
type Cloneable interface {
Clone() Cloneable
}
type PrototypeManager struct {
prototypes map[string]Cloneable
}
func NewPrototypeManager() *PrototypeManager {
return &PrototypeManager{
prototypes: make(map[string]Cloneable),
}
}
func (p *PrototypeManager) Get(name string) Cloneable {
return p.prototypes[name]
}
func (p *PrototypeManager) Set(name string, prototype Cloneable) {
p.prototypes[name] = prototype
}
单例模式
使用懒惰模式的单例模式,使用双重检查加锁保证线程安全
singleton.go
package singleton
import "sync"
//Singleton 是单例模式类
type Singleton struct{}
var singleton *Singleton
var once sync.Once
//GetInstance 用于获取单例模式对象
func GetInstance() *Singleton {
once.Do(func() {
singleton = &Singleton{}
})
return singleton
}
singleton_test.go
package singleton
import (
"sync"
"testing"
)
const parCount = 100
func TestSingleton(t *testing.T) {
ins1 := GetInstance()
ins2 := GetInstance()
if ins1 != ins2 {
t.Fatal("instance is not equal")
}
}
func TestParallelSingleton(t *testing.T) {
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(parCount)
instances := [parCount]*Singleton{}
for i := 0; i < parCount; i++ {
go func(index int) {
instances[index] = GetInstance()
wg.Done()
}(i)
}
wg.Wait()
for i := 1; i < parCount; i++ {
if instances[i] != instances[i-1] {
t.Fatal("instance is not equal")
}
}
}
