Solr4.8.0源码分析(20)之SolrCloud的Recovery策略(一)
题记:
我们在使用SolrCloud中会经常发现会有备份的shard出现状态Recoverying,这就表明SolrCloud的数据存在着不一致性,需要进行Recovery,这个时候的SolrCloud建索引是不会写入索引文件中的(每个shard接受到update后写入自己的ulog中)。关于Recovery的内容包含三篇,本文是第一篇介绍Recovery的原因以及总体流程。
1. Recovery的起因
Recovery一般发生在以下三个时候:
- SolrCloud启动的时候,主要由于在建索引的时候发生意外关闭,导致一些shard的数据与leader不一致,那么在启动的时候刚起的shard就会从leader那里同步数据。
- SolrCloud在进行leader选举中出现错误,一般出现在leader宕机引起replica进行选举成leader过程中。
- SolrCloud在进行update时候,由于某种原因leader转发update至replica没有成功,会迫使replica进行recoverying进行数据同步。
前面两种情况暂时不介绍,本文先介绍下第三种情况。大致原理如下图所示:
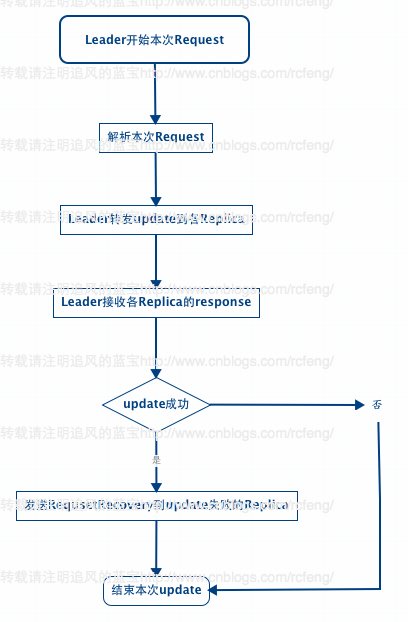
之前在<Solr4.8.0源码分析(15) 之 SolrCloud索引深入(2)>中讲到,不管update请求发送到哪个shard 分片中,最后在solrcloud里面进行分发的顺序都是从Leader发往Replica。Leader接受到update请求后先将document放入自己的索引文件以及update写入ulog中,然后将update同时转发给各个Replica分片。这就流程在就是之前讲到的add的索引链过程。
那么在索引链的add过程完毕后,SolrCloud会再依次调用finish()函数用来接受每一个Replica的响应,检查Replica的update操作是否成功。如果一旦有一个Replica没有成功,就会向update失败的Replica发送RequestRecovering命令强迫该分片进行Recoverying。
1 private void doFinish() { 2 // TODO: if not a forward and replication req is not specified, we could 3 // send in a background thread 4 5 cmdDistrib.finish(); 6 List<Error> errors = cmdDistrib.getErrors(); 7 // TODO - we may need to tell about more than one error... 8 9 // if its a forward, any fail is a problem - 10 // otherwise we assume things are fine if we got it locally 11 // until we start allowing min replication param 12 if (errors.size() > 0) { 13 // if one node is a RetryNode, this was a forward request 14 if (errors.get(0).req.node instanceof RetryNode) { 15 rsp.setException(errors.get(0).e); 16 } else { 17 if (log.isWarnEnabled()) { 18 for (Error error : errors) { 19 log.warn("Error sending update", error.e); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 // else 24 // for now we don't error - we assume if it was added locally, we 25 // succeeded 26 } 27 28 29 // if it is not a forward request, for each fail, try to tell them to 30 // recover - the doc was already added locally, so it should have been 31 // legit 32 33 for (final SolrCmdDistributor.Error error : errors) { 34 if (error.req.node instanceof RetryNode) { 35 // we don't try to force a leader to recover 36 // when we cannot forward to it 37 continue; 38 } 39 // TODO: we should force their state to recovering ?? 40 // TODO: do retries?? 41 // TODO: what if its is already recovering? Right now recoveries queue up - 42 // should they? 43 final String recoveryUrl = error.req.node.getBaseUrl(); 44 45 Thread thread = new Thread() { 46 { 47 setDaemon(true); 48 } 49 @Override 50 public void run() { 51 log.info("try and ask " + recoveryUrl + " to recover"); 52 HttpSolrServer server = new HttpSolrServer(recoveryUrl); 53 try { 54 server.setSoTimeout(60000); 55 server.setConnectionTimeout(15000); 56 57 RequestRecovery recoverRequestCmd = new RequestRecovery(); 58 recoverRequestCmd.setAction(CoreAdminAction.REQUESTRECOVERY); 59 recoverRequestCmd.setCoreName(error.req.node.getCoreName()); 60 try { 61 server.request(recoverRequestCmd); 62 } catch (Throwable t) { 63 SolrException.log(log, recoveryUrl 64 + ": Could not tell a replica to recover", t); 65 } 66 } finally { 67 server.shutdown(); 68 } 69 } 70 }; 71 ExecutorService executor = req.getCore().getCoreDescriptor().getCoreContainer().getUpdateShardHandler().getUpdateExecutor(); 72 executor.execute(thread); 73 74 } 75 }
2. Recovery的总体流程
Replica接收到来自Leader的RequestRecovery命令后就会开始进行RecoveryStrategy线程,然后进行Recovery。总体流程如下图索引:
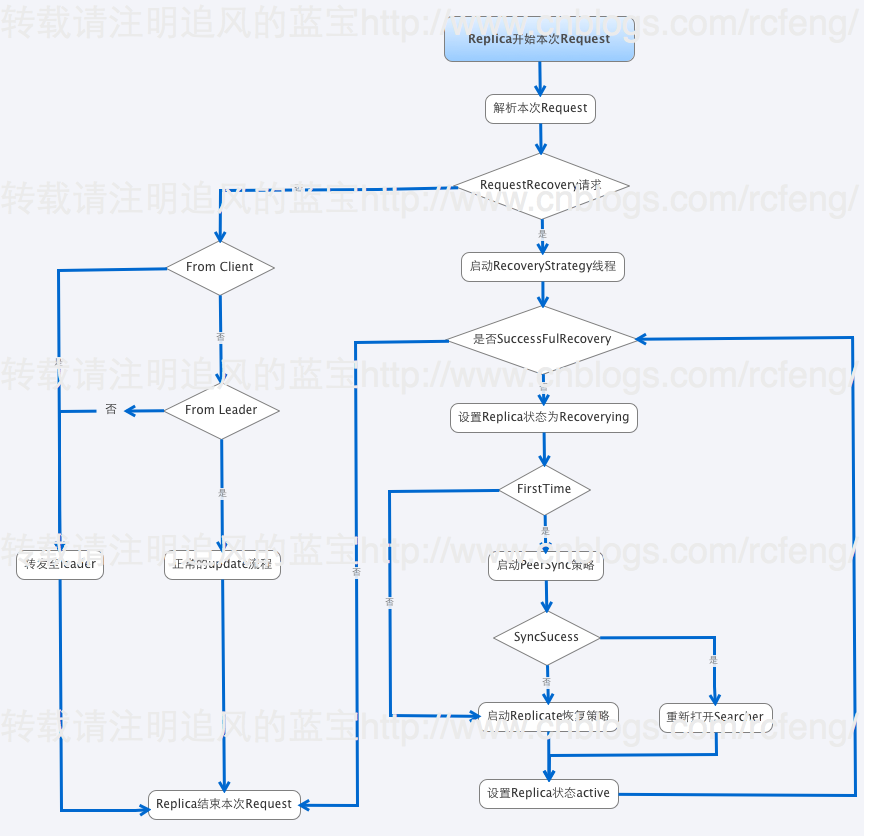
- 在RequestRecovery请求判断中,我例举了一部分(不是全部)请求命令,这是正常的索引链过程。
- 如果接受到的是RequestRecovery命令,那么本分片就会启动RecoveryStrategy线程来进行Recovery。
1 // if true, we are recovering after startup and shouldn't have (or be receiving) additional updates (except for local tlog recovery) 2 boolean recoveringAfterStartup = recoveryStrat == null; 3 4 recoveryStrat = new RecoveryStrategy(cc, cd, this); 5 recoveryStrat.setRecoveringAfterStartup(recoveringAfterStartup); 6 recoveryStrat.start(); 7 recoveryRunning = true;
- 分片会设置分片的状态recoverying。需要指出的是如果一旦检测到本分片成为了leader,那么Recovery过程就会退出。因为Recovery是从leader中同步数据的。
1 zkController.publish(core.getCoreDescriptor(), ZkStateReader.RECOVERING);
- 这里要判断下firsttime是否为true(在重启分片的时候会检查之前是否进行replication且没做完就被关闭了),firsttime是控制是否先进入PeerSync Recovery策略的,如果为false则跳过PeerSync进入Replicate。
1 if (recoveringAfterStartup) { 2 // if we're recovering after startup (i.e. we have been down), then we need to know what the last versions were 3 // when we went down. We may have received updates since then. 4 recentVersions = startingVersions; 5 try { 6 if ((ulog.getStartingOperation() & UpdateLog.FLAG_GAP) != 0) { 7 // last operation at the time of startup had the GAP flag set... 8 // this means we were previously doing a full index replication 9 // that probably didn't complete and buffering updates in the 10 // meantime. 11 log.info("Looks like a previous replication recovery did not complete - skipping peer sync. core=" 12 + coreName); 13 firstTime = false; // skip peersync 14 } 15 } catch (Exception e) { 16 SolrException.log(log, "Error trying to get ulog starting operation. core=" 17 + coreName, e); 18 firstTime = false; // skip peersync 19 } 20 }
- 最后进行选择进入是PeerSync策略和Replicate策略,在<Solr In Action 笔记(4) 之 SolrCloud分布式索引基础>中简单提到过两者的区别。关于具体的不同将在后面两节详细介绍。
- Peer sync, 如果中断的时间较短,recovering node只是丢失少量update请求,那么它可以从leader的update log中获取。这个临界值是100个update请求,如果大于100,就会从leader进行完整的索引快照恢复。
- Replication, 如果节点下线太久以至于不能从leader那进行同步,它就会使用solr的基于http进行索引的快照恢复。
- 最后设置分片的状态为active。并判断是否是sucessfulrrecovery,如果否则会多出尝试Recovery。
总结:
本文主要介绍了Recovery的起因以及Recovery过程,由于是简述所以内容较简单,主要提到了两种不同的Recovery策略,后续两文种将分别详细介绍。