获取类功能
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "anAdEfg"; System.out.println("String类的获取功能"); //获取字符串的长度 int length = str.length(); //获取指定索引位置的字符 char c1 = str.charAt(0); //返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 int c2 = str.indexOf('n'); //返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的索引 int c3 = str.indexOf("fg"); //返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。 int c4= str.indexOf('f', 2); //返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。 int c5 = str.indexOf("fg", 2); //从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾 String c6 = str.substring(2); //从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串 String c7 = str.substring(2, 4); //注意4是位置不是长度 System.out.println(length); System.out.println(c1); System.out.println(c2); System.out.println(c3); System.out.println(c4); System.out.println(c5); System.out.println(c6); System.out.println(c7); } }

判断类
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "axcde"; String str2 = "Axcde"; System.out.println("String类的判断功能"); //比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写 boolean b = str1.equals(str2); //比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写 boolean b1 = str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2); //判断字符串中是否包含传递进来的字符串 boolean b2 = str1.contains("cde"); //判断字符串是否以传递进来的字符串开头 boolean b3 = str1.startsWith("ax"); //判断字符串是否以传递进来的字符出结尾 boolean b4 = str2.endsWith("de"); //判断字符串的内容是否为空 boolean b5 = str1.isEmpty(); System.out.println(b1); System.out.println(b2); System.out.println(b3); System.out.println(b4); System.out.println(b5); } }

等于判断:
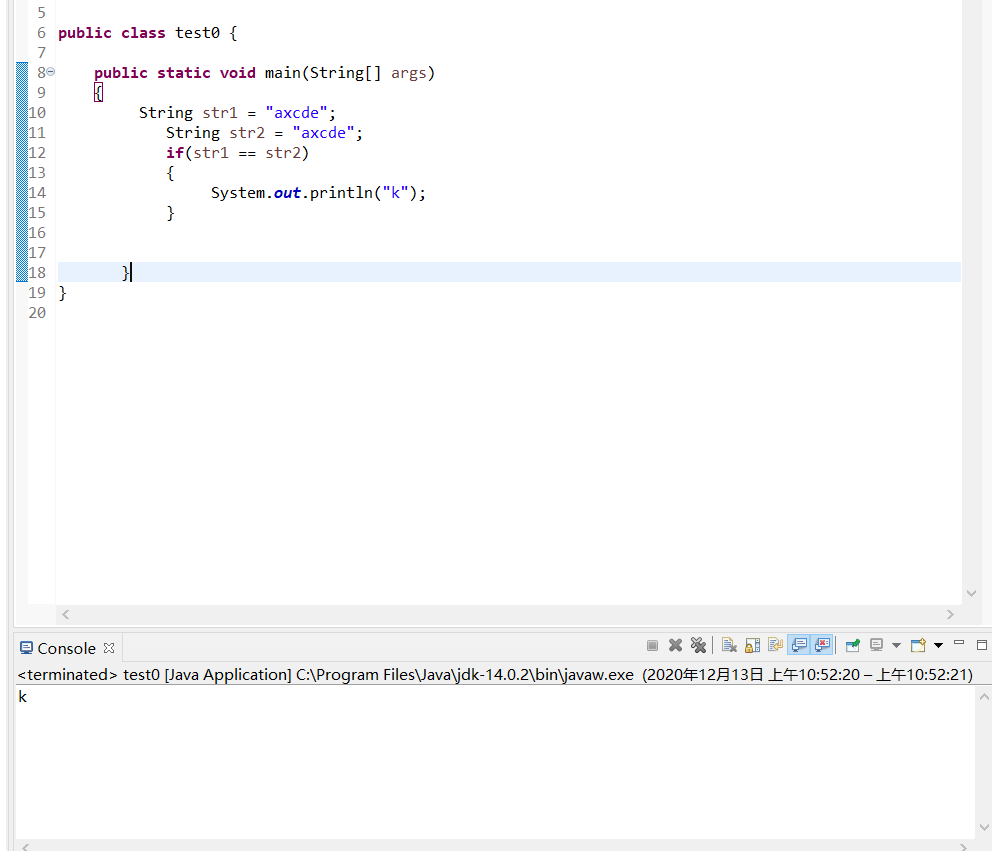
不支持[]操作符
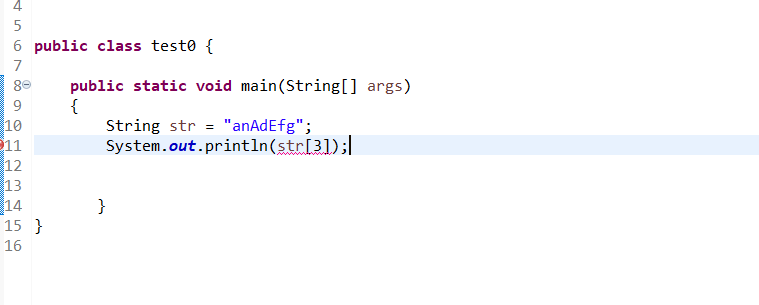
常见string转换
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "anAdEfg"; String str1 = "axcde"; int a=123323; //把字符串转换为字节数组 byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { System.out.print(bytes[i]+" "); } System.out.println(); //把字符串转换为字符数组 char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) { System.out.print(chars[i]+" "); } System.out.println(); //把字符数组转换成字符串 String s2 = new String (chars); System.out.println(s2); //把i.nt类型的数据转成字符串 String s3 = Integer.toString(a); System.out.println(s3); //把字符串转换成小写 String s = str.toLowerCase(); System.out.println(s); //把字符串变成大写 String s1 = str.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(s1); //字符串拼接 String s4 = str.concat(str1); System.out.println(s4); } }

public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = " anAdEfg "; @SuppressWarnings("unused") String str1 = "axcde"; //将指定字符进行互换 String s = str.replace('a', 'b'); System.out.println(s); //将指定字符串进行互换 String s1 = str.replace("an", "qq"); System.out.println(s1); //去除两端空格 String s2 = str.trim(); System.out.println(s2); //通过字典顺序去比较 返回的值是 ASCII 码的差值 调用者减去传入者 int i = "BCc".compareTo("ABc"); System.out.println(i); //如果前面几个字母一样会根据两个字符串长度进行减法运算返回该减法的结果 (通过长度去比) int i1 = "abc".compareTo("a"); System.out.println(i1); //忽略大小写的比较 int i2 = "abc".compareToIgnoreCase("ABC"); System.out.println(i2); } }

string 和int 转换
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { //i/n/t->String int i = 1234567; String s = ""; s = i + "";//会产生两个String对象 System.out.println(s); String s1 = String.valueOf(i);//使用String类的静态方法,只产生一个String对象 System.out.println(s1); String s2 = Integer.toString(i); System.out.println(s2); //String->i/n/t String str = "12345"; int i1 = Integer.parseInt(str);//直接使用静态方法,不会产生多余的对象 System.out.println(i1); int i2 = Integer.valueOf(str).intValue(); System.out.println(i2); } }

string.equal 和== 的不同
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//判断字符串内容 System.out.println(s1 == s2);//判断字符串引用 } }

字符串排序
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { String sortStr = "ACDFE"; char[] arrayCh = sortStr.toCharArray(); //1,把sortStr转换为字符数组 Arrays.sort(arrayCh);//2,利用数组帮助类自动排序 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayCh));//3,输出 } }

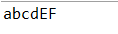
Java StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类
public class test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer("abcd"); sBuffer.append("EF"); System.out.println(sBuffer); } }
string 的读取
package Test; import java.util.Scanner; public class test0 { public static void main (String []args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); System.out.println(s); String s2 = input.next(); System.out.println(s2 ); } }

参考:
https://www.runoob.com/java/java-stringbuffer.html