部分匹配表
(Partial Match Table)
- 前缀:除了最后一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部头部组合
- 后缀:除了第一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部尾部组合。
- "部分匹配值"就是"前缀"和"后缀"的最长的共有元素的长度
算法搜索的思路
- 说明:绿色代表已经表过并且相等的部分。黄色代表当前待表的位置
- 目标串:"ABCFABD",原串"ABCFABCDABCFABD"

- 比较到如图中位置时,已经标绿的两个字符序列相等。
- 黄色部分的两个字符不相等。若采用传统的搜索方法,只将目标串后移一位,效率很低。如下图所示

- 实际上对于已经匹配的绿色子串“ABCFAB”,如果我们找出它的匹配子串(即“AB”)则只需将目标便宜到与原串中第二个“AB”序列对齐,并从第三个字符开始比较即可。
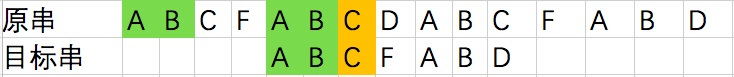 亦即,移动位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应的部分匹配值。
亦即,移动位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应的部分匹配值。 - 接着比较

- 因为D与F不相等,目标串需要往后移。这时,已匹配序列为("ABC"),对应的"部分匹配值"为0。所以,移动位数 为3 - 0=3。
 如此一直往下
##部分匹配表的计算
###字符串索引的计算
如此一直往下
##部分匹配表的计算
###字符串索引的计算 - 目标字符表示待搜索的字符,记为T。而搜索的串记为O
- 字符串的索引从零开始
- 用next数组来表示部分匹配表,数组下标从0开始。next[i]代表结束字符索引为i字串的最大匹配长度
- 串的长度为len,开始索引为begin,结束索引为end。则有 end - begin + 1 = len; ####简单示例 如:"ABCDABD" next[1] = 0(前缀和后缀都是空集) next[2] = 0 next[3] = 0 next[4] = 0 next[5] = 1 next[6] = 2 next[7] = 0 ###部分匹配表递推 ####推算前提
- 假设next[m-1]的值已知,根据部分匹配表的定义可知前next[m-1]个字符序列(T[0]~T[next[m-1] - 1])与字符序列(T[m - next[m - 1]]~T[m-1] )是相同的(如下图,记为Sub1)
 ####若T[m] == T[next[m-1]]
则T[0]~T[next[m-1]]与字符序列T[m - next[m-1]]~T[m]是相同的。(如下图,记为Sub2)
####若T[m] == T[next[m-1]]
则T[0]~T[next[m-1]]与字符序列T[m - next[m-1]]~T[m]是相同的。(如下图,记为Sub2)

若T[m] != T[next[m-1]]
- 由推算前提可知,字符序列(T[m - next[m - 1]]~T[m-1] )与(T[0]~T[next[m-1] - 1])序列是相同的。只是这两个字序列在向后扩展时遇到了分歧。
- 因此我们找出字串Sub1的最长部分匹配子串(记为Sub3,假设长度为k,k = next[next[m - 1] - 1])。因为T[m]前边存在Sub1串,而Sub3又是Sub1的子串。因此T[m]前边肯定存在Sub3串。只需要比较T[k - 1]和T[m]即可
- 如果T[k - 1]和T[m]仍旧不等,一直往下。直到找不到部分匹配字串。
计算示例

说明
- 绿色代表已经匹配的序列
- 蓝色代表待计算的next值,黄色代表求改next值时尾部待比较的字符
初始
因为前四个字符在当前遍历到的位置都是唯一的,所以next值肯定为0。
next[4]

标黄部分相等,因此next[5]为1
next[5]~next[6]


next[7]

- 标黄部分不相等,因此查找标黄的“D”前面的绿色序列“ABC”的部分匹配字串。
- 查表知道next[6]为3,我们回溯去看长度为3的字序列的部分匹配序列的长度(也就是next[2],值为0)
- 结束,next[5]为0.
next[14]

- 标黄部分不相等,因此查找标黄的“D”前面的绿色序列“ABCFAB”的部分匹配字串。
- 由next[13]为6去查看next[5]的值(也就是序列“ABCFAB”的部分匹配序列的长度,此处为2)
- 比较T[2] 与T14

- T[2] 与T[14]不相等,继续找出“AB”的部分匹配长度,为零。终止迭代,因此next[14]为0。
源程序
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Print(int* array,int length)
{
for(int i = 0;i < length; ++ i)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int CalculateNext(const string& str,int** array)
{
int len = str.size();
int* next = (int *)new int[len];
next[0] = 0;//对于只包含第一个字符的字符序列来说,前缀和后缀都是空集。因此部分匹配长度为0;
int prefix_tail_index = 0;//前缀串中下一次待比较的索引数,因为一开始的时候,都未比较过,索引前缀从零开始
for(int suffix_tail_index = 1;suffix_tail_index < len; ++ suffix_tail_index)
{
while(prefix_tail_index != 0 && str[prefix_tail_index] != str[suffix_tail_index] )
{
//如果前缀的待比较位与后缀最后一位不相等,那么找出长度为suffix_tail_index - 1的字串的最长部分匹配字串
// 从该串的后面一位开始与str[suffix_tail_index]
prefix_tail_index = next[prefix_tail_index - 1];
}
if(str[prefix_tail_index] == str[suffix_tail_index])
{
//在求出了next[i - 1]的基础上发现最长部分匹配序列可以向后扩展一位。
prefix_tail_index ++;
//记录最长部分匹配长度为prefix_tail_index,但是前缀串的最后一个字符的索引为prefix_tail_index - 1;
next[suffix_tail_index] = prefix_tail_index;
continue;
}
else
{
next[suffix_tail_index] = 0;
}
}
*array = next;
return len;
}
int KMP(const string& o_str,const string& target)
{
int *pmt;
int tlen = CalculateNext(target,&pmt);
int match_bits = 0;//比较过程两个序列前面已经相同的位数
int start_pos = 0;//某次比较过程中,原串的起始比较位置
int olen = o_str.size();
while(match_bits < tlen && start_pos + match_bits < olen)
{
if(target[match_bits] == o_str[start_pos + match_bits])
{
match_bits ++;
cout << "match_bits:" << match_bits << endl;
}
else
{
if(match_bits == 0)
{
//前面没有发现匹配的字符
start_pos += 1;
}
else
{
//移动位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应的部分匹配值
int offset = match_bits - pmt[match_bits - 1];
start_pos += offset;
match_bits = pmt[match_bits - 1];
}
cout << "start_pos:" << start_pos << ",match_bits:" << match_bits << endl;
}
}
if(match_bits == tlen)
return start_pos;
else
return -1;
}
int main()
{
// string str1("ABCDABD");
string str1("ABCFABCDABCFABD");
// string str2("ABD");
string str2("ABCFABD");
cout << KMP(str1,str2) << endl;
return 0;
}