public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>
Integer 由final修饰了,所以该类不能够被继承,同时 Integer 继承了Number类,因此可以将Integer转换成 int 、double、float、long、byte和short类型的数据,另外,也实现了comparable接口,因此Integer类也可以进行自然排序。
构造方法只有两个:
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
this.value = parseInt(s, 10);
}
我们主要看第二个构造方法,传入一个字符串,然后调用parseInt方法,接下来进入parseInt的源码:
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
int result = 0;
// //是否为负数
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
//这里加个负号是防止数据溢出,int的数值范围 -2的31次方到2的31次方减一
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//最小基数
int multmin;
//十进制数字
int digit;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
//第一个字符小于0,有可能是"-","+"或其他字符
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
//为负数
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+')//非数字
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
/**
* 最小基数,主要防止 result *= radix; 这个操作时数据过大
* 导致数据丢失的问题,因为所以带符号32位int类型整数为-2147483648~2147483647
*/
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
//转换十进制,这里获取的是radix进制下相对应的10进制数字,如:
//Character.digit('a',16),则返回 10;
//若输入字符不在进制的范围之内,则返回 -1:
//Character.digit('t',16),返回 -1,Character.digit('a',10),返回 -1
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
//返回-1说明字符非法
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
//超过了数据范围
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
/**
*在转换时从高位向地位方向转换
*/
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
return negative ? result : -result;
}
这个方法中最核心的步骤是1、result *= radix; 2、result -= digit; 经过这两个步骤将字符串转换成数值类型。大概流程是这样的:
假如字符串"1234" 转换成int类型,result 的初始值为0,radix默认为10;
首先截取字符串的第一个字符1(这里忽略各种检查),经过第一步计算 result = 0*10 = 0;第二部计算 result = 0 - 1 = -1;
第一遍循环结束后,result 的值 变成了 -1
截取第二个字符 2 ,result = -1 * 10 = -10,result = -10 - 2 = -12;
截取第三个字符 3 ,result = -12 * 10 = -120,result = -120 - 3 = -123;
截取第四个字符 4 ,result = -123 * 10 = -1230 ,result = -1230-4 = -1234;
循环结束,此时result的值为 -1234,完成字符串向整数型的转换,返回是取反即可。
下面我将从一个面试题引出问题,然后通过阅读源码来解决这个问题。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 100;
Integer i2 = 100;
Integer i3 = 200;
Integer i4 = 200;
Integer i5 = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer i6 = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer i7 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println("i1 == i2 的结果是:" + (i1 == i2));
System.out.println("i3 == i4 的结果是:" + (i3 == i4));
System.out.println("i5 == i6 的结果是:" + (i5 == i6));
System.out.println("i1 == i5 的结果是:" + (i1 == i5));
System.out.println("i1 == i7 的结果是:" + (i1 == i7));
}
运行结果为:
i1 == i2 的结果是:true
i3 == i4 的结果是:false
i5 == i6 的结果是:true
i1 == i5 的结果是:true
i1 == i7 的结果是:false
我们先来看第一和第二条结果,同样是比较两个相同数值,为什么会有不同的结果呢?接下我将通过源码来解释原因。
首先,我们通过编译获取到class文件的字节码
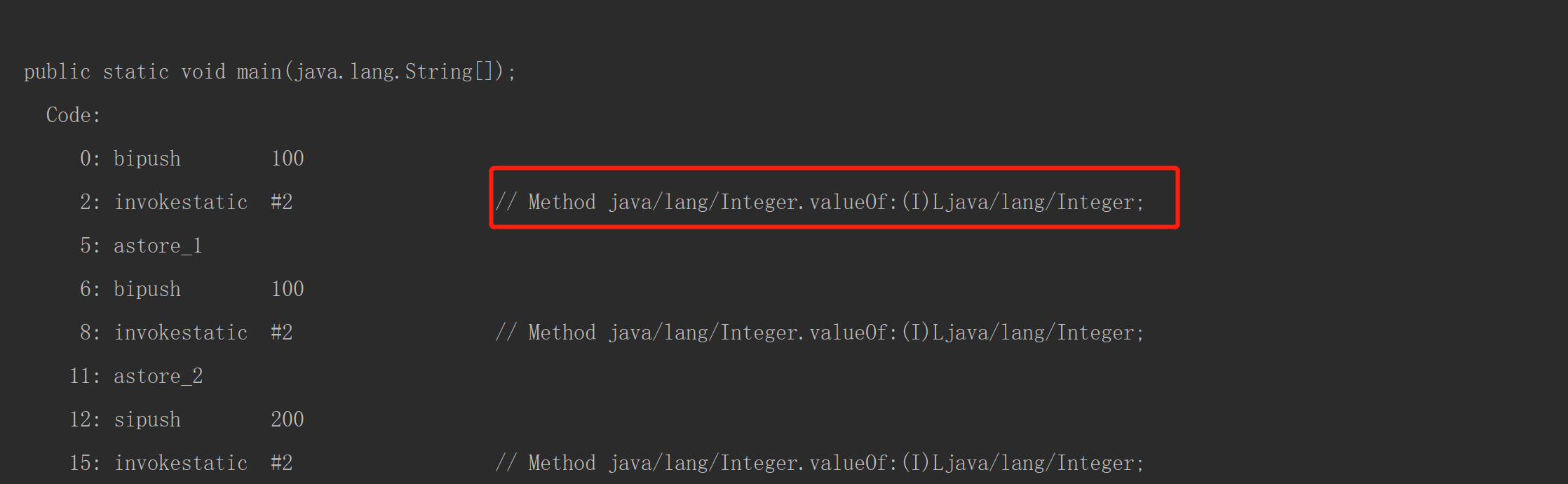
从图中我们可以看到,在执行 Integer i1 = 100 这条命令的时候,编译器会调用Integer中的静态方法 valueOf,接下来我们看看 valueOf方法是怎么实现的吧。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
这个代码看起来很简单,Integer 中有一个静态内部类 IntegerCache,调用该方法时首先会判断该值是否在缓存的范围内,如果在则直接将缓存中的数值返回,否则返回一个新对象。看到这里我们似乎已经知道了上面的问题的答案了,接下来继续看静态内部类吧
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
//缓存范围最小(也是默认范围)为 (-128)~ 127,如果配置java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high
//high 的值可从配置文件中读取
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
//获取配置文件和127之间的最大值
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
//最大值范围
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
//创建缓存数组
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
//将数字缓存起来默认 -128 ~ 127
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
我们知道内部类只有在所在类实例化时才会被实例化,而且只会实例化一次,缓存操作是在静态代码块中完成,也就是说在类被实例化的时候数据就已经被缓存好了,接下使用的时候可以直接使用缓存的数据。
现在我们回归到上面的问题,结果1中两个数据均为 100,在缓存的范围中,因此i1和i2都指向的是同一个内存地址,因此返回true。结果2中 两个数都是200,超出了缓存的范围,所以直接new 出了两个对象,因此他们的内存地址不一致,返回结果为false;另外,使用valueOf 和 使用 = 操作符赋值时一样的,所以结果3和结果4返回结果为 true,结果5中 是直接使用new关键字创建对象,所以他们的内存地址肯定不一致,结果为false。
那么,现在问题又来了,那我怎么判断两个整数的大小呢?继续看源码
/**
* The value of the {@code Integer}.
*
* @serial
*/
private final int value;
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
public int intValue() {
return value;
}
是的,没错,比较两个数值大小时可以使用equals方法来比较,源码中value的类型为 int型,intValue返回的也是value,因此可以判断两个数的大小。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = 200;
Integer i2 = 200;
System.out.println("i1 == i2 的结果是:" + i1.equals(i2)); //true
}
补充:equals 与 == 的区别:
equals 比较的是两个数值的大小,== 有两种情况,如果比较的是 基本数据类型,则 == 跟equals一样都是比较的大小,如果是引用类型或数组,则比较是内存地址。
getChars方法:
static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {
int q, r;
int charPos = index;
char sign = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sign = '-';
i = -i;
}
// Generate two digits per iteration
//每次循环获取后两位数
while (i >= 65536) {
q = i / 100;
// really: r = i - (q * 100);
//使用位移运算的效率高于乘法运算,r为后两位数
r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));
i = q;
//获取后两位数的个位
buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
//十位
buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
}
// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
// assert(i <= 65536, i);
//每次只取个位数
for (;;) {
//相当于i*(52429/524288)=i*0.10000038146972656=i*0.1=i/10
//这里选 52429 和 2的19次方相除,得到的结果精度更加高,更加接近于 i/10的结果
//之所以要这样转换,是因为在计算机运算中位移的效率 > 乘法效率 > 除法效率
q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);
r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...
buf [--charPos] = digits [r];
i = q;
if (i == 0) break;
}
if (sign != 0) {
buf [--charPos] = sign;
}
}