FreeRTOS延时简易分析
- 架构:Cortex-M3
- 版本:FreeRTOS V9.0.0
- 前言:在很多情况,需要使用延时来达到一些效果,那么FreeRTOS的延时是怎么实现的
1.相对延时vTaskDelay
只有一个参数就是等待时间
void vTaskDelay( const TickType_t xTicksToDelay )
{
BaseType_t xAlreadyYielded = pdFALSE;
/* A delay time of zero just forces a reschedule. */
if( xTicksToDelay > ( TickType_t ) 0U )
{
configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 0 );
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
traceTASK_DELAY();
/* A task that is removed from the event list while the
scheduler is suspended will not get placed in the ready
list or removed from the blocked list until the scheduler
is resumed.
This task cannot be in an event list as it is the currently
executing task. */
prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( xTicksToDelay, pdFALSE );
}
xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* Force a reschedule if xTaskResumeAll has not already done so, we may
have put ourselves to sleep. */
if( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE )
{
portYIELD_WITHIN_API();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
具体调用prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList
static void prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( TickType_t xTicksToWait, const BaseType_t xCanBlockIndefinitely )
{
TickType_t xTimeToWake;
const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount;
#if( INCLUDE_xTaskAbortDelay == 1 )
{
/* About to enter a delayed list, so ensure the ucDelayAborted flag is
reset to pdFALSE so it can be detected as having been set to pdTRUE
when the task leaves the Blocked state. */
pxCurrentTCB->ucDelayAborted = pdFALSE;
}
#endif
/* Remove the task from the ready list before adding it to the blocked list
as the same list item is used for both lists. */
if( uxListRemove( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) ) == ( UBaseType_t ) 0 )
{
/* The current task must be in a ready list, so there is no need to
check, and the port reset macro can be called directly. */
portRESET_READY_PRIORITY( pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority, uxTopReadyPriority );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
#if ( INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend == 1 )
{
if( ( xTicksToWait == portMAX_DELAY ) && ( xCanBlockIndefinitely != pdFALSE ) )
{
/* Add the task to the suspended task list instead of a delayed task
list to ensure it is not woken by a timing event. It will block
indefinitely. */
vListInsertEnd( &xSuspendedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) );
}
else
{
/* Calculate the time at which the task should be woken if the event
does not occur. This may overflow but this doesn't matter, the
kernel will manage it correctly. */
xTimeToWake = xConstTickCount + xTicksToWait;
/* The list item will be inserted in wake time order. */
listSET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ), xTimeToWake );
if( xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount )
{
/* Wake time has overflowed. Place this item in the overflow
list. */
vListInsert( pxOverflowDelayedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) );
}
else
{
/* The wake time has not overflowed, so the current block list
is used. */
vListInsert( pxDelayedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) );
/* If the task entering the blocked state was placed at the
head of the list of blocked tasks then xNextTaskUnblockTime
needs to be updated too. */
if( xTimeToWake < xNextTaskUnblockTime )
{
xNextTaskUnblockTime = xTimeToWake;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
}
}
#else /* INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend */
{
/* Calculate the time at which the task should be woken if the event
does not occur. This may overflow but this doesn't matter, the kernel
will manage it correctly. */
xTimeToWake = xConstTickCount + xTicksToWait;
/* The list item will be inserted in wake time order. */
listSET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ), xTimeToWake );
if( xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount )
{
/* Wake time has overflowed. Place this item in the overflow list. */
vListInsert( pxOverflowDelayedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) );
}
else
{
/* The wake time has not overflowed, so the current block list is used. */
vListInsert( pxDelayedTaskList, &( pxCurrentTCB->xStateListItem ) );
/* If the task entering the blocked state was placed at the head of the
list of blocked tasks then xNextTaskUnblockTime needs to be updated
too. */
if( xTimeToWake < xNextTaskUnblockTime )
{
xNextTaskUnblockTime = xTimeToWake;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
/* Avoid compiler warning when INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend is not 1. */
( void ) xCanBlockIndefinitely;
}
#endif /* INCLUDE_vTaskSuspend */
}
首先挂起全部任务,把当前任务从状态链表中移除。
如果等待的时间为portMAX_DELAY,则把当前任务插入到xSuspendedTaskList的尾部。
如果等待时间小于portMAX_DELAY,设置等待的时间(把当前时间xConstTickCount加上等待时间xTicksToWait),如果xTimeToWake < xConstTickCount意味着时间溢出了,会把当前任务挂载到另一条delayList上(FreeRTOS维护着两条delayList,就是为了解决溢出的问题:当前时间溢出时,FreeRTOS就会选择另一条delayList作为延时List)。如果没有溢出就正常挂载到当前delayList上。
2.vTaskDelayUntil
void vTaskDelayUntil( TickType_t * const pxPreviousWakeTime, const TickType_t xTimeIncrement )
{
TickType_t xTimeToWake;
BaseType_t xAlreadyYielded, xShouldDelay = pdFALSE;
configASSERT( pxPreviousWakeTime );
configASSERT( ( xTimeIncrement > 0U ) );
configASSERT( uxSchedulerSuspended == 0 );
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* Minor optimisation. The tick count cannot change in this
block. */
const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount;
/* Generate the tick time at which the task wants to wake. */
xTimeToWake = *pxPreviousWakeTime + xTimeIncrement;
if( xConstTickCount < *pxPreviousWakeTime )
{
/* The tick count has overflowed since this function was
lasted called. In this case the only time we should ever
actually delay is if the wake time has also overflowed,
and the wake time is greater than the tick time. When this
is the case it is as if neither time had overflowed. */
if( ( xTimeToWake < *pxPreviousWakeTime ) && ( xTimeToWake > xConstTickCount ) )
{
xShouldDelay = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
/* The tick time has not overflowed. In this case we will
delay if either the wake time has overflowed, and/or the
tick time is less than the wake time. */
if( ( xTimeToWake < *pxPreviousWakeTime ) || ( xTimeToWake > xConstTickCount ) )
{
xShouldDelay = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
/* Update the wake time ready for the next call. */
*pxPreviousWakeTime = xTimeToWake;
if( xShouldDelay != pdFALSE )
{
traceTASK_DELAY_UNTIL( xTimeToWake );
/* prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList() needs the block time, not
the time to wake, so subtract the current tick count. */
prvAddCurrentTaskToDelayedList( xTimeToWake - xConstTickCount, pdFALSE );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
xAlreadyYielded = xTaskResumeAll();
/* Force a reschedule if xTaskResumeAll has not already done so, we may
have put ourselves to sleep. */
if( xAlreadyYielded == pdFALSE )
{
portYIELD_WITHIN_API();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
传入的参数1其实是会上次任务结束阻塞的时间,参数2是周期性等待时间。
首先把所有任务挂起,xTimeToWake就是下次结束阻塞的时间,如果xConstTickCount < *pxPreviousWakeTime说明溢出了,如果没有溢出的话,检查是否到结束阻塞的时间,如果没到,就把当前任务挂载到DelayedList。
3 为什么说vTaskDelay是相对延时?而vTaskDelayUntil是绝对延时
有一个任务A,它首先会执行2S的某个程序后,调用vTaskDelay延时10s。
void TaskA(void * pvParameters)
{
whlie(1)
{
dosomething(2);
vTaskDelay(10);
}
}
这10s内会全部执行其它任务,具体如图:
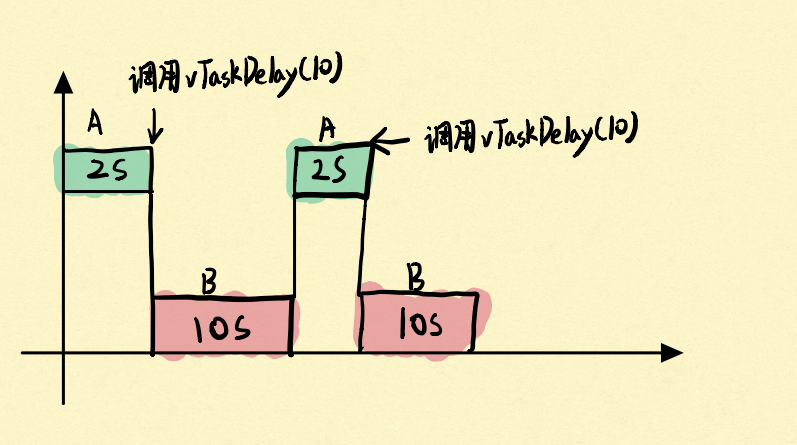
而如果任务A,调用vTaskDelayUntil延时10s,
void TaskA(void * pvParameters)
{
static portTickType s_SystickCount;
s_SystickCount = xTaskGetTickCount();
whlie(1)
{
dosomething(2);
vTaskDelayUntil(&s_SystickCount,10);
}
}
那么只有8秒会去执行其它程序,如图:

这就是区别。