| 这个作业属于哪个班级 | 数据结构--网络2011/2012 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的地址 | DS博客作业02--栈和队列 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习栈和队列的结构设计及运算操作 |
| 姓名 | 骆梦钒 |
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结(0-5分)
1.1 栈
1.画一个栈的图形,介绍如下内容。

2.顺序栈的结构、操作函数
栈空条件:s->top-1
栈满条件:s->topMaxSize-1
进栈:s->top++;s->data[top]=e;
出栈:e=s->data[top--];
//(1)结构体
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(2)初始化栈
void InitStack(SqStack *&s)
{
s=(SqStack*)malloc(sizeof(SqStack));
s->top=-1;
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack *&s,ElemType e)
{
if(s->top==MaxSize-1)
return flase;
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=e;
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack *&s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top==-1)
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
3.链栈的结构、操作函数
栈空:s->next=NULL;
栈满;不存在
进栈:头插法
出栈:取出首结点的data值并将其删除
与顺序栈相比,链栈的结点空间可以动态申请,因此,不存在栈满上溢的情况。
链栈的基本操作包括:
(1)链栈的初始化操作。链栈的初始化操作就是把链栈初始化为空,设栈顶指针为top,初始化时,不带头结点top==NULL;带头结点top->next ==NULL;
(2)判断链栈是否为空。判断链栈是否为空,就是判断链栈的头结点指针域是否为空,即:top->next NULL;带头结点,不带头结点的链栈栈空条件为:topNULL;
(3)进栈操作。进栈操作就是将数据元素data插入到链栈的栈顶,就是将新结点插入到链表的第一个结点之前,将新结点插入到链表中分为3个步骤p->data = data; p->next = top->next; top->next = p;p为指向新结点的指针;
(4)出栈操作。出栈操作就是将栈的第一个结点删除,并将结点元素赋值给data,在元素出栈前要判断栈是是否为空;
(5)取栈顶元素。取栈顶元素就是把栈顶的元素取出,并返回。在去栈顶元素之前,同样要判断栈是否为空;
(6)求链栈的长度。求链表的长度就是返回链栈中的元素个数,从栈顶指针开始,通过指针域找到下一个结点,并使用变量计数,直到栈底为止;
(7)销毁链栈操作。链栈的空间是动态申请的,在程序结束时要把这些结点空间通过free函数释放;
打印栈中元素。打印栈中元素即:将栈中元素输出。
//链栈的结构体
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node
{
DataType data;
struct Node* next;
}LStackNode,*LinkStack;
//(1)初始化栈
void InitStack(LinkStNode *&s)
{
s=(LinkStNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
s->next=NULL;
}
//(2)销毁栈
void DestroyStack(LinkStNode *&s)
{
LinkStNode *pre=s,*p=s->next;
while(p)
{
free(pre);
pre=p;
p=pre->next;
}
free(pre);
}
//(4)进栈
void Push(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType e)
{
LinkStNode *p;
p=(LinkStNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkStNode));
p->data=e;
p->next=s->next;
s->next=p’
}
//(5)出栈
bool Pop(LinkStNode *&s,ElemType &e)
{
LinkStNode *p;
if(s->next==NULL)
return false;
p=s->next;
e=p->data;
s->next=p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//(6)取栈顶元素
bool GetTop(LinkStNode *s,ElemType &e)
{
if(s->next==NULL)
return false;
e=s->next->data;
return true;
}
1.2 栈的应用
1.数制转换应用:
十进制数N和其他d进制数的转换是计算机实现计算的基本问题,其解决方法很多,其中一个简单算法基于下列原理:
N = (N div d) * d + N mod d(其中:div为整除运算,mod为求余运算)
void conversion()
{
SqStack S;
int N,M,e;
InitStack_Sq(S);
cout<<"请输入要转换的数字"<<endl;
cin>>N;
cout<<"请选择要转换的进制数:"<<endl;
cin>>M;
while(N)
{
Push_Sq(S,N%M);
N=N/M;
}
cout<<N<<"进制的数转化为"<<M<<"进制后为:";
while(!StackEmpty_Sq(S))
{
Pop_Sq(S,e);
cout<<e;
}
cout<<endl;
2.表达式转换算法:
所谓中缀表达式就是人类能正常阅读的算术表达式,就像我们上述例子中的输入一样:4+(6-10+22)2。而后缀表达式是让计算机读的,有了后缀表达式之后再求值就非常简单。
在依次读入字符的过程中遇到操作符先不求值,对于优先级高的栈顶操作符,将之弹出加入操作数队列(队列也是一种数据结构)即可,最后输出整个队列,就是后缀表达式。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int IsNum(char ch);
int Zhengfu(char ch);
int compare(char a,char b);
void F(char *a,int len);
int main()
{
char a[25];
scanf("%s",a);
int len=strlen(a);
F(a,len);
return 0;
}
int IsNum(char ch)
{
return ch>='0'&&ch<='9'||ch=='.';
}
int Zhengfu(char ch)
{
return ch=='+'||ch=='-';
}
int compare(char a,char b)
{ //判断是否出栈
if(b==')') return 1;
if(a=='('||b=='(') return 0;
if(b=='+'||b=='-') return 1;
else if(b=='*'||b=='/')
{
if(a=='+'||a=='-') return 0;
else if(a=='*'||a=='/') return 1;
}
}
void F(char *a,int len)
{
char stack[25];
int top=0;
int space = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(IsNum(a[i]))
{
if(space)
{
printf(" ");
space = 0;
}
printf("%c",a[i]);
}
else if(Zhengfu(a[i])&&(i?!IsNum(a[i-1])&&a[i-1]!=')':1)){//如果不是运算符,则直接输出
if(a[i]=='-'){ //只输出负号
if(space)
{
printf(" ");
space=0;
}
printf("%c",a[i]);
}
}
else
{
if(top)
{
if(a[i]==')')
while(top--)
{
if(stack[top]=='(') break;
printf(" %c",stack[top]);
}
else
{
while(top)
{
if(compare(stack[top-1],a[i]))
{
printf(" %c",stack[--top]);
}
else break;
}
stack[top++]=a[i];
}
}
else stack[top++]=a[i];
for(int j=0;j<top;j++)
if(stack[j]!='(')
{
space = 1;
break;
}
}
}
while(top)
{
printf(" %c",stack[--top]);
}
}
3.迷宫求解
求迷宫从入口到出口的所有路径是一个经典的程序设计问题。由于计算机解迷宫时,通常用的是“穷举求解”的方法,即从入口出发,顺某一方向向前探索,若能走通,则继续往前走;否则沿原路退回,换一个方向再继续探索,直至所有可能的通路都探索到为止。
为了保证在任何位置都能沿原路退回,显然需要用一个后进先出的结构来保存从入口到当前位置的路径。因此在迷宫求解时应用“栈”也就是自然而然的事情了。
用一个二维数组来表示一个迷宫,如下图所示:
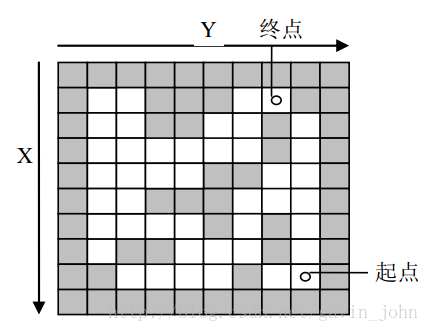

初始化,将起点加入堆栈;
while(堆栈不为空)
{
取出栈顶位置为当前位置;
如果 当前位置是终点,
则 使用堆栈记录的路径标记从起点至终点的路径;
否则
{
按照从下、右、上、左的顺序将当前位置下一个可以探索的位置入栈;
如果 当前位置的四周均不通
则 当前位置出栈;
}
}
class Cell {
private int x; // 单元所在行
private int y; // 单元所在列
private char c; // 字符,通道对应'0',墙对应'1'
private boolean isVisited;// 是否访问过
public Cell(int x, int y, char c, boolean isVisited) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.c = c;
this.isVisited = isVisited;
}
public char getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
public boolean isVisited() {
return isVisited;
}
public void setVisited(boolean isVisited) {
this.isVisited = isVisited;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Cell other = (Cell) obj;
if (x != other.x)
return false;
if (y != other.y)
return false;
return true;
}
public String toString() {
return this.getC() + "("+this.getX()+", "+this.getY() + ")";
}
}
public class Maze {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char maze[][] = { { '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '1', '1', '1', '0', '0', '1', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '1', '1', '0', '0', '1', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '1', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '0', '0', '1', '1', '0', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '1', '1', '1', '0', '0', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '0', '0', '0', '1', '0', '1', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '0', '1', '1', '0', '0', '0', '1', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '1', '0', '0', '0', '0', '1', '0', '0', '1' },
{ '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1' }, };
mazeExit(maze, 8, 8, 1, 7);
}
public static void mazeExit(char maze[][], int in_x, int in_y, int out_x, int out_y) {
Cell[][] cells = createMaze(maze);
printMaze(cells);
Cell start = cells[in_x][in_y];
Cell end = cells[out_x][out_y];
ArrayStack<Cell> stack = new ArrayStack<>();
stack.push(start);
start.setVisited(true);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Cell now = stack.peek();
if (now.equals(end)) {
// 找到路径
int x = out_x;
int y = out_y;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Cell cell = stack.pop();
// 要注意的是,只有和上一次的cell相邻的cell才是路径上的通道
if(Math.abs(cell.getX()-x) + Math.abs(cell.getY()- y) <= 1){
cell.setC('*');
}
x = cell.getX();
y = cell.getY();
}
System.out.println("找到路径:");
printMaze(cells);
return;
} else {
// 向四个方向探索
boolean isDead = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Cell next_cell = getCell(cells, now, i);
if (isValid(next_cell)) {
next_cell.setVisited(true);
stack.push(next_cell);
isDead = false;
}
}
// 四个方向都不能走,则该点为死胡同,出栈
if(isDead){
stack.pop();
}
}
}
System.out.println("找不到路径");
}
/**
* 判断一个cell是否是通道
*/
public static boolean isValid(Cell cell) {
return cell.getC() == '0' && !cell.isVisited();
}
/**
* 根据方向得到下一个cell
*/
public static Cell getCell(Cell[][] cells, Cell now, int direction) {
int x = now.getX();
int y = now.getY();
Cell cell = null;
switch (direction) {
case 0:
// 向下
cell = cells[x + 1][y];
break;
case 1:
// 向右
cell = cells[x][y + 1];
break;
case 2:
// 向上
cell = cells[x - 1][y];
break;
case 3:
// 向左
cell = cells[x][y - 1];
break;
}
return cell;
}
private static Cell[][] createMaze(char[][] maze) {
Cell[][] cells = new Cell[maze.length][maze[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < maze.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < maze[i].length; j++) {
char c = maze[i][j];
Cell cell = new Cell(i, j, c, false);
cells[i][j] = cell;
}
}
return cells;
}
private static void printMaze(Cell[][] cells) {
for (int i = 0; i < cells.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cells[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(cells[i][j].getC() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
所谓当前位置可通,指的是未曾走到过的通道块,即要求该位置不但是通道块,而且不在当前路径上(否则所求的路径就是简单路径),也不是曾经纳入过路径的通道块(否则只能在死胡同内转悠)。
注意:因为迷宫四周有墙,因此从当前位置向四周探索时,数组下标不会越界;如果迷宫四周没有墙,则在向四周探索时,要验证位置的下标是否越界。
4.括号匹配检验
假设表达式中包含三种括号:圆括号、方括号和花括号,并且它们可以任意嵌套。例如{()[{}]}或[{()}([])]等为正确格式,而{[}()]或[({)]为不正确的格式。
算法需要一个栈,在读入字符的过程中,如果是左括号,则直接入栈,等待相匹配的同类右括号;如果是右括号,且与当前栈顶左括号匹配,则将栈顶左括号出栈,如果不匹配则属于不合法的情况。另外,如果碰到一个右括号,而堆栈为空,说明没有左括号与之匹配,则非法。
那么,当字符读完的时候,如果是表达式合法,栈应该是空的,如果栈非空,那么则说明存在左括号没有相应的右括号与之匹配,也是非法的情况。
public class Match {
public static boolean match(String s){
ArrayStack<Character> stack = new ArrayStack<>();
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
switch (c) {
case ')':
if(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.pop() == '('){
break;
}else{
return false;
}
case ']':
if(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.pop() == '['){
break;
}else{
return false;
}
case '}':
if(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.pop() == '{'){
break;
}else{
return false;
}
default:
stack.push(c);
break;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(match("{[()]()[{}]}"));
System.out.println(match("{[()]}}"));
}
}
1.3 队列
1.画一个队列的图形,介绍如下内容。
2.顺序队列的结构、操作函数
队列是一种先进先出的线性表,是一种常用的数据结构。
它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作
队空条件:q->frontq->rear;
队满条件:q->rearMaxSize-1;
进队:q->rear++;q->data[q->rear]=e;
出队:q->front++;e=q->data[q->front]
//(1)初始化队列
void InitQueue(SqQueue *&q)
{
q=(SqQueue*)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue));
q->front=q->rear=-1;
}
//(2)进队列
bool enQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType e)
{
if(q->rear==MaxSize-1)
return false;
q->rear++;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
//(3)出队列
bool deQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType &e)
{
if(q->front==q->rear)
return false;
q->front++;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
3.环形队列的结构、操作函数
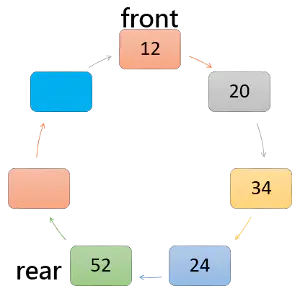
(1)队头指针front循环增1:q->front=(q->front+1)%MaxSize
(2)队尾指针rear循环增1:rear=(rear+1)%MaxSize
//(1)初始化队列
void InitQueue(SqQueue *&q)
{
q=(SqQueue*)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue));
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
//(2)进队
int EnQueue(Cseque &q,Elemtype x)/* 进队操作, 返回1:队满 */
{
if((q.rear+1)%MAXN==q.front)
{
cout << "队满" << endl; return 0;
}
else
{
q.rear = (q.rear + 1) % MAXN;
q.data[q.rear] = x;
return 1;
}
}
//(3)出队
int DeQueue(Cseque &q, Elemtype *x)/* 出队操作 返回1:队空 */
{
if(q.front==q.rear)
{
cout << "队空" << endl; return 0;
}
else
{
q.front = (q.front + 1) % MAXN;
*x = q.data[q.front ];
return 1;
}
}
//(4)输出元素
void OutputQueue(Cseque &q) /* 输出队列中元素 */
{
if (q.front==q.rear) cout << "队空" << endl;
int i = q.front + 1;
while (i<=q.rear)
{
cout << q.data[i] << " ";
i++;
}
cout << endl;
}
4.链队列的结构、操作函数
队空:q->rear==NULL
队满:不考虑
元素e进队:新建结点存放e(由p指向它),将结点p插入作为尾结点
出队:取出队首结点的data值并将其删除
//(1)进队
void EnQueue(LQueue *q,Elemtype x) /* 进队操作 */
{
QNode *p;
p =(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
p->data = x; p->next = NULL;
q->rear->next = p;
q->rear = p;
}
//(2)判断队列是否为空
int EmptyQue(LQueue *q)//队列是否为空
{
if (q->front == q->rear) return 0;
else return 1;
}
//(3)出队
int DeQueue(LQueue *q, Elemtype *x) /* 出队操作 1:对空 */
{
QNode *p;
if(!EmptyQue(q))
{
cout << "队空" << endl; return 0;
}
else
{
p = q->front->next;
q->front->next = p->next;
*x = p->data; free(p);
if (q->front->next == NULL)
q->rear = q->front; //队中只有一个元素的情况下,出队后修改队尾指针
return 1;
}
}
//(4)输出队列元素
void OutputQueue(LQueue *q) /* 输出队列中元素 */
{
QNode *p;
p = q->front->next;
if (!EmptyQue(q)) cout << "队空";
while (p)
{
cout << p->data<< " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
//(5)取队尾元素
void GetBack(LQueue *q)//获取尾元素
{
cout <<"队尾元素为:"<< q->rear->data;
cout << endl;
}
//(6)取队头元素
void GetHead(LQueue *q)//获取头元素
{
cout << "队头元素为:" << q->front->next->data;
cout << endl;
}
5.队列应用,要有具体代码操作。
1.双指针维护
例:给你n个正整数,问至少连续选多少个数,才能使它们的和不小于S?
n<=2000000
看到很直观的做法,前缀和维护加暴力寻找区间 O(n^2)
再想想,答案具有连续性。那就二分,转成判定性问题。O(nlogn) 还是超时
这明显是要一个O(n)的做法
假设已找到一段区间,刚好满足题目条件。我们先用他更新答案,后将左端点缩进一位,右端点继续暴力拓展
因为如果该区间满足题目要求,那右端点无论再怎么继续拓展,虽然满足条件,但都不可能成为最优
int s=1,t=0,sum=0,ans=0x3f3f3f3f;
while(1)
{
while(sum<s&&t<n){t++;sum+=a[t];
}
if(sum>=s)
ans=min(ans,t-s+1);
while(sum>=s&&s<=t){sum-=a[s];s++;
{
if(t==n)
break;
}
2.单调队列
单调队列,顾名思义,要维护一条具有单调性的队列
例:维护以下操作:
(1)将一个数x压入队列中
(2)求队列中数的最大值
(3)弹出队列位的数
(4)求队列中的最大前缀和
操作次数Q<=100000
用单调队列维护最大值和最大前缀和就好了
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=100000+5;
int q1[N],q2[N],q3[N];
int w1[N],w2[N],w3[N];
int main()
{
int Q;
cin>>Q;
int t1=0,t2=0,t3=0;
int s1=1,s2=1,s3=1;
int q=0;
while(Q--)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x;
if(x==1)
{
cin>>y;
q1[++t1]=y;w1[t1]=Q;
while(y>=q2[t2]&&s2<=t2)t2--;
q2[++t2]=y;w2[t2]=Q;
if(s3<=t3)y=q3[t3]+y;
while(y>q3[t3]&&s3<=t3)t3--;
q3[++t3]=y;
w3[t3]=Q;
}
if(x==2)if(s2<=t2)cout<<q2[s2]<<endl;else cout<<0<<endl;
if(x==3)
{
if(w1[s1]==w2[s2])s2++;
if(w1[s1]==w3[s3])s3++;
q+=q1[s1];
s1++;
if(s1>t1) q=0;
}
if(x==4)
if(s3<=t3) cout<<q3[s3]-q<<endl;
else cout<<0<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.PTA实验作业(4分)
此处请放置下面2题代码所在码云地址(markdown插入代码所在的链接)。如何上传VS代码到码云
2.1 符号配对
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stack>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
stack <char> q;
int main()
{
char s[100];
scanf("%s", s);
int len = strlen(s);
int i;
char t;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (s[i] != '{' && s[i] != '[' && s[i] != '(' && s[i] != '}' && s[i] != ']' && s[i] != ')')
continue;
if (s[i] == '{' || s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '(')
q.push(s[i]);
else if (s[i] == ']' || s[i] == ')' || s[i] == '}')
{
if (q.empty())
break;
else
{
if ((s[i] == ']' && q.top() == '[') || (s[i] == ')' && q.top() == '(') || (s[i] == '}' && q.top() == '{'))
q.pop();
}
}
}
if (q.empty()&&i==len)
cout << "yes";
else if (q.empty())
cout << "no";
else
{
cout << q.top() << "
";
cout << "no";
}
}
2.1.1 解题思路及伪代码
1.解题思路
先定义字符型数组s 输入s,
for循环i=0 to i<len
如果不是符号 跳过以下语句
如果为左符号 进栈
如果为右符号
栈空 退出程序(因为右符号没有左符号和它配对 表达式已经配对错误了)
为右符号且配对 出栈
结束for循环
接下来判断是否配对成功
栈空且i=len 配对成功
i不等于len 配对失败,输出no以及栈顶(栈为空不输出)
2.伪代码
int main()
{
scanf;//输入字符串s
for i = 0 to len
if s[i]不等于{}、[]、()
then continue
if s[i]等于{ [(
then q.push(s[i])//出栈
else if s[i]等于 }] )
then
if q.empty()
then break;
else
if (s[i]等于]且q.top()等于[或s[i]等于)且q.top()等于(或s[i]等于}且q.top()等于 {)
then q.pop();
end
if(q.empty()且i等于len)
then 输出yes
else if q.empty()
then 输出no
else
输出q.top,no
}
2.1.2 总结解题所用的知识点
1.一开始提交有两个测试点无法通过,发现忘了最重要的在出栈时没判断栈是否为空,导致程序崩溃
2.有时候如果只有右符号,栈一直是空的,但是很明显是配对错误的,所以引入一个len,当i<len时,即使栈中为空也是配对错误。
3.在遇到右符号时候,得先判断栈是否为空,栈空则错误则返回
4.在写程序的时候不要想得非常具体,而是要基于这两种结构想他们的特点,这些特点能解决什么问题,解决问题的过程具体要怎么样,在脑子中构建出这整个过程。
5.栈跟队列一样,也是一种特殊的线性表,其特殊的地方也是在存取这方面。队列的特性是先进先出,栈则是后进先出,像叠盘子一样。在C++中,有类stack类封装了对栈的实现。
2.2 银行业务队列简单模拟
#include<bits/stdc++.h>///基于顺序表的队列
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1010;
typedef struct
{
int *base;
int front;
int rear;
} sqQueue;
bool initsqQueue(sqQueue &q)
{
q.base = new int[maxn];
if(!q.base) return false;
q.front = q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
bool Push(sqQueue &s, int e)
{
if((s.rear + 1)%maxn == s.front) return false;
s.base[s.rear++] = e;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n, x;
sqQueue A, B;
initsqQueue(A);
initsqQueue(B);
scanf("%d", &n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
if(x%2 == 0) Push(B, x);
else Push(A, x);
}
int i=0;
while( A.rear != A.front || B.rear != B.front )
{
int sizes = 2;
while(sizes--)
{
if(A.rear != A.front)
{
if(i) printf(" ");
printf("%d", A.base[A.front]);
A.front++;
i++;
}
}
if(B.rear != B.front)
{
if(i) printf(" ");
printf("%d", B.base[B.front]);
B.front++;
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
2.2.1 解题思路及伪代码
1.解题思路
这道题单从题目就可以得知可以通过构造队列求解;除此之外还可以知道它所涉及的队列运用的都是基础的知识就可以解决的。利用队列的先进先出原则,这道题可以很容易求解,不过需要注意的是来的顾客需要考虑特殊情况:
最基本的情况就是既有偶数,也有奇数,偶数顾客一次输出两个,奇数顾客一次输出一个,如果它们输出的次数长短不一样,就直接将多余的全部输出即可;
比较特殊的情况就是只有奇数顾客或者只有偶数顾客,当然这在编程的时候必须分为两种情况来讨论。不管是一般情况还是特殊情况,我们都需要注意它的输出格式,也就是第一个输出前面没有空格,且最后一个输出后面无空格输出。要不然会有一个两分的测试点无法通过(格式错误)。
2.伪代码
bool initsqQueue(sqQueue& q)
{
if !q.base
then return false;//返回错误
q.front = q.rear = 0;
return true;
}
bool Push(sqQueue& s, int e)
{
if (s.rear + 1) % maxn == s.front
then return false;
s.base[s.rear加一] = e;
return true;
}
int main()
{
initsqQueue(A);//创建
initsqQueue(B);
scanf("%d", &n);//输入n
while n--
scanf("%d", &x);//输入x
if x % 2 == 0
then Push(B, x);//入队列
else Push(A, x);
end
while A.rear 不等于 A.front 或 B.rear 不等于 B.front
while sizes--
if A.rear 不等于 A.front
then
if (i)
then printf(" ");//输出
printf("%d", A.base[A.front]);
A.front加一;
i加一;
end
if (B.rear 不等于 B.front)
then
if (i)
then printf(" ");
printf("%d", B.base[B.front]);
B.front加一;
i加一;
end
return 0;
}
2.2.2 总结解题所用的知识点
1.每次输出完k要置为0,否则导致错误,而后面输出的判断条件少了一句,i大于sum的情况,也就是k不等于2情况下。
2.通过构造队列以及利用队列先进先出的的特性来解题
3.本题还运用了循环队列,通过循环队列中的front和rear进行循环依次输出
3.阅读代码(0--1分)
找1份优秀代码,理解代码功能,并讲出你所选代码优点及可以学习地方。
3.1 题目及解题代码
可截图,或复制代码,需要用代码符号渲染。
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int ans = 0;
stack<int> stk;
int n = height.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while (!stk.empty() && height[i] > height[stk.top()]) {
int top = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (stk.empty()) {
break;
}
int left = stk.top();
int currWidth = i - left - 1;
int currHeight = min(height[left], height[i]) - height[top];
ans += currWidth * currHeight;
}
stk.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
/*作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/jie-yu-shui-by-leetcode-solution-tuvc/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
*/
3.2 该题的设计思路及伪代码
1.设计思路
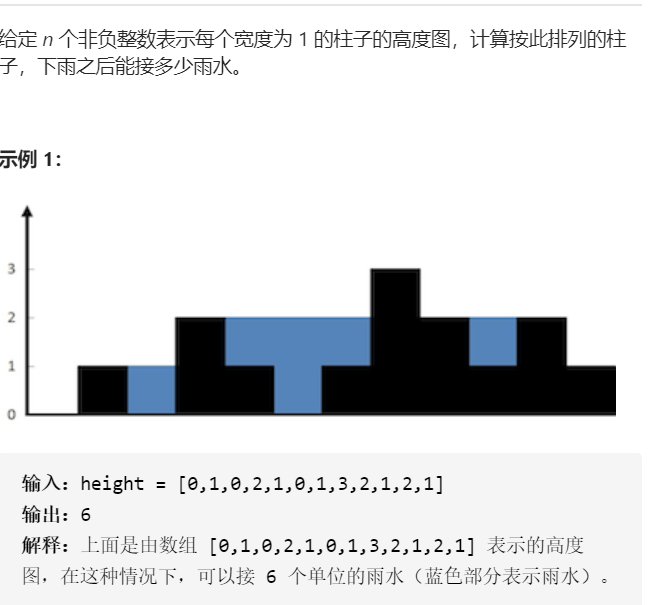
维护一个单调栈,单调栈存储的是下标,满足从栈底到栈顶的下标对应的数组 height 中的元素递减。
从左到右遍历数组,遍历到下标 ii 时,如果栈内至少有两个元素,记栈顶元素为 top,top 的下面一个元素是 left,则一定有height[left]≥height[top]。如果 height[i]>height[top],则得到一个可以接雨水的区域,该区域的宽度是i−left−1,高度是min(height[left],height[i])−height[top],根据宽度和高度即可计算得到该区域能接的雨水量。
为了得到left,需要将top 出栈。在对 top 计算能接的雨水量之后,left 变成新的 top,重复上述操作,直到栈变为空,或者栈顶下标对应的 height 中的元素大于或等于 height[i]。
在对下标 ii 处计算能接的雨水量之后,将 ii 入栈,继续遍历后面的下标,计算能接的雨水量。遍历结束之后即可得到能接的雨水总量。
下面用一个例子 height=[0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 来帮助读者理解单调栈的做法。
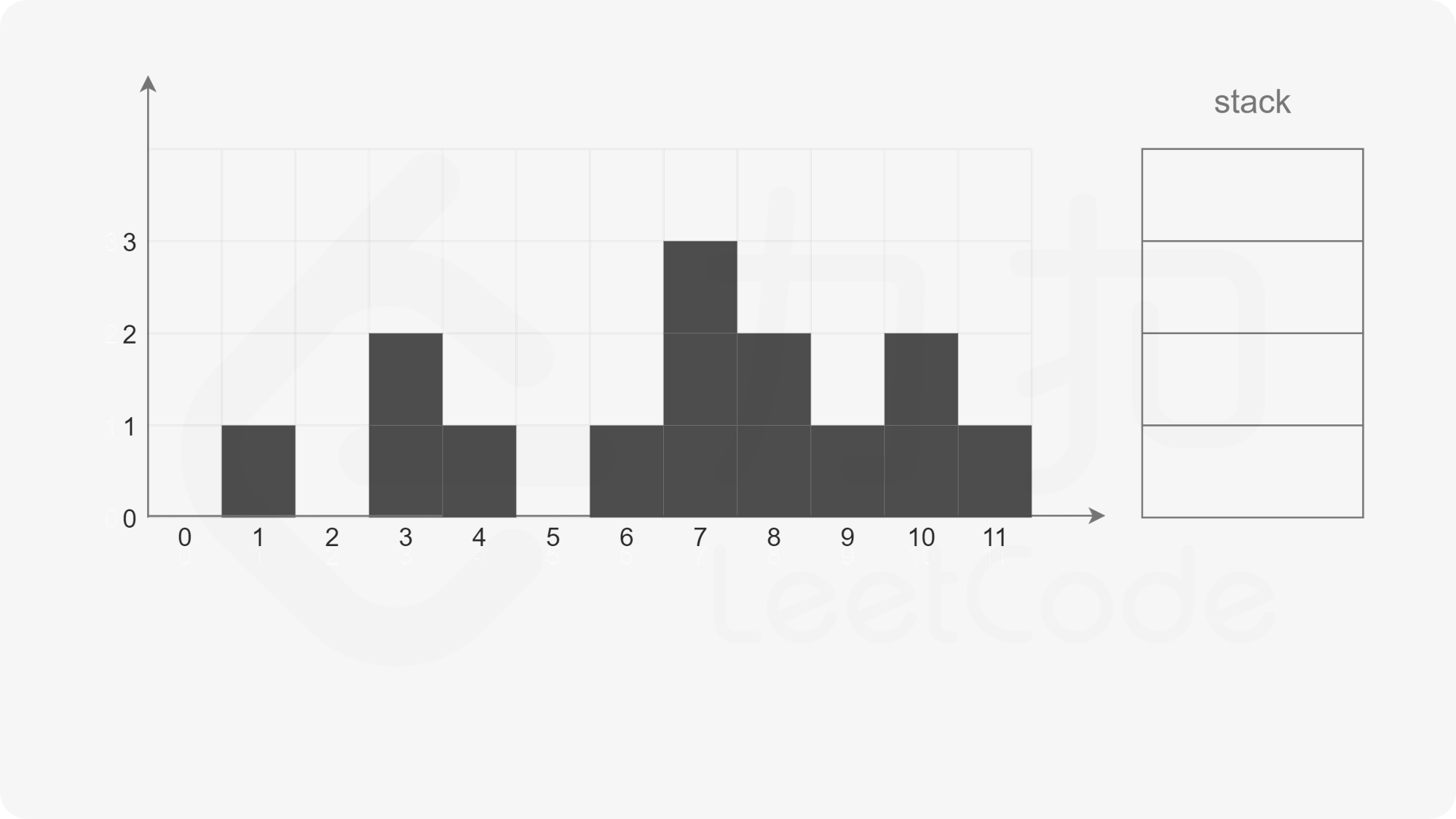
2.复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n是数组height 的长度。从 0 到 n-1 的每个下标最多只会入栈和出栈各一次。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是数组height 的长度。空间复杂度主要取决于栈空间,栈的大小不会超过 n。
3.伪代码
int trap(vector<int>&height)
{
for i=0 to n
while !stk.empty且height[i]大于height[stk.top()]
if stk.empty//栈为空
then break;
ans+=currWidth*currHeight//宽度:currWidth = i - left - 1,高度currHeight = min(height[left], height[i]) - height[top]
//根据宽度高度可的出能接的雨水量
end
stk.push(i);//出栈
end
return ans;
}
3.3 分析该题目解题优势及难点。
1.解题优势
(1)无论是时间复杂度还是空间复杂度都较小,程序效率高
(2)维护一个单调栈,单调栈存储的是下标,满足从栈底到栈顶的下标对应的数组height 中的元素递减
(3)该解法只需要通过遍历数组来求得宽度高度,根据宽度和高度即可直接计算得到该区域能接的雨水量
2.难点
(1)在求left时,需要将 top 出栈。在对top 计算能接的雨水量之后,left 变成新的 top,要重复操作,直到栈变为空
(2)用栈来跟踪可能储水的最长的条形块,通过使用栈达到在一次遍历内完成计算的目的