模型使用
使用caffe训练得到的模型进行测试,一般需要如下文件:
1.训练好的caffemodel模型
此处使用lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel。
2.测试网络deploy
可以对lenet_train_test.prototxt做修改。
主要修改的地方包括输入数据,最后的top,权值初始化,第一个卷积层名称不能和训练网络conv1同名。
也可以直接用下面代码生成,对应lenet.
# coding: utf8 from caffe import layers as L,params as P,to_proto root='C:/Users/jj/Documents/caffe-windows/' deploy=root+'examples/mnist/deploy.prototxt' #文件保存路径 def create_deploy(): #少了第一层,data层 conv1=L.Convolution(bottom='data', kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=20, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier')) pool1=L.Pooling(conv1, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2) conv2=L.Convolution(pool1, kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=50, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier')) pool2=L.Pooling(conv2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2) ip1=L.InnerProduct(pool2, num_output=500,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier')) relu1=L.ReLU(ip1, in_place=True) ip2 = L.InnerProduct(relu1, num_output=10,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier')) #最后没有accuracy层,但有一个Softmax层 prob=L.Softmax(ip2) return to_proto(prob) def write_deploy(): with open(deploy, 'w') as f: f.write('name:"Lenet" ') f.write('input:"data" ') f.write('input_dim:1 ') f.write('input_dim:3 ') f.write('input_dim:28 ') f.write('input_dim:28 ') f.write(str(create_deploy())) if __name__ == '__main__': write_deploy()
3.均值文件
Caffe的C++接口用到的均值文件为binaryproto类型,python接口均值文件为npy类型。
使用python需要将compute_image_mean.exe生成的mean.binaryproto转换成mean.npy。
SET GLOG_logtostderr=1 Buildx64Releasecompute_image_mean.exe examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb examples/mnist/number.binaryproto pause
# coding: utf8 import numpy as np import caffe caffe_root = 'C:/Users/jj/Documents/caffe-windows/' # 路径 MEAN_PROTO_PATH = (caffe_root+'examples/mnist/number.binaryproto' ) # 待转换的pb格式图像均值文件路径 MEAN_NPY_PATH = (caffe_root+'examples/mnist/number_mean.npy') # 转换后的numpy格式图像均值文件路径 blob = caffe.proto.caffe_pb2.BlobProto() # 创建protobuf blob data = open(MEAN_PROTO_PATH, 'rb' ).read() # 读入mean.binaryproto文件内容 blob.ParseFromString(data) # 解析文件内容到blob array = np.array(caffe.io.blobproto_to_array(blob))# 将blob中的均值转换成numpy格式,array的shape (mean_number,channel, hight, width) mean_npy = array[0] # 一个array中可以有多组均值存在,故需要通过下标选择其中一组均值 np.save(MEAN_NPY_PATH ,mean_npy)
由于训练中实际并没有用到均值文件,可以直接生成全为0的或者不用。
import numpy as np n=np.zeros((28,28,1),dtype=np.float32) np.save('number.npy',n)
4.测试图片
随便截的一张图。
也可以用数据生成(28*28),对尺寸没有要求。
import numpy as np from PIL import Image import cPickle f=open('mnist.pkl','rb') a,b,c=cPickle.load(f) r=a[0][10] g=np.reshape(r,(28,28)) g=g*255 g=np.array(g) x=Image.fromarray(g) if x.mode != 'RGB': x = x.convert('RGB') x.save('n.jpg')
特征提取
教程来自http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/examples/00-classification.ipynb
根据网页中的教程,略作修改。
下面代码分两部分,分类无误可以再进行特征提取。
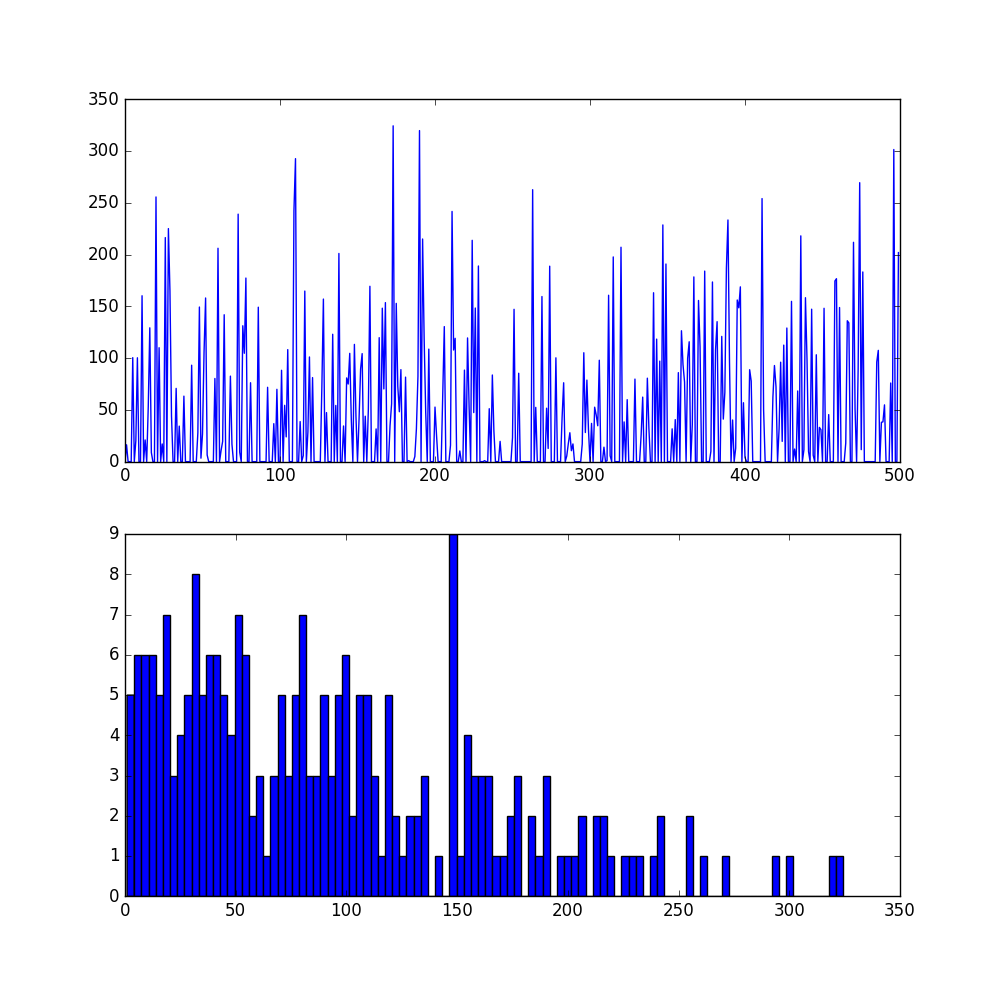
# set up Python environment: numpy for numerical routines, and matplotlib for plotting import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt GPU=1 # display plots in this notebook # set display defaults plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 10) # large images plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' # don't interpolate: show square pixels plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' # use grayscale output rather than a (potentially misleading) color heatmap # The caffe module needs to be on the Python path; # we'll add it here explicitly. import sys caffe_root = 'C:/Users/jj/Documents/caffe-windows/' # this file should be run from {caffe_root}/examples (otherwise change this line) # sys.path.insert(0, caffe_root + 'python') # no need for win. import caffe # If you get "No module named _caffe", either you have not built pycaffe or you have the wrong path. import os if os.path.isfile(caffe_root + 'models/bvlc_reference_caffenet/bvlc_reference_caffenet.caffemodel'): print 'CaffeNet found.' else: print 'Downloading pre-trained CaffeNet model...' #../scripts/download_model_binary.py ../models/bvlc_reference_caffenet if GPU: caffe.set_device(0) # if we have multiple GPUs, pick the first one caffe.set_mode_gpu() else: caffe.set_mode_cpu() model_def = caffe_root + 'examples/mnist/deploy.prototxt' # deploy.prototxt' lenet_train_test_d2.prototxt model_weights = caffe_root + 'examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel' net = caffe.Net(model_def, # defines the structure of the model model_weights, # contains the trained weights caffe.TEST) # use test mode (e.g., don't perform dropout) # load the mean ImageNet image (as distributed with Caffe) for subtraction #mu = np.load(caffe_root + 'examples/mnist/m.npy') #mu = mu.mean(1).mean(1) # average over pixels to obtain the mean (BGR) pixel values # print 'mean-subtracted values:', zip('BGR', mu) # create transformer for the input called 'data' transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape}) transformer.set_transpose('data', (2,0,1)) # move image channels to outermost dimension #transformer.set_mean('data', mu) # subtract the dataset-mean value in each channel transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255) # rescale from [0, 1] to [0, 255] #transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2,1,0)) # swap channels from RGB to BGR # set the size of the input (we can skip this if we're happy # with the default; we can also change it later, e.g., for different batch sizes) # net.blobs['data'].reshape(50, # batch size # 1, # 3-channel (BGR) images # 227, 227) # image size is 227x227 image = caffe.io.load_image(caffe_root + 'examples/images/8.jpg',color=False) transformed_image = transformer.preprocess('data', image) plt.imshow(image[:,:,0]) # 28,28,1 to 28,28 [,'gray'] already set plt.show() # copy the image data into the memory allocated for the net net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image ### perform classification output = net.forward() output_prob = output['Softmax1'][0] # the output probability vector for the first image in the batch print 'predicted class is:', output_prob.argmax() if 1 : # load ImageNet labels labels_file = caffe_root + 'data/mnist/mnist_words.txt' if not os.path.exists(labels_file): print 0 # !../ data / ilsvrc12 / get_ilsvrc_aux.sh labels = np.loadtxt(labels_file, str, delimiter=' ') print 'output label:', labels[output_prob.argmax()] # sort top five predictions from softmax output top_inds = output_prob.argsort()[::-1][:5] # reverse sort and take five largest items print 'probabilities and labels:', zip(output_prob[top_inds], labels[top_inds]) # for each layer, show the output shape for layer_name, blob in net.blobs.iteritems(): print layer_name + ' ' + str(blob.data.shape) for layer_name, param in net.params.iteritems(): print layer_name + ' ' + str(param[0].data.shape), str(param[1].data.shape) def vis_square(data): """Take an array of shape (n, height, width) or (n, height, width, 3) and visualize each (height, width) thing in a grid of size approx. sqrt(n) by sqrt(n)""" # normalize data for display data = (data - data.min()) / (data.max() - data.min()) # force the number of filters to be square n = int(np.ceil(np.sqrt(data.shape[0]))) padding = (((0, n ** 2 - data.shape[0]), (0, 1), (0, 1)) # add some space between filters + ((0, 0),) * (data.ndim - 3)) # don't pad the last dimension (if there is one) data = np.pad(data, padding, mode='constant', constant_values=1) # pad with ones (white) # tile the filters into an image data = data.reshape((n, n) + data.shape[1:]).transpose((0, 2, 1, 3) + tuple(range(4, data.ndim + 1))) data = data.reshape((n * data.shape[1], n * data.shape[3]) + data.shape[4:]) if len(data.shape)==3: plt.imshow(data[:,:,0]) else: plt.imshow(data) plt.axis('off') plt.show() # the parameters are a list of [weights, biases] filters = net.params['Convolution1'][0].data vis_square(filters.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)) feat = net.blobs['Convolution1'].data[0, :36] vis_square(feat) feat = net.blobs['Pooling1'].data[0] vis_square(feat) feat = net.blobs['InnerProduct1'].data[0] plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot(feat.flat) plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) _ = plt.hist(feat.flat[feat.flat > 0], bins=100) feat = net.blobs['Softmax1'].data[0] plt.figure(figsize=(15, 3)) plt.plot(feat.flat) plt.show()