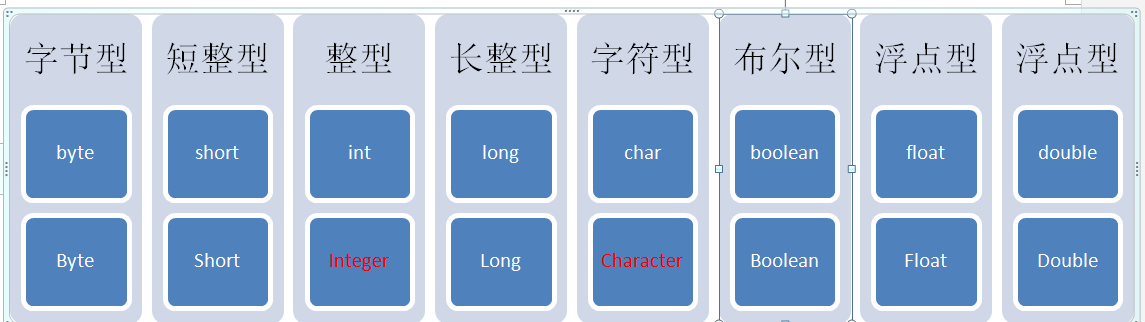
1.基本类型包装类概述:
实现字符串与基本数据之间转换,Java中提供了相应的对象来解决该问题,基本数据类型对象包装类。
1.字符串转成基本类型:
parseXXX(String s);其中XXX表示基本类型,参数为可以转成基本类型的字符串,如果字符串无法转成基本类型,将会发生数字转换的问题 NumberFormatException。
2.基本类型转串:
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //字符串转基本数据类型 String s1="123"; int i1=Integer.parseInt(s1); System.out.println(i1); //基本数据类型转串 //1.加"" String s2=123+""; //2.valueof,String类方法,直接调用 String s3=String.valueOf(i1); //3. toString,包装类方法,直接调用 String s4=Integer.toString(1); } }
2.基本类型和对象转换
l 自动拆箱:对象自动直接转成基本数值
l 自动装箱:基本数值自动直接转成对象
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1,转成包装类型,通过构造方法 Integer i1=new Integer(123); Integer i2=new Integer("123"); //2,通过Integer 普通方法 Integer i3=Integer.valueOf(123); Integer i4=Integer.valueOf("123"); //包装类——>基本类型 int ii=i1.intValue(); } }
public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { //JDK1.5以后的新特性 //自动装箱,基本数据类型——>包装类 //自动拆箱,包装类——>基本数据类型 //Integer i=new Integer(123); Integer i=123; } }
当数值在byte范围之内时,进行自动装箱,不会新创建对象空间而是使用已有的空间。
public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer s1=new Integer(5); Integer s2=new Integer(5); System.out.println(s1==s2);//false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true //在byte范围内,不会新创建对象空间,而是将byte常量池的地址赋值给对象 Integer s3=127; Integer s4=127; System.out.println(s3==s4);//true System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true } }
3 System类概念
ystem中代表程序所在系统,提供了对应的一些系统属性信息,和系统操作。
System类不能手动创建对象,因为构造方法被private修饰,阻止外界创建对象。System类中的都是static方法,类名访问即可。
1.类方法
l currentTimeMillis() 获取当前系统时间与1970年01月01日00:00点之间的毫秒差值
l exit(int status) 用来结束正在运行的Java程序。参数传入一个数字即可。通常传入0记为正常状态,其他为异常状态
l gc() 用来运行JVM中的垃圾回收器,完成内存中垃圾的清除。
l getProperty(String key) 用来获取指定键(字符串名称)中所记录的系统属性信息
l arraycopy方法,用来实现将源数组部分元素复制到目标数组的指定位置
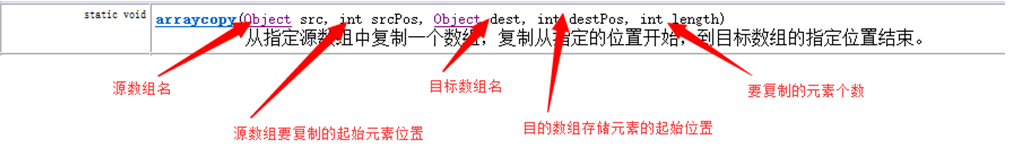
public class Demo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取指定键(字符串名称)中所记录的系统属性信息 System.out.println(System.getProperties()); } }
public class Demo09 { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] arr={"a","b","c","d"}; String[] arr2={"e","f","g"}; System.arraycopy(arr, 2, arr2, 1, 2); for(int i=0;i<arr2.length;i++){ System.out.println(arr2[i]); } } }