之前梳理过依赖注入和控制反转,总结来说,控制反转是一种思想,依赖注入是一种设计模式,控制反转的思想可以利用依赖注入的设计模式实现,反射是依赖注入实现过程的核心技术。这里不在详述依赖注入、控制反转和反射。本文的重心是梳理依赖注入设计模式在ASP.NET Core的应用。
一、ASP.NET Core依赖注入的原理
ASP.NET Core 支持依赖关系注入 (DI) 软件设计模式,这是一种在类及其依赖关系之间实现控制反转 (IoC) 的技术。上文中也提到利用DI要做的两个功能是:
- 注册服务
- 注入服务
那么在ASP.NET Core中是如何实现这两个功能的呢?
1、注册服务的实现
就从startup.cs中的ConfigureServices方法说起,先来看下定义:
public virtual void ConfigureServices (Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.IServiceCollection services);
这里涉及到一个概念IServiceCollection,先来看下IServiceCollection的命名空间和定义:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection { /// <summary> /// Specifies the contract for a collection of service descriptors. /// </summary> public interface IServiceCollection : IList<ServiceDescriptor> { } }
发现又涉及到一个概念ServiceDescriptor,这里不对ServiceDescriptor展开,总结来说,ServiceDescriptor对象用来描述一种服务,包括该服务的类型、实现和生存期。所以说IServiceCollection是为ServiceDescriptor集合指定协定,即IServiceCollection用来管理ServiceDescriptor集合。先来看下IServiceCollection的实现ServiceCollection:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection { /// <summary> /// Default implementation of <see cref="IServiceCollection"/>. /// </summary> public class ServiceCollection : IServiceCollection { private readonly List<ServiceDescriptor> _descriptors = new List<ServiceDescriptor>(); /// <inheritdoc /> public int Count => _descriptors.Count; /// <inheritdoc /> public bool IsReadOnly => false; /// <inheritdoc /> public ServiceDescriptor this[int index] { get { return _descriptors[index]; } set { _descriptors[index] = value; } } /// <inheritdoc /> public void Clear() { _descriptors.Clear(); } /// <inheritdoc /> public bool Contains(ServiceDescriptor item) { return _descriptors.Contains(item); } /// <inheritdoc /> public void CopyTo(ServiceDescriptor[] array, int arrayIndex) { _descriptors.CopyTo(array, arrayIndex); } /// <inheritdoc /> public bool Remove(ServiceDescriptor item) { return _descriptors.Remove(item); }
void ICollection<ServiceDescriptor>.Add(ServiceDescriptor item) { _descriptors.Add(item); } /// <inheritdoc /> public int IndexOf(ServiceDescriptor item) { return _descriptors.IndexOf(item); } /// <inheritdoc /> public void Insert(int index, ServiceDescriptor item) { _descriptors.Insert(index, item); } /// <inheritdoc /> public void RemoveAt(int index) { _descriptors.RemoveAt(index); } } }
接下来解析下ServiceCollection代码,代码中定义了ServiceDescriptor的集合_descriptors :
private readonly List<ServiceDescriptor> _descriptors = new List<ServiceDescriptor>();
然后就是对ServiceDescriptor集合进行增删改查相关的操作,因此我们可以认为ServiceDescriptor对象就是一个服务,ServiceDescriptor集合就是服务容器,IServiceCollection的实现类ServiceCollection提供了对服务容器进行注册、移除等相关的管理。这里就算是完成了依赖注入需要完成的功能1:注册服务。
2、注入服务的实现
上边介绍了ASP.NET Core利用IServiceCollection和ServiceDescriptor完成了服务的注册,那么服务的注入如何实现呢?如何在需要的地方能够注入相应的服务呢?
IServiceCollection的实现类ServiceCollection提供了注册服务的相关方法,那么有没有提供服务注入的方法呢?先来看下ServiceCollection的扩展方法:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection { /// <summary> /// Extension methods for building a <see cref="ServiceProvider"/> from an <see cref="IServiceCollection"/>. /// </summary> public static class ServiceCollectionContainerBuilderExtensions { /// <summary> /// Creates a <see cref="ServiceProvider"/> containing services from the provided <see cref="IServiceCollection"/>. /// </summary> /// <param name="services">The <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> containing service descriptors.</param> /// <returns>The <see cref="ServiceProvider"/>.</returns> public static ServiceProvider BuildServiceProvider(this IServiceCollection services) { return BuildServiceProvider(services, ServiceProviderOptions.Default); } /// <summary> /// Creates a <see cref="ServiceProvider"/> containing services from the provided <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> /// optionally enabling scope validation. /// </summary> /// <param name="services">The <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> containing service descriptors.</param> /// <param name="validateScopes"> /// <c>true</c> to perform check verifying that scoped services never gets resolved from root provider; otherwise <c>false</c>. /// </param> /// <returns>The <see cref="ServiceProvider"/>.</returns> public static ServiceProvider BuildServiceProvider(this IServiceCollection services, bool validateScopes) { return services.BuildServiceProvider(new ServiceProviderOptions { ValidateScopes = validateScopes }); } /// <summary> /// Creates a <see cref="ServiceProvider"/> containing services from the provided <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> /// optionally enabling scope validation. /// </summary> /// <param name="services">The <see cref="IServiceCollection"/> containing service descriptors.</param> /// <param name="options"> /// Configures various service provider behaviors. /// </param> /// <returns>The <see cref="ServiceProvider"/>.</returns> public static ServiceProvider BuildServiceProvider(this IServiceCollection services, ServiceProviderOptions options) { if (services == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(services)); } if (options == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(options)); } return new ServiceProvider(services, options); } } }
ServiceCollection扩展方法提供了构建IServiceProvider的方法,先来了解下IServiceProvider的定义:
namespace System { public interface IServiceProvider { object GetService(Type serviceType); } }
IServiceProvider提供给了一个根据类型获取对象的功能。
读到这里先来梳理下,算是承上启下吧:上边说道ServiceCollection提供了管理服务集合的方法,即注册服务;ServiceCollection的扩展方法提供了构建IServiceProvider的方法,而IServiceProvider提供给了一个根据类型获取对象的功能。
理论上说Asp.net core利用IServiceCollection、ServiceDescriptor和IServiceProvider实现了注册服务和注入服务的功能。
那么这里有个疑问?IServiceProvider是如何实现注入服务的呢?接下来我们分析下IServiceProvider实现类ServiceProvider 的源码:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection { /// <summary> /// The default IServiceProvider. /// </summary> public sealed class ServiceProvider : IServiceProvider, IDisposable, IServiceProviderEngineCallback, IAsyncDisposable { private readonly IServiceProviderEngine _engine; private readonly CallSiteValidator _callSiteValidator; internal ServiceProvider(IEnumerable<ServiceDescriptor> serviceDescriptors, ServiceProviderOptions options) { IServiceProviderEngineCallback callback = null; if (options.ValidateScopes) { callback = this; _callSiteValidator = new CallSiteValidator(); } switch (options.Mode) { case ServiceProviderMode.Default: #if !NETCOREAPP _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); #else if (RuntimeFeature.IsSupported("IsDynamicCodeCompiled")) { _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); } else { // Don't try to compile Expressions/IL if they are going to get interpreted _engine = new RuntimeServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); } #endif break; case ServiceProviderMode.Dynamic: _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; case ServiceProviderMode.Runtime: _engine = new RuntimeServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; #if IL_EMIT case ServiceProviderMode.ILEmit: _engine = new ILEmitServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; #endif case ServiceProviderMode.Expressions: _engine = new ExpressionsServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; default: throw new NotSupportedException(nameof(options.Mode)); } if (options.ValidateOnBuild) { List<Exception> exceptions = null; foreach (var serviceDescriptor in serviceDescriptors) { try { _engine.ValidateService(serviceDescriptor); } catch (Exception e) { exceptions = exceptions ?? new List<Exception>(); exceptions.Add(e); } } if (exceptions != null) { throw new AggregateException("Some services are not able to be constructed", exceptions.ToArray()); } } } /// <summary> /// Gets the service object of the specified type. /// </summary> /// <param name="serviceType">The type of the service to get.</param> /// <returns>The service that was produced.</returns> public object GetService(Type serviceType) => _engine.GetService(serviceType); /// <inheritdoc /> public void Dispose() { _engine.Dispose(); } void IServiceProviderEngineCallback.OnCreate(ServiceCallSite callSite) { _callSiteValidator.ValidateCallSite(callSite); } void IServiceProviderEngineCallback.OnResolve(Type serviceType, IServiceScope scope) { _callSiteValidator.ValidateResolution(serviceType, scope, _engine.RootScope); } /// <inheritdoc/> public ValueTask DisposeAsync() { return _engine.DisposeAsync(); } } }
从上面代码中我们看到ServiceProvider实现了GetService方法:
public object GetService(Type serviceType) => _engine.GetService(serviceType);
但是里面涉及到一个对象_engine,它是什么呢?我们接着分析_engine初始化的代码:
internal ServiceProvider(IEnumerable<ServiceDescriptor> serviceDescriptors, ServiceProviderOptions options) { IServiceProviderEngineCallback callback = null; if (options.ValidateScopes) { callback = this; _callSiteValidator = new CallSiteValidator(); } switch (options.Mode) { case ServiceProviderMode.Default: #if !NETCOREAPP _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); #else if (RuntimeFeature.IsSupported("IsDynamicCodeCompiled")) { _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); } else { // Don't try to compile Expressions/IL if they are going to get interpreted _engine = new RuntimeServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); } #endif break; case ServiceProviderMode.Dynamic: _engine = new DynamicServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; case ServiceProviderMode.Runtime: _engine = new RuntimeServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; #if IL_EMIT case ServiceProviderMode.ILEmit: _engine = new ILEmitServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; #endif case ServiceProviderMode.Expressions: _engine = new ExpressionsServiceProviderEngine(serviceDescriptors, callback); break; default: throw new NotSupportedException(nameof(options.Mode)); } if (options.ValidateOnBuild) { List<Exception> exceptions = null; foreach (var serviceDescriptor in serviceDescriptors) { try { _engine.ValidateService(serviceDescriptor); } catch (Exception e) { exceptions = exceptions ?? new List<Exception>(); exceptions.Add(e); } } if (exceptions != null) { throw new AggregateException("Some services are not able to be constructed", exceptions.ToArray()); } } }
从上面代码可以看出_engine是一个与ServiceDescriptor关联的IServiceProviderEngine对象。而且根据ServiceProviderMode枚举内容的不同,_engine有不同的初始化方案,下面看下ServiceProviderMode的枚举值:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection { internal enum ServiceProviderMode { Default, Dynamic, Runtime, Expressions, ILEmit } }
这里有个疑问:IServiceProviderEngine是什么?为什么_engine有不同的初始化方案?ServiceProviderMode中的方案都代表着什么?
为了解决上边的疑问,接下来探究下IServiceProviderEngine的定义:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.ServiceLookup { internal interface IServiceProviderEngine : IServiceProvider, IDisposable, IAsyncDisposable { IServiceScope RootScope { get; } void ValidateService(ServiceDescriptor descriptor); } }
好像看不出来什么,接下来看下IServiceProviderEngine的实现类ServiceProviderEngine:
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.ServiceLookup { internal abstract class ServiceProviderEngine : IServiceProviderEngine, IServiceScopeFactory { private readonly IServiceProviderEngineCallback _callback; private readonly Func<Type, Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>> _createServiceAccessor; private bool _disposed; protected ServiceProviderEngine(IEnumerable<ServiceDescriptor> serviceDescriptors, IServiceProviderEngineCallback callback) { _createServiceAccessor = CreateServiceAccessor; _callback = callback; Root = new ServiceProviderEngineScope(this); RuntimeResolver = new CallSiteRuntimeResolver(); CallSiteFactory = new CallSiteFactory(serviceDescriptors); CallSiteFactory.Add(typeof(IServiceProvider), new ServiceProviderCallSite()); CallSiteFactory.Add(typeof(IServiceScopeFactory), new ServiceScopeFactoryCallSite()); RealizedServices = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>>(); } internal ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>> RealizedServices { get; } internal CallSiteFactory CallSiteFactory { get; } protected CallSiteRuntimeResolver RuntimeResolver { get; } public ServiceProviderEngineScope Root { get; } public IServiceScope RootScope => Root; public void ValidateService(ServiceDescriptor descriptor) { if (descriptor.ServiceType.IsGenericType && !descriptor.ServiceType.IsConstructedGenericType) { return; } try { var callSite = CallSiteFactory.GetCallSite(descriptor, new CallSiteChain()); if (callSite != null) { _callback?.OnCreate(callSite); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new InvalidOperationException($"Error while validating the service descriptor '{descriptor}': {e.Message}", e); } } public object GetService(Type serviceType) => GetService(serviceType, Root); protected abstract Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object> RealizeService(ServiceCallSite callSite); public void Dispose() { _disposed = true; Root.Dispose(); } public ValueTask DisposeAsync() { _disposed = true; return Root.DisposeAsync(); } internal object GetService(Type serviceType, ServiceProviderEngineScope serviceProviderEngineScope) { if (_disposed) { ThrowHelper.ThrowObjectDisposedException(); } var realizedService = RealizedServices.GetOrAdd(serviceType, _createServiceAccessor); _callback?.OnResolve(serviceType, serviceProviderEngineScope); DependencyInjectionEventSource.Log.ServiceResolved(serviceType); return realizedService.Invoke(serviceProviderEngineScope); } public IServiceScope CreateScope() { if (_disposed) { ThrowHelper.ThrowObjectDisposedException(); } return new ServiceProviderEngineScope(this); } private Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object> CreateServiceAccessor(Type serviceType) { var callSite = CallSiteFactory.GetCallSite(serviceType, new CallSiteChain()); if (callSite != null) { DependencyInjectionEventSource.Log.CallSiteBuilt(serviceType, callSite); _callback?.OnCreate(callSite); return RealizeService(callSite); } return _ => null; } } }
具体分析下上边的代码:
- ValidateService方法:在_engine初始化的代码中(即ServiceProvider构造函数中)调用过,针对该方法,这里不做展开,知道是用来验证服务是否符合规则的就可以了。
从上述代码中看出,ServiceProviderEngine构造函数中调用了CreateServiceAccessor方法,在CreateServiceAccessor方法中又调用了RealizeService方法,而ServiceProviderEngine中的RealizeService方法是个抽象方法,具体的实现体现了_engine初始化的方案:
- DynamicServiceProviderEngine类:间接继承了ServiceProviderEngine类,重写了RealizeService方法。
- ILEmitServiceProviderEngine类:继承了ServiceProviderEngine类,重写了RealizeService方法。
- ExpressionsServiceProviderEngine类:继承了ServiceProviderEngine类,重写了RealizeService方法。
- RuntimeServiceProviderEngine类:继承了ServiceProviderEngine类,重写了RealizeService方法。
这四个类都重写了RealizeService方法,但是他们的目的都是一样的:编译一个类型为Func <ServiceProvider,object>的委托,并被缓存起来服务于后续针对同一个类型的服务提供请求,该委托对象与对应服务类型之间的映射关系就保存在RealizedServices属性中。简单的说RealizeService方法就是将对注册的服务做一个类型映射关系,然后将该关系保存在RealizedServices字典中,RealizedServices是一个ConcurrentDictionary字典对象。
现在又回归到前面说到的ServiceProvider是如何实现注入服务的:先来看下RealizedServices的定义:
internal ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>> RealizedServices { get; }
RealizedServices = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>>();
用于存储类型与Func<ServiceProviderEngineScope, object>委托的关系,而ServiceProviderEngineScope继承了IServiceProvider,并且ServiceProviderEngineScope类中实现了GetService方法:
public object GetService(Type serviceType) { if (_disposed) { ThrowHelper.ThrowObjectDisposedException(); } return Engine.GetService(serviceType, this); }
而Engine调用ServiceProviderEngine中GetService方法,进而从RealizedServices获取相应的服务。
internal object GetService(Type serviceType, ServiceProviderEngineScope serviceProviderEngineScope) { if (_disposed) { ThrowHelper.ThrowObjectDisposedException(); } var realizedService = RealizedServices.GetOrAdd(serviceType, _createServiceAccessor); _callback?.OnResolve(serviceType, serviceProviderEngineScope); DependencyInjectionEventSource.Log.ServiceResolved(serviceType); return realizedService.Invoke(serviceProviderEngineScope); }
二、ASP.NET Core中注册服务
上边仔细研读了ASP.NET Core的源码,并且分析了依赖注入的实现原理。接下来就是说下在应用层面上应该如何使用。在startup类中,可以在ConfigureServices方法中注册服务:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
1、IServiceCollection中的方法和扩展方法
下面可用于服务的注册,即服务注册的方法:
AddScoped,添加服务,服务实例的生命周期为Scoped。 AddTransient,添加服务,服务实例的生命周期为Transient(每次被使用都创建新对象)。 AddSingleton,添加服务,服务实例的生命周期为单例。 AddMvc,添加所有MVC所需的服务。 AddMvcCore,仅添加核心必要的MVC所需的服务。 AddControllers,添加启用Controller 所需要的服务,不包括View和Pages所需要的服务。 AddControllersWithViews,添加启用 Controller 以及 Razor 页面所需要的服务。 AddRazorPages,添加 Razor Pages 所需要的服务。 AddAntiforgery,添加防止CSRF攻击的服务。 AddAuthentication,添加启用Authentication中间件所需的服务。 AddAuthenticationCore,添加启用Authentication中间件所需的核心服务。 AddAuthorization,添加启用Authorization中间件所需的服务。 AddAuthorizationCore,添加启用Authorization中间件所需的核心服务。 AddAuthorizationPolicyEvaluator,添加 Authorization 策略评估服务。 AddCertificateForwarding,添加CertificateForwarding中间件所需的服务。 AddConnections,添加 http://ASP.NET Core Connection Handlers 所需的服务。 AddCors,添加CORS中间件 所需的服务。 AddDataProtection,添加 http://ASP.NET Core Data Protection 所需的服务。 AddDirectoryBrowser,添加 DirectoryBrowser 中间件所需的服务。 AddDistributedMemoryCache,添加分布式缓冲服务IDistributedCache,默认的实现将缓冲保存在内存中,要实现实际上的分布式缓冲你需要提供一个保存缓存的实现(Redis或数据库,如AddStackExchangeRedisCache和AddDistributedSqlServerCache)。 AddHealthChecks,添加HealthChecks中间件所需的服务。 AddHostedService,添加宿主服务,如持续运行的服务。 AddHostFiltering,添加HostFiltering中间件所需的服务。 AddHsts,添加HSTS中间件所需的服务。 AddHttpClient,添加IHttpClientFactory服务用于获取在服务器端发起Http请求的HttpClient对象。 AddHttpContextAccessor,添加Http上下文访问器服务,在例如Controller里有HttpContext属性的地方优先使用HttpContext,但如果在一个自定义的服务里你就需要IHttpContextAccessor服务来获取Http上下文。 AddHttpsRedirection,为HttpsRedirection中间件添加所需的服务。 AddIdentity,添加默认的身份系统,并制定 Role和User类型。 AddIdentityCore,添加默认身份执行的核心部分,并制定User类型。 AddLocalization,添加本地化服务。 AddLogging,添加日志服务。 AddMemoryCache,添加非分布式的内存缓存服务。 AddOptions,添加 Option 服务。 AddResponseCaching,为ResponseCaching中间件添加所需的服务。 AddResponseCompression,为ResponseCompression中间件添加所需的服务。 AddRouting,添加Routing中间件所需的服务。 AddSignalR,添加SignalR所需的服务。 AddSignalRCore,添加SignalR所需的核心服务。 AddServerSideBlazor,添加 Server-Side Blazor所需的服务。 AddWebEncoders,添加 HtmlEncoder,JavaScriptEncoder,UrlEncoder 三个服务。
2、自定义的IServiceCollection扩展方法
这里不在详述。
三、ASP.NET Core中注入服务
1、构造函数注入
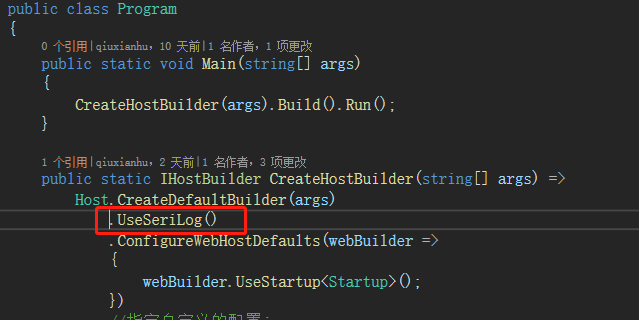
(1)示例一:Serilog日志服务
自定义一个IHostBuilder扩展方法UseSeriLog,并注册该服务,如下图:
在ValuesController中注入该服务:
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { private readonly ILogger _logger; public ValuesController(ILogger logger) { _logger = logger; } // GET api/<ValuesController>/5 [HttpGet("{id}")] public string Get(int id) { _logger.Information("构造函数注入"); return "value"; } } }
看下效果:
(2)示例二:IHostEnvironment
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController1 : ControllerBase { private readonly IHostEnvironment _hostEnvironment; public ValuesController1(IHostEnvironment hostEnvironment) { _hostEnvironment = hostEnvironment; } // GET: api/<ValuesController> [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<string> Get() { var path = _hostEnvironment.ContentRootPath; return new string[] { path }; } } }
看下效果:
2、特性FromServices注入
FromServicesAttribute 允许将服务直接注入到操作方法,而无需使用构造函数注入。
(1)示例一:Serilog日志服务
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { // GET: api/<ValuesController> [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<string> Get([FromServices] ILogger logger) { logger.Information("利用特性FromServices注入服务"); return new string[] { "value1", "value2" }; } } }
查看下效果:
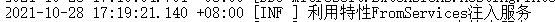
(2)示例二:IHostEnvironment
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController1 : ControllerBase { // GET: api/<ValuesController> [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<string> Get([FromServices] IHostEnvironment hostEnvironment) { var path = hostEnvironment.ContentRootPath; return new string[] { path }; } } }
看下效果:
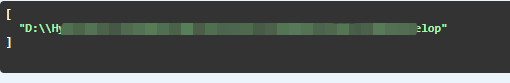
3、利用IServiceProvider的扩展方法GetRequiredService来检索服务
GetRequiredService是IServiceProvider的扩展方法,可以从System.IServiceProvider获取类型为T的服务。
(1)示例一:Serilog日志服务
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { // POST api/<ValuesController> [HttpPost] public void Post([FromBody] string value) { var logger = HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<ILogger>(); logger.Information("GetRequiredService来检索服务"); } } }
看下效果:
(2)示例二:IHostEnvironment
namespace CrmRedevelop.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController1 : ControllerBase { // GET: api/<ValuesController> [HttpGet] public IEnumerable<string> Get() { var hostEnvironment = HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IHostEnvironment>(); var path=hostEnvironment.ContentRootPath; return new string[] { path }; } } }
四、ASP.NET Core中服务的生命周期
上边介绍依赖注入在ASP.NET Core实现的时候,并没有提到生命周期的知识,这里单独梳理下,在ConfigureServices方法中的注册服务的时候,Asp.NET Core都可以为每个服务提供三种服务生命周期:
-
Transient(暂时):每次请求都会创建一个新的实例。这种生命周期最适合轻量级,无状态服务。
-
Scoped(作用域):在同一个作用域内只初始化一个实例 ,可以理解为每一个请求只创建一个实例,同一个请求会在一个作用域内。
-
Singleton(单例):整个应用程序生命周期以内只创建一个实例,后续每个请求都使用相同的实例。如果应用程序需要单例行为,建议让服务容器管理服务的生命周期,而不是在自己的类中实现单例模式。
下面通过示例验证下:
1、定义三个接口
public interface IUser { } public interface IAnimal { } public interface ITree { }
2、定义三个实现类
public class User : IUser { } public class Animal : IAnimal { } public class Tree : ITree { }
3、在startup中注册三个服务
//演示生命周期 services.AddTransient<IUserService, UserService>(); services.AddScoped<IAnimalService, AnimalService>(); services.AddSingleton<ITreeService, TreeService>();
4、测试
namespace xx { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { private readonly IUserService _userService1; private readonly IUserService _userService2; private readonly IAnimalService _animalService1; private readonly IAnimalService _animalService2; private readonly ITreeService _treeService1; private readonly ITreeService _treeService2; public ValuesController1(IUserService userService1, IUserService userService2, IAnimalService animalService1, IAnimalService animalService2, ITreeService treeService1, ITreeService treeService2) { _userService1 = userService1; _userService2 = userService2; _animalService1 = animalService1; _animalService2 = animalService2; _treeService1 = treeService1; _treeService2 = treeService2; } // GET: api/<ValuesController> [HttpGet] public string Get() { var sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.Append("transient1:" + _userService1.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); sb.Append("transient2:" + _userService2.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); sb.Append("scope1:" + _animalService1.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); sb.Append("scope2:" + _animalService2.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); sb.Append("singleton1:" + _treeService1.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); sb.Append("singleton2:" + _treeService2.GetHashCode() + "<br />"); return sb.ToString(); } } }
第一次刷新:
transient1:12314717 transient2:30850230 scope1:13632691 scope2:13632691 singleton1:38865907 singleton2:38865907
第二次刷新:
transient1:2272647
transient2:56816183
scope1:11118446
scope2:11118446
singleton1:38865907
singleton2:38865907
因此:
-
transient类型的生命周期,每次使用都不一样,不同的类或不同的方法使用都不一样
-
scope类型的生命周期,在同一个请求内是一样的
-
singleton类型的生命周期,每次请求都是一样的
所以理解了生命周期的作用,在开发的时候就可以根据需要对不同的服务选择不同的生命周期。