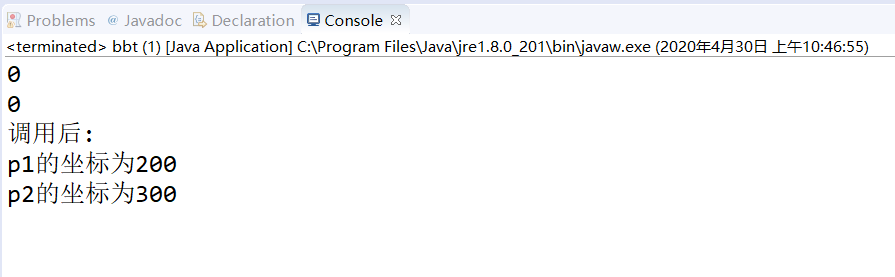
1、定义一个点类Point,包含2个成员变量x、y分
表示x和y坐标,2个构造器Point()和Point(int
x0,y0),以及一个movePoint(int dx,int dy)方法实
现点的位置移动,创建两个Point对象p1、p2,分
别调用movePoint方法后,打印p1和p2的坐标。[
必作题]
package bbt; public class Point { int x; int y; Point() { System.out.println(x); System.out.println(y); System.out.println("调用后:"); } Point(int x0, int y) { x = x; y = y; System.out.println(x); System.out.println(y); } void movePoint(int dx, int dy) { dx = x + 100; dy = y + 100; System.out.println("p1的坐标为" + dx + " " + "p2的坐标为" + dy); } } package bbt; public class bbt { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Point p=new Point(); p.x=100; p.y=200; p.movePoint(p.x,p.y); } }
2、定义一个矩形类Rectangle:(知识点:对象的
创建和使用)[必做题]
• 2.1 定义三个方法:getArea()求面积、getPer()求
周长,showAll()分别在控制台输出长、宽、面积
、周长。
• 2.2 有2个属性:长length、宽width
• 2.3 通过构造方法Rectangle(int width, int length),
分别给两个属性赋值
• 2.4 创建一个Rectangle对象,并输出相关信息
package sdd; public class Rectangle { int length; int width; public void getPer() { System.out.println("矩形的周长=" + (length + width) * 2); } public void getArea() { System.out.println("矩形的面积=" + length * width); } public void showAll() { System.out.println("长=" + length); System.out.println("宽=" + width); getArea(); getPer(); } } package sdd; import java.util.Scanner; public class Tese { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Rectangle a = new Rectangle(); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入长:"); a.length = input.nextInt(); System.out.print("请输入宽:"); a.width = input.nextInt(); a.showAll(); } }

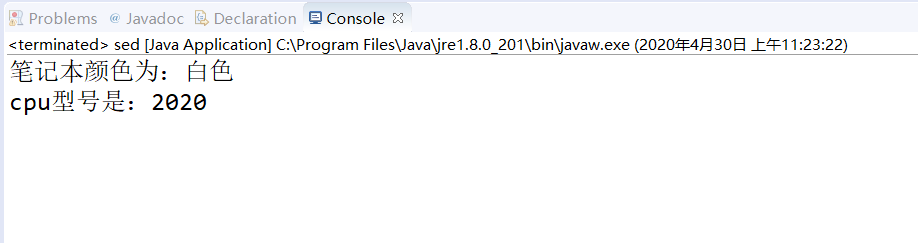
3、定义一个笔记本类,该类有颜色(char)和cpu
型号(int)两个属性。 [必做题]
• 3.1 无参和有参的两个构造方法;有参构造方法可
以在创建对象的同时为每个属性赋值;
• 3.2 输出笔记本信息的方法
• 3.3 然后编写一个测试类,测试笔记本类的各个
方法。
package Test; public class Bijiben { char yanse; int cpu; public void Showyanse() { System.out.println("笔记本颜色为:" + yanse+"色"); } public void Showcpu() { System.out.print("cpu型号是:" + cpu); } } package Test; public class sed { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Bijiben a = new Bijiben(); a.yanse = '白'; a.cpu = 2020; a.Showyanse(); a.Showcpu(); } }
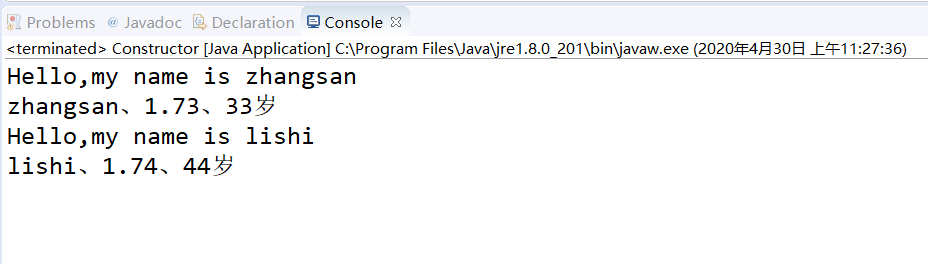
4、定义两个类,描述如下: [必做题]
• 4.1定义一个人类Person:
• 4.1.1定义一个方法sayHello(),可以向对方发出
问候语“hello,my name is XXX”
• 4.1.2有三个属性:名字、身高、年龄
• 4.1.3通过构造方法,分别给三个属性赋值
• 4.2定义一个Constructor类:
• 4.2.1创建两个对象,分别是zhangsan,33岁,
1.73;lishi,44,1.74
• 4.2.2分别调用对象的sayHello()方法。
package Test; public class Person { String name; int nianling; double shengao; int tizhong; public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello,my name is " + name); System.out.println(name + '、' + shengao + '、' + nianling + "岁"); } } package Test; public class Constructor { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Person a = new Person(); a.name = "zhangsan"; a.shengao = 1.73; a.nianling = 33; a.sayHello(); Person b = new Person(); b.name = "lishi"; b.shengao = 1.74; b.nianling = 44; b.sayHello(); } }