线程同步
多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案:引入线 程同步机制,使得另一线程要使用该方法,就只 能等待。
⚫ 在Java中解决多线程同步问题的方法有两种:
1.- Java SE 5.0中引入ReentrantLock类(P648页)。
2.- 在共享内存的类方法前加synchronized修饰符。
……
public synchronized static void sub(int m)
……
解决方案一:锁对象与条件对象
用ReentrantLock保护代码块的基本结构如下:
myLock.lock();
try {
critical section
} finally{
myLock.unlock(); }
有关锁对象和条件对象的关键要点:
➢ 锁用来保护代码片段,保证任何时刻只能有一 个线程执行被保护的代码。
➢ 锁管理试图进入被保护代码段的线程。
➢ 锁可拥有一个或多个相关条件对象。
➢ 每个条件对象管理那些已经进入被保护的代码 段但还不能运行的线程。
解决方案二: synchronized关键字
synchronized关键字作用:
➢ 某个类内方法用synchronized 修饰后,该方法被称为同步方法;
➢ 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法,其他线程欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞,直至线程从同步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程,其他线程方可能进入同步方法。
➢ 一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题的需要,必须使用wait()方法使本线程等待,暂时让出CPU的使用权,并允许其它线程使用这个同步方法。
➢ 线程如果用完同步方法,应当执行notifyAll()方 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方法而处于等待的 线程结束等待。
第二部分:实验部分——线程同步控制
实验时间 2018-12-10
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
(2) 线程综合编程练习
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
1.在Elipse环境下调试教材651页程序14-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握利用锁对象和条件对象实现的多线程同步技术。
package synch;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;
/**
一个银行有许多银行帐户,使用锁序列化访问 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bank
{
private final double[] accounts;
private Lock bankLock;
private Condition sufficientFunds;
/**
* 建设银行。
* @param n 账号
* @param initialBalance 每个账户的初始余额
*/
public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
{
accounts = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
bankLock = new ReentrantLock();
sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition();
}
/**
* 把钱从一个账户转到另一个账户。
* @param 从账户转账
* @param 转到要转账的账户
* @param 请允许我向你转达
*/
public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
{
bankLock.lock();
try
{
while (accounts[from] < amount)
sufficientFunds.await();
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
accounts[from] -= amount;
System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
accounts[to] += amount;
System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
sufficientFunds.signalAll();
}
finally
{
bankLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取所有帐户余额的总和。
* @return 总余额
*/
public double getTotalBalance()
{
bankLock.lock();
try
{
double sum = 0;
for (double a : accounts)
sum += a;
return sum;
}
finally
{
bankLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取银行中的帐户数量。
* @return 账号
*/
public int size()
{
return accounts.length;
}
}
package synch;
/**
* 这个程序显示了多个线程如何安全地访问数据结构。
* @version 1.31 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SynchBankTest
{
public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 10;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
{
int fromAccount = i;
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
while (true)
{
int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
}
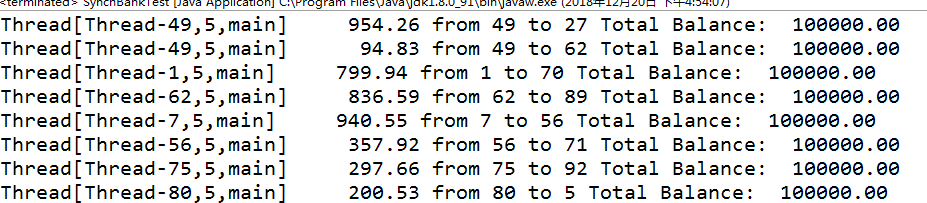
测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材655页程序14-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握synchronized在多线程同步中的应用。
实验代码:
package synch2;
import java.util.*;
/**
* A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives.
* @version 1.30 2004-08-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bank
{
private final double[] accounts;
/**
* Constructs the bank.
* @param n the number of accounts
* @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account
*/
public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
{
accounts = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
}
/**
* Transfers money from one account to another.
* @param from the account to transfer from
* @param to the account to transfer to
* @param amount the amount to transfer
*/
public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
{
while (accounts[from] < amount)
wait();
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
accounts[from] -= amount;
System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
accounts[to] += amount;
System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
notifyAll();
}
/**
* Gets the sum of all account balances.
* @return the total balance
*/
public synchronized double getTotalBalance()
{
double sum = 0;
for (double a : accounts)
sum += a;
return sum;
}
/**
* Gets the number of accounts in the bank.
* @return the number of accounts
*/
public int size()
{
return accounts.length;
}
}
package synch2;
/**
* This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure,
* using synchronized methods.
* @version 1.31 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SynchBankTest2
{
public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 10;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
{
int fromAccount = i;
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
while (true)
{
int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
}
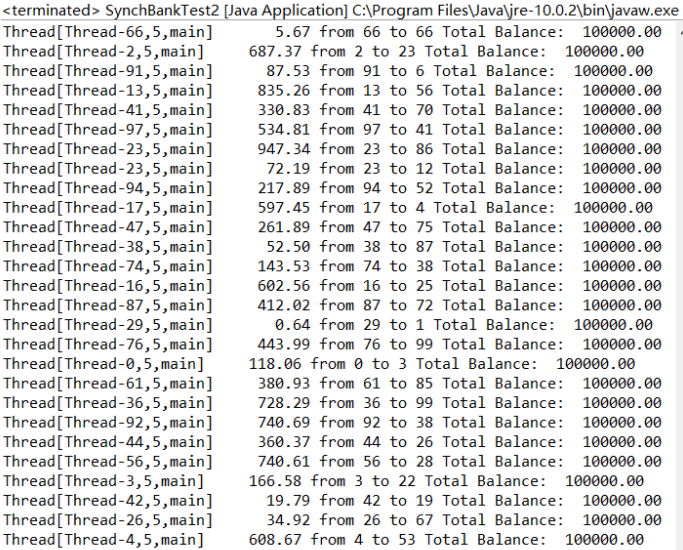
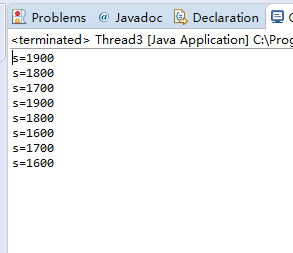
测试程序3:
l 在Elipse环境下运行以下程序,结合程序运行结果分析程序存在问题;
l 尝试解决程序中存在问题。
class Cbank
{
private static int s=2000;
public static void sub(int m)
{
int temp=s;
temp=temp-m;
try {
Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random()));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) { }
s=temp;
System.out.println("s="+s);
}
}
class Customer extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for( int i=1; i<=4; i++)
Cbank.sub(100);
}
}
public class Thread3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Customer customer1 = new Customer();
Customer customer2 = new Customer();
customer1.start();
customer2.start();
}
}
修改之后如下:
import javax.sql.rowset.spi.SyncFactory;
class Cbank{ private static int s=2000; public synchronized static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } }class Customer extends Thread{ public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } }public class Thread3{ public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); }}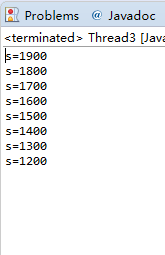
实验2 编程练习
利用多线程及同步方法,编写一个程序模拟火车票售票系统,共3个窗口,卖10张票,程序输出结果类似(程序输出不唯一,可以是其他类似结果)。
Thread-0窗口售:第1张票
Thread-0窗口售:第2张票
Thread-1窗口售:第3张票
Thread-2窗口售:第4张票
Thread-2窗口售:第5张票
Thread-1窗口售:第6张票
Thread-0窗口售:第7张票
Thread-2窗口售:第8张票
Thread-1窗口售:第9张票
Thread-0窗口售:第10张票
package xaincheng;
import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Mythread mythread= new Mythread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(mythread);
Thread t2 = new Thread(mythread);
Thread t3 = new Thread(mythread);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class Mythread implements Runnable{
int t=1;
boolean flag=true;
public void run() {
while(flag) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (this) {
if(t<=10){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"窗口售:第"+t+"张票");
t++;
}
if(t>10){
flag=false;
}
}
}
}
}

实验总结:通过本学期对Java这门课程的学习收获了很多,也很感谢老师还有助教学长对我们无微不至的关心,也通过这次试验加深了对多线程的理解,知道了并发多线程的解决方法。