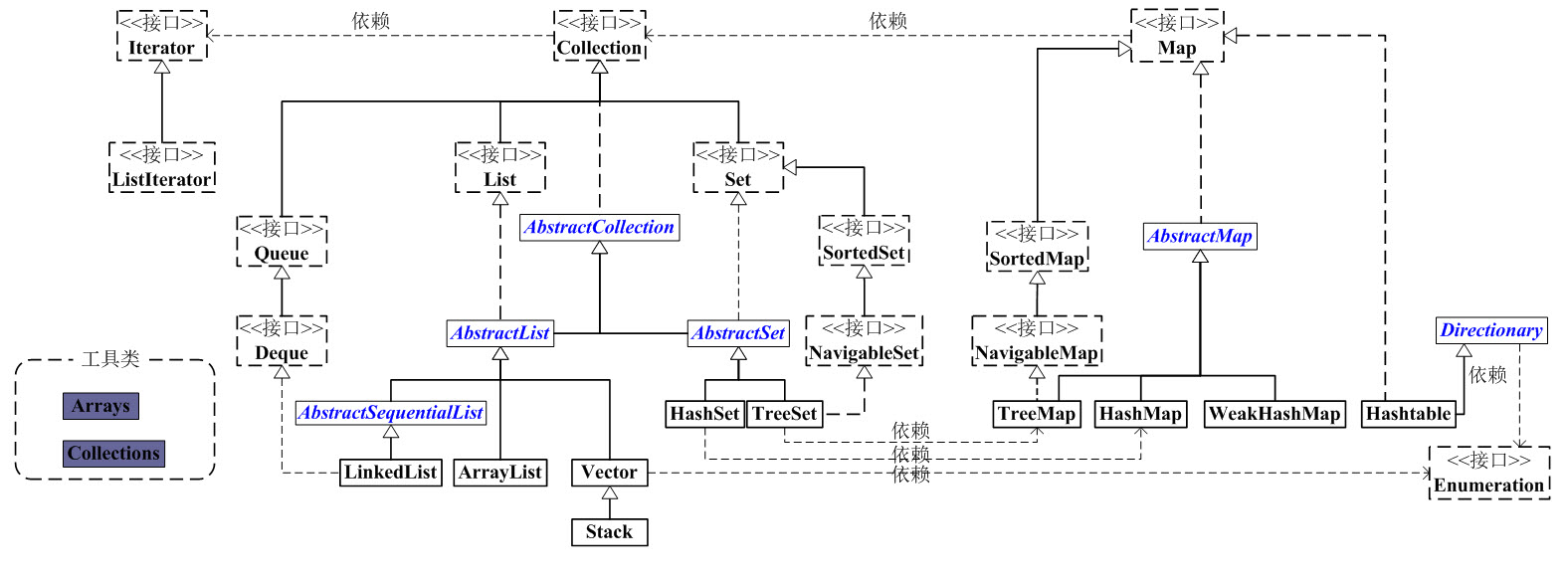
盗图一张,找不到原作者了,如有知道原链接的朋友,请告知,谢谢。
java的集合继承关系,第一个让我感觉有些头疼的JAVA知识点,初学时复杂的继承关系让我有点无所适从。今天开始重新梳理自己半年来的知识点,补充体系上的漏洞,个人水平还属于初级阶段,有概念错误或疏漏,也请各位朋友指正与补充,谢谢。
从List入手,依次梳理各常用数据结构的源码与原理,List下面常用的数据结构有ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector(线程安全,效率问题目前基本不用)。
ArrayList,动态数组,内部包含了一个数组,在此基础之上根据继承关系,封装了一组方法,常用的方法如下:
- ArrayList()
- ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
- ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
- boolean add(E e)
- public Iterator<E> iterator()
ArrayList()
1 /** 2 * 构造一个空的ArrayList,初始容量为10. 3 */ 4 5 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 6 7 public ArrayList() { 8 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 9 }
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
1 /** 2 * 以指定的容量创建一个ArrayList,其中每一个元素均为空 3 * 4 */ 5 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 6 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 7 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 8 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 9 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 10 } else { 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ 12 initialCapacity); 13 } 14 }
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
1 /** 2 * 以现有的集合作为初始值,创建一个新的ArrayList, 3 * 新的ArrayList为原集合的一个副本。 4 * 5 * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list 6 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 7 */ 8 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 9 elementData = c.toArray(); 10 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 11 // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) 12 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 13 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 14 } else { 15 // replace with empty array. 16 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 17 } 18 }
boolean add(E e)
ArrayList添加新元素,需要计算添加一个新元素后,当前ArrayList的容量是否足够。如果容量不够,需要将当前容量扩充至当前容量的1.5倍,如果超过虚拟机的最大限制,则截断详细如下:
1 /** 2 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 3 * 4 * @param e element to be appended to this list 5 * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 6 */ 7 public boolean add(E e) { 8 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 9 elementData[size++] = e; 10 return true; 11 } 12 13 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 14 ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); 15 } 16 17 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 18 modCount++; 19 20 // overflow-conscious code 21 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 22 grow(minCapacity); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the 27 * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. 28 * 29 * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity 30 */ 31 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 32 // overflow-conscious code 33 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 34 //容量扩充至当前的1.5倍,如果依然容纳不下实际元素数量,则将实际元素数量作为新的数组的容量,如果 35 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 36 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 37 newCapacity = minCapacity; 38 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 39 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 40 // 创建新数组的拷贝 41 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 42 } 43 44 add(E e)
public Iterator<E> iterator():返回一个Iterator类型的内部类对象,该对象包含了可以操作ArrayList对象的一些Iterator方法,入next、hasNext等方法
1 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 2 return new Itr(); 3 } 4 5 /** 6 * Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence. 7 * 8 * <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>. 9 * 10 * @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence 11 */ 12 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 13 return new Itr(); //创建一个新的内部类对象,该对象包含了对ArrayList对象的常用操作方法,next()、hasNext()、remove()等方法 14 } 15 16 /** 17 * An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr 18 */ 19 private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { 20 int cursor; // 当前被操作的元素,默认为0 21 int lastRet = -1; // 上一个被操作的元素,如果没有则为-1(初始时或上一个元素被删除时,则为0) 22 int expectedModCount = modCount; 23 24 public boolean hasNext() { 25 return cursor != size; 26 } 27 28 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 29 public E next() { 30 checkForComodification(); 31 int i = cursor; 32 if (i >= size) 33 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 34 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 35 if (i >= elementData.length) 36 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 37 cursor = i + 1; 38 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; 39 } 40 41 public void remove() { 42 if (lastRet < 0) 43 throw new IllegalStateException(); 44 checkForComodification(); 45 46 try { 47 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); 48 cursor = lastRet; 49 lastRet = -1; 50 expectedModCount = modCount; 51 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 52 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 53 } 54 } 55 }
以上是ArrayList中常用且典型的方法源码,理解上面的源码有助于帮助我们理解ArrayList的工作原理和特点。ArrayList在集合中是比较简单,但是非常常用的数据结构,了解了ArrayList可以让我们在合适的场景去使用它。