简述
对于普通的servlet接口,我们必须重写5个方法

但真正核心的方法是service方法,对于其他四个方没有那么重要。
于是GenericServlet让编写servlet更加容易。它提供生命周期方法init和destroy的简单实现,要编写一般的servlet方法只需重写抽象方法service就行。
GenericServlet开发servlet
我们在servlet包里创建GenServlet,并继承GenericServlet。因为GenericServlet是抽象类,所以我们是继承而不是实现接口。
可以进入GenericServlet看到,该抽象类继承了Servlet接口,并实现了除service的四个必需方法,把service定义为了抽象方法,留给我们重写

package javax.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Enumeration; public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private transient ServletConfig config; public GenericServlet() { } public void destroy() { } public String getInitParameter(String name) { return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name); } public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() { return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames(); } public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return this.config; } public ServletContext getServletContext() { return this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); } public String getServletInfo() { return ""; } public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { this.config = config; this.init(); } public void init() throws ServletException { } public void log(String msg) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg); } public void log(String message, Throwable t) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t); } public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; public String getServletName() { return this.config.getServletName(); } }
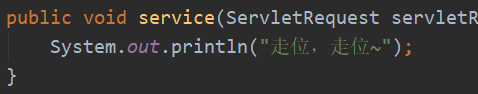
我们现在在service方法里写上输出语句
然后配置好我们的web.xml

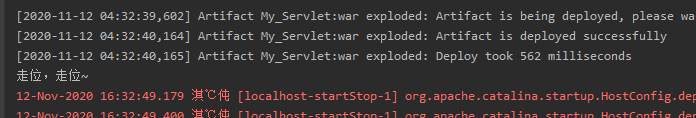
启动服务器,输入我们的URL为gs,我们可以看到控制台成功输出了信息
HttpServlet开发servlet
HttpServlet是继承GenericServlet的基础上进行进一步的扩展。
提供将要被子类化以创建用于web站点的HTTP servlet的抽象类。
HttpServlet最大的不同就是它已经实现了service方法,它里面写了什么呢

protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); long lastModified; if (method.equals("GET")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1L) { this.doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince; try { ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) { ifModifiedSince = -1L; } if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) { this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(304); } } } else if (method.equals("HEAD")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("POST")) { this.doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("PUT")) { this.doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("DELETE")) { this.doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) { this.doOptions(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("TRACE")) { this.doTrace(req, resp); } else { String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method}; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(501, errMsg); } }
我们可以看到service方法实际上是进行了请求的分流,根据请求的不同,调用不同的响应方法

所以开发者重写的就不应该是service方法,重写的应该是进行分流后的dopost,doget等响应方法
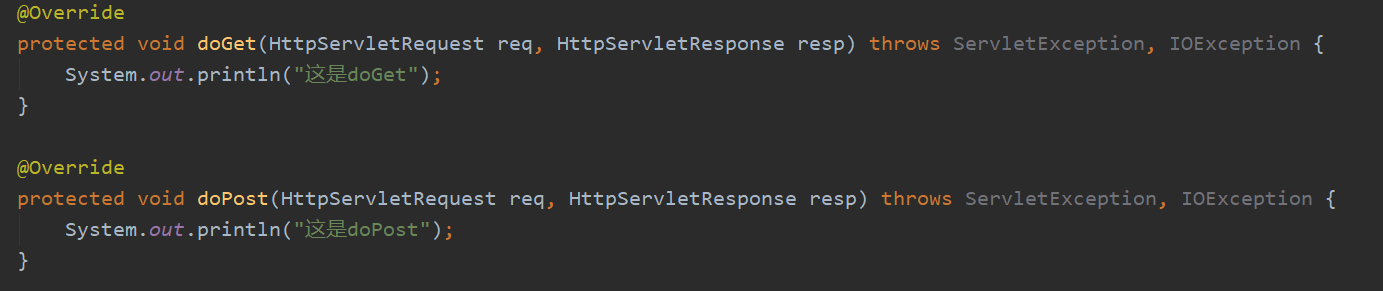
我们在HtServlet里重写我们的doget方法和dopost方法
配好web.xml
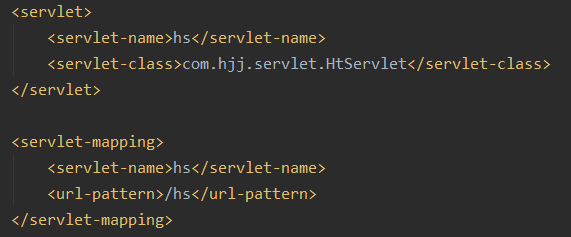
我们输入URL为gs,可以看到doGet方法被调用了
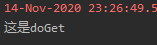
业务流程是怎么样的呢——tomcat服务器启动、浏览器请求gs、HttpServlet中的service方法判断该请求是Get请求,调用重写后的doGet方法响应
