线程的概念:
几乎每种操作系统都支持进程的概念 ----进程就是在某种程度上互相隔离的、独立运行的程序。
进程---程序之间轮询利用CPU时间。 进程是CPU任务。
线程---程序内部,轮询利用程序得到的执行时间。线程是某个程序的任务。
多进程(Multi-Thread)扩展了多进程(Multi-Process)操作的概念,将任务的划分下降到了程序级别,使得各个程序似乎可以在同一时间内执行多个任务。
每个任务称为一个线程,能够同时运行多个线程的程序称为多线程程序。
多进程和多线程作为资源调度的两种方式,已经存在了很久了。但是将线程显示地作为程序语言的特征,而不是单纯当底层操作系统的调度,Java是第一个主流的编程语言
其实,每个Java应用程序都至少有一个线程---主线程。当一个Java应用程序启东时,JVM会创建主线程,并在该线程中调用程序的main()方法。
多进程和多线程有什么区别?对于进程来说,每个进程都有自己的一组完整的变量,而线程则共享相同的数据。
我们知道:计算机程序得以执行的三个要素是:CPU、程序代码和可存取的数据。在Java语言中,多线程的机制是通过虚拟CPU来实现的。
可以形象的理解为,在一个Java程序内部虚拟了多台计算机,每台计算机对应一个线程,有自己的CPU,可以获取所需的代码和数据,因此能独立执行任务,
相互间还可以公用代码和数据。Java的线程是通过java.lang.Thread类来实现的,它内部实现了虚拟CPU的功能,能够接收和处理传递给它的代码和数据,并提供了
独立的运行控制功能。
JVM还通常会创建一些其他的线程,不过,这些线程对我们而言通常是不可见的。例如,用于自动垃圾收集的线程、对象终止或者其他的JVM处理任务相关的线程。
-
线程的创建方式:
方式一(继承Thread类):
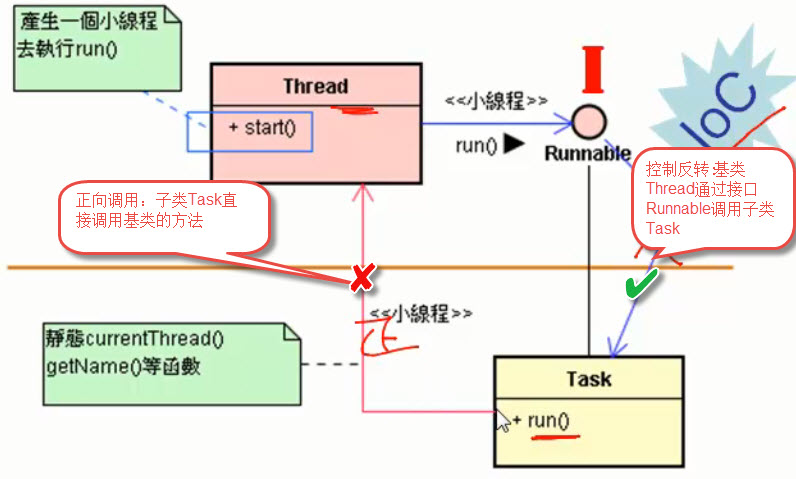
将一个类继承Thread,然后覆盖Thread中的run()方法,这样就让这个类本身也就成了线程类:
public class Aclass extends Thread{ … public void run(){ …. } … } Aclass a=new Aclass(); a.start();//使用start()方法,线程进入Runnable(可运行状态),它将向线程调度器注册这个线程。不会马上进入运行状态(Running)
方式二(实现Runnable接口):
public Bclass implements Runnable{ public void run(){ … } } Bclass b =new Bclass(); b.start();
补充知识:
public class Thread{ ….. ….. public Thread(Runnable target) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } private Runnable target; public void run() { if (target != null) { target.run(); } } /** * Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine * calls the <code>run</code> method of this thread. * 让这个线程执行;JVM调用这个线程的run方法。 * <p> * The result is that two threads are running concurrently: the * current thread (which returns from the call to the * <code>start</code> method) and the other thread (which executes its * <code>run</code> method). * 结果是运行了两个线程:当前线程(通过调用start方法)和另一个线程(执行了它的run方法) * <p> * It is never legal to start a thread more than once. * 一个线程的start方法从来不会被调用两次。 * In particular, a thread may not be restarted once it has completed * execution. *通常,一个线程可能别调用一次并执行完成后,不必再次被执行。 * @exception IllegalThreadStateException if the thread was already * started. * @see #run() * @see #stop() */ public synchronized void start() { /** * This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system" * group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added * to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM. * * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW". */ if (threadStatus != 0 || this != me) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); group.add(this); start0(); if (stopBeforeStart) { stop0(throwableFromStop); } } private native void start0(); ….. ….. }
我是一个线程:http://kb.cnblogs.com/page/542462/