简介
TcpConnection类,TcpServer类,Acceptor类是构成非阻塞TCP网络编程库的重要组成部分。
本文主要针对muduo源码进行分析。(Acceptor类在上篇中已经分析过了)
muduo网络库的单线程设计方式,即一个EventLoop 处理所有的事件,包括链接的建立、IO、计算、以及链接的销毁,多线程的方式即每一个连接一个EventLoop。(one loop per thread)
TcpServer
多线程的muduo::TcpServer,主要通过添加一个EventLoopThreadPool 事件循环线程池实现,新建TcpConnection时从event loop pool里挑选一个loop给TcpConnection用。 也就是说多线程TcpServer自己的EventLoop只用来接受新连接, 而新连接会用其他EventLoop来执行IO。 (单线程TcpServer的EventLoop是与TcpConnection共享的。)
EventLoopThreadPooll 按one loop per thread的思想实现多线程TcpServer, 此时主线程循环只负责TCP链接的建立,及任务的分配,需要让哪个线程干活, 就把timer或IO(如TCP连接) 注册到那个线程的循环里即可;对实时性有要求的connection可以单独用一个线程; 数据量大的connection可以独占一个线程;并把数据处理任务分摊到另几个计算线程中(用线程池);其他次要的辅助性connections共享一个线程。
线程池设计模式
池是一种设计模式,线程是是一种资源,线程池设计模式通常是事先申请一定的资源,当需要使用时,去资源池中申请资源,用完后再放回资源池中。EventLoopThreadPool 正是借鉴了这种设计模式,虽然使用的线程并不会放回资源池中,但是本身的一个EventLoop即一个Reactor,本身就具备等待机制了。
TcpServer每次新建一条TcpConnection就会通过EventLoopThreadPool::getNextLoop()方法来取一个EventLoop, 目前的getNextLoop()只是循环的从池中取一条loop,如果提供给每条TcpConncetion的是均等的服务,那么这样就能很均匀的分配系统的资源了。
TcpServer的工作方式取决于EventLoopThreadPool中线程的创建数量。
0 意味着所有的I/O 都在TcpServer的主事件循环中,不会创建新的线程。
1 意味着所有的 I/O 在另一个线程中 ,TcpServer的主线程只负责建立连接。
N 意味着新的连接会被循环的分配到N条线程中工作。
下面是源码(带有注释)
TcpServer.h
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) // // This is a public header file, it must only include public header files. /* 这个类相当于把TcpConnection以及Accept类整合起来,完全能够实现Tcp通信,也就是socket函数都实现了 * 总结一下整个TCP通信过程: * 一个TcpServer类中,有Acceptor,EventLoopThreadPool各一个,以及多个TcpConnection类的指针, * 在TcpServer类的启动函数中,先开启EventLoopThreadPool线程池,然后将Acceptor监听函数放入eventloop中去执行 * 在TcpServer类的构造函数中,就已经把一个成功连接的回调函数绑定在Acceptor类的连接回调函数中,如果Acceptor监听 * 到有连接进来,先调监听socket描述符的回调函数,把这个连接accept进来,然后再调用newConnectionCallback_函数 * 来处理连接,每个连接都有一个对应的TcpConnection类来作为缓冲区 * */ #ifndef MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_H #define MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_H #include <muduo/base/Types.h> #include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h> #include <map> #include <boost/noncopyable.hpp> #include <boost/scoped_ptr.hpp> namespace muduo { namespace net { class Acceptor; class EventLoop; class EventLoopThreadPool; /// /// TCP server, supports single-threaded and thread-pool models. /// /// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details. class TcpServer : boost::noncopyable { public: typedef boost::function<void(EventLoop *)> ThreadInitCallback; //TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr); TcpServer(EventLoop *loop, const InetAddress &listenAddr, const string &nameArg); ~TcpServer(); // force out-line dtor, for scoped_ptr members. const string &hostport() const { return hostport_; } const string &name() const { return name_; } /// Set the number of threads for handling input. /// /// Always accepts new connection in loop's thread. /// Must be called before @c start /// @param numThreads /// - 0 means all I/O in loop's thread, no thread will created. /// this is the default value. /// - 1 means all I/O in another thread. /// - N means a thread pool with N threads, new connections /// are assigned on a round-robin basis. void setThreadNum(int numThreads); void setThreadInitCallback( const ThreadInitCallback &cb) { threadInitCallback_ = cb; }//这个函数会作为EventLoopThreadPool::start的入口参数 /// Starts the server if it's not listenning. /// /// It's harmless to call it multiple times. /// Thread safe. void start(); /// Set connection callback. /// Not thread safe. // 设置连接到来或者连接关闭回调函数,这个函数指针会赋值给TcpConnection::connectionCallback_函数,就是在连接建立之后,和连接断开之前会调用 void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback &cb) { connectionCallback_ = cb; } /// Set message callback. /// Not thread safe. // 设置消息到来回调函数,这个函数指针在TcpConnection::handleread函数中调用,也就是TcpConnection的Channel的读函数的一部分 void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback &cb) { messageCallback_ = cb; } /// Set write complete callback. /// Not thread safe. /// 在发送完消息以后调用,这个函数指针会赋值给TcpConnection::writeCompleteCallback_函数 void setWriteCompleteCallback(const WriteCompleteCallback &cb) { writeCompleteCallback_ = cb; } private: /// Not thread safe, but in loop void newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress &peerAddr); //这个函数会赋值给Acceptor::newConnectionCallback_,在新连接建立以后调用 /// Thread safe. /// 会赋值给TcpConnection::closeCallback_函数,也就是当连接描述符关闭以后调用这个 void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn); /// Not thread safe, but in loop,在上面这个函数removeConnection中调用 void removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn); typedef std::map <string, TcpConnectionPtr> ConnectionMap; EventLoop *loop_; // the acceptor loop const string hostport_; // 服务的ip:端口 const string name_; // 服务名 boost::scoped_ptr <Acceptor> acceptor_; // avoid revealing Acceptor boost::scoped_ptr <EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_; ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; MessageCallback messageCallback_; WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 数据发送完毕,会回调此函数 ThreadInitCallback threadInitCallback_; // IO线程池中的线程在进入事件循环前,会回调用此函数 bool started_; // always in loop thread int nextConnId_; // 下一个连接ID,每次增加一个就加1 ConnectionMap connections_; // 连接列表 }; } } #endif // MUDUO_NET_TCPSERVER_H
TcpServer.cc
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) #include <muduo/net/TcpServer.h> #include <muduo/base/Logging.h> #include <muduo/net/Acceptor.h> #include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h> #include <muduo/net/EventLoopThreadPool.h> #include <muduo/net/SocketsOps.h> #include <boost/bind.hpp> #include <stdio.h> // snprintf using namespace muduo; using namespace muduo::net; TcpServer::TcpServer(EventLoop *loop, const InetAddress &listenAddr, const string &nameArg) : loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)), hostport_(listenAddr.toIpPort()), name_(nameArg), acceptor_(new Acceptor(loop, listenAddr)), threadPool_(new EventLoopThreadPool(loop)), connectionCallback_(defaultConnectionCallback), messageCallback_(defaultMessageCallback), started_(false), nextConnId_(1) { // Acceptor::handleRead函数中会回调用TcpServer::newConnection // _1对应的是socket文件描述符,_2对应的是对等方的地址(InetAddress) acceptor_->setNewConnectionCallback( boost::bind(&TcpServer::newConnection, this, _1, _2)); } TcpServer::~TcpServer() { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); LOG_TRACE << "TcpServer::~TcpServer [" << name_ << "] destructing"; for (ConnectionMap::iterator it(connections_.begin()); it != connections_.end(); ++it) { TcpConnectionPtr conn = it->second; it->second.reset(); // 释放当前所控制的对象,引用计数减一 conn->getLoop()->runInLoop( boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn)); conn.reset(); // 释放当前所控制的对象,引用计数减一 } } void TcpServer::setThreadNum(int numThreads) { assert(0 <= numThreads); threadPool_->setThreadNum(numThreads); } // 该函数多次调用是无害的 // 该函数可以跨线程调用 void TcpServer::start() { if (!started_) { started_ = true; threadPool_->start(threadInitCallback_); } if (!acceptor_->listenning()) { // get_pointer返回原生指针 loop_->runInLoop( boost::bind(&Acceptor::listen, get_pointer(acceptor_))); } } void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress &peerAddr)//建立新连接以后的回调函数 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); // 按照轮叫的方式选择一个EventLoop EventLoop *ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop(); char buf[32]; snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, ":%s#%d", hostport_.c_str(), nextConnId_);//buf的内容是 ip:端口#nextConnId_ ++nextConnId_; string connName = name_ + buf; LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_ << "] - new connection [" << connName << "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort(); InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd)); // FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection // FIXME use make_shared if necessary /*TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(loop_, connName, sockfd, localAddr, peerAddr));*/ TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop, connName, sockfd, localAddr, peerAddr)); LOG_TRACE << "[1] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); connections_[connName] = conn;//将连接名和TCPConnection的指针拷贝进连接列表中,这样就有两个shared_ptr指针指向conn了, //如果没有这一句程序,这个conn在newConnection函数执行结束以后就会析构掉,所以真正要删除时,也要把这个列表中的对应元素也删除了。 LOG_TRACE << "[2] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); //设置回调函数 conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_); conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_); conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);//无论是否非空,都可以先设置,在使用之前会有判断 conn->setCloseCallback( boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // conn->connectEstablished(); ioLoop->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn)); //个人理解bind在绑定类成员函数时,后面跟的参数一定比输入参数多一个,就是一个类指针,表明这个函数属于那个类变量的, //一般都使用this,而这里是用的TcpConnectionPtr LOG_TRACE << "[5] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); } void TcpServer::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn) { /* loop_->assertInLoopThread(); LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [" << name_ << "] - connection " << conn->name(); LOG_TRACE << "[8] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); size_t n = connections_.erase(conn->name()); LOG_TRACE << "[9] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); (void)n; assert(n == 1); loop_->queueInLoop( boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn)); LOG_TRACE << "[10] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); */ loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop, this, conn)); } void TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn)//就是把TcpConnection从Eventloop中移除 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [" << name_ << "] - connection " << conn->name(); LOG_TRACE << "[8] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); size_t n = connections_.erase(conn->name()); LOG_TRACE << "[9] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); (void) n; assert(n == 1); EventLoop *ioLoop = conn->getLoop(); ioLoop->queueInLoop( boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn)); //loop_->queueInLoop( // boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn)); LOG_TRACE << "[10] usecount=" << conn.use_count(); }
TcpConnection
TcpConnection类主要负责封装一次TCP连接,向Channel类注册回调函数(可读、可写、可关闭、错误处理),将来当Channel类上的事件发生时,调用相应的回调函数进行数据收发或者错误处理。
TcpConnection是使用shared_ptr来管理的类,因为它的生命周期模糊。TcpConnection表示已经建立或正在建立的连接,建立连接后,用户只需要在上层类如TcpServer中设置连接到来和消息到来的处理函数,继而回调TcpConnection中的 setConnectionCallback和setMessageCallback函数,实现对事件的处理。用户需要关心的事件是有限的,其他都由网络库负责。
TcpConnection中封装了InputBuffer和OutputBuffer,用来表示应用层的缓冲区。在发送数据时,如果不能一次将Buffer中的数据发送完毕,它还会继续关注Channel中的可写事件,当sockfd可写时,会再次发送。
前面提到TcpConnection的生存期模糊,主要是因为我们不能在TcpServer中直接erase掉TcpConnection对象,因为此时有可能Channel中的handleEvent还在执行,如果析构TcpConnection对象,那么他的成员channel_也会被析构,会导致core dump。也就是说我们需要TcpConnection 对象生存期要长于handleEvent() 函数,直到执行完connectDestroyed() 后才会析构。
断开连接:
TcpConnection的断开是采用被动方式,即对方先关闭连接,本地read(2)返回0后,调用顺序如下:
handleClose()->TcpServer::removeConnection->TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()。
连接关闭时序图:
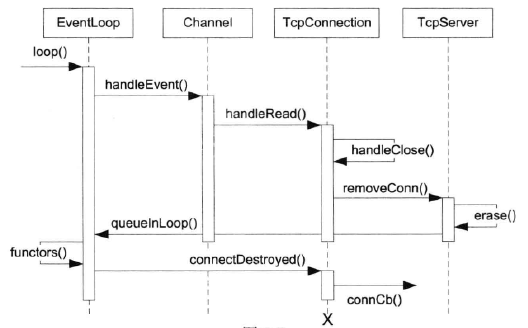
当连接到来,创建一个TcpConnection对象,立刻用shared_ptr来管理,引用计数为1,在Channel中维护一个weak_ptr(tie_),将这个shared_ptr对象赋值给_tie,引用计数仍然为1。当连接关闭时,在handleEvent中,将tie_提升,得到一个shard_ptr对象,引用计数就变成了2。当shared_ptr的计数不为0时,TcpConnection不会被销毁。
TcpConnection.h源码分析
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) // // This is a public header file, it must only include public header files. /*我所理解的这个类,主要用来和buffer类一起作为非阻塞IO的一个读取桥梁,其中主要封装的函数是从文件描述符中读取传输的数据到 *接受缓冲区中,或者把规定数据,或者触发写事件的输出缓冲区的数据写入对应的文件描述符中。 */ #ifndef MUDUO_NET_TCPCONNECTION_H #define MUDUO_NET_TCPCONNECTION_H #include <muduo/base/Mutex.h> #include <muduo/base/StringPiece.h> #include <muduo/base/Types.h> #include <muduo/net/Callbacks.h> #include <muduo/net/Buffer.h> #include <muduo/net/InetAddress.h> #include <boost/any.hpp> #include <boost/enable_shared_from_this.hpp> #include <boost/noncopyable.hpp> #include <boost/scoped_ptr.hpp> #include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp> namespace muduo { namespace net { class Channel; class EventLoop; class Socket; /// /// TCP connection, for both client and server usage. /// /// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details. class TcpConnection : boost::noncopyable,public boost::enable_shared_from_this<TcpConnection> { public: /// Constructs a TcpConnection with a connected sockfd /// /// User should not create this object. TcpConnection(EventLoop *loop,const string &name,int sockfd, const InetAddress &localAddr, const InetAddress &peerAddr); ~TcpConnection(); EventLoop *getLoop() const { return loop_; }//获取当前TcpConnection所在的Eventloop const string &name() const { return name_; }// const InetAddress &localAddress() { return localAddr_; } const InetAddress &peerAddress() { return peerAddr_; } bool connected() const { return state_ == kConnected; } // void send(string&& message); // C++11 void send(const void *message, size_t len); void send(const StringPiece &message); // void send(Buffer&& message); // C++11 void send(Buffer *message); // this one will swap data void shutdown(); // NOT thread safe, no simultaneous calling void setTcpNoDelay(bool on); void setContext(const boost::any &context) { context_ = context; } const boost::any &getContext() const//得到常数值的context_ { return context_; } boost::any *getMutableContext()//得到可以改变的context_ { return &context_; } void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback &cb) { connectionCallback_ = cb; } //在handleClose,connectEstablished,connectDestroyed中调用,个人理解这个连接回调函数主要起到 //显示作用,就是在和连接描述符建立连接或者关闭连接前,显示连接状态的,表明还在连接中 void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback &cb) { messageCallback_ = cb; } //在handleRead函数当中调用了,也可以理解为channel_写函数的一部分 void setWriteCompleteCallback(const WriteCompleteCallback &cb) { writeCompleteCallback_ = cb; } //在handleWrite和sendInLoop写函数中,写完调用的 void setHighWaterMarkCallback(const HighWaterMarkCallback &cb, size_t highWaterMark) { highWaterMarkCallback_ = cb; highWaterMark_ = highWaterMark; }//都在sendInLoop中调用了 Buffer *inputBuffer() { return &inputBuffer_; } /// Internal use only. void setCloseCallback(const CloseCallback &cb) { closeCallback_ = cb; }//在handleClose函数中调用 // called when TcpServer accepts a new connection void connectEstablished(); // should be called only once // called when TcpServer has removed me from its map void connectDestroyed(); // should be called only once private: enum StateE { kDisconnected, kConnecting, kConnected, kDisconnecting }; void handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime);//绑定channel_的读函数 void handleWrite();//绑定channel_的写函数 void handleClose();//绑定channel_的关闭函数,同时也在handleRead中调用 void handleError();////绑定channel_的错误函数 void sendInLoop(const StringPiece &message); void sendInLoop(const void *message, size_t len); void shutdownInLoop(); void setState(StateE s) { state_ = s; }//设置状态位 EventLoop *loop_; // 所属EventLoop string name_; // 连接名 StateE state_; // FIXME: use atomic variable // we don't expose those classes to client. //连接状态 boost::scoped_ptr <Socket> socket_; boost::scoped_ptr <Channel> channel_; //channel_在TCPServer中绑定了连接套接字,就是能够实现通信的那个connfd套接字,这个套接字是从Socket::accept函数得到的 //在Tcpclient绑定的是创建的套接字,因为客户端只需要一个套接字就可以了,这个套接字是从socket()函数中得到的 InetAddress localAddr_;//当前服务端的地址 InetAddress peerAddr_;//当前建立连接的客户端地址 ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; MessageCallback messageCallback_; WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; // 数据发送完毕回调函数,即所有的用户数据都已拷贝到内核缓冲区时回调该函数 // outputBuffer_被清空也会回调该函数,可以理解为低水位标回调函数 HighWaterMarkCallback highWaterMarkCallback_; // 高水位标回调函数 CloseCallback closeCallback_; size_t highWaterMark_; // 高水位标 Buffer inputBuffer_; // 应用层接收缓冲区 Buffer outputBuffer_; // 应用层发送缓冲区 boost::any context_; // 绑定一个未知类型的上下文对象,一般用来放HttpContext类的 }; typedef boost::shared_ptr <TcpConnection> TcpConnectionPtr; } } #endif // MUDUO_NET_TCPCONNECTION_H
TcpConnection.cc源码分析
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) #include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h> #include <muduo/base/Logging.h> #include <muduo/net/Channel.h> #include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h> #include <muduo/net/Socket.h> #include <muduo/net/SocketsOps.h> #include <boost/bind.hpp> #include <errno.h> #include <stdio.h> using namespace muduo; using namespace muduo::net; void muduo::net::defaultConnectionCallback(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn)//默认的连接回调函数,输出连接状态 { LOG_TRACE << conn->localAddress().toIpPort() << " -> " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort() << " is " << (conn->connected() ? "UP" : "DOWN"); } void muduo::net::defaultMessageCallback(const TcpConnectionPtr &, Buffer *buf, Timestamp) //默认的有消息时执行的回调函数,把缓冲区读指针和写指针回到初始化的位置 //可以理解为将缓冲区清零 { buf->retrieveAll(); } TcpConnection::TcpConnection(EventLoop *loop, const string &nameArg, int sockfd, const InetAddress &localAddr, const InetAddress &peerAddr) : loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)), // 所属EventLoop name_(nameArg),// 连接名 state_(kConnecting),//连接状态 socket_(new Socket(sockfd)),//连接套接字 channel_(new Channel(loop, sockfd)), //channel_在TCPServer中绑定了连接套接字,就是能够实现通信的那个connfd套接字,这个套接字是从Socket::accept函数得到的 //在Tcpclient绑定的是创建的套接字,因为客户端只需要一个套接字就可以了,这个套接字是从socket()函数中得到的 localAddr_(localAddr),//当前服务端的地址 peerAddr_(peerAddr),//当前建立连接的客户端地址 highWaterMark_(64 * 1024 * 1024) { // 通道可读事件到来的时候,回调TcpConnection::handleRead,_1是事件发生时间 channel_->setReadCallback(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleRead, this, _1)); // 通道可写事件到来的时候,回调TcpConnection::handleWrite channel_->setWriteCallback(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleWrite, this)); // 连接关闭,回调TcpConnection::handleClose channel_->setCloseCallback(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleClose, this)); // 发生错误,回调TcpConnection::handleError channel_->setErrorCallback(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleError, this)); LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::ctor[" << name_ << "] at " << this<< " fd=" << sockfd; socket_->setKeepAlive(true);//定期探测连接是否存在,类似于心跳包 } TcpConnection::~TcpConnection() { LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::dtor[" << name_ << "] at " << this << " fd=" << channel_->fd(); } // 线程安全,可以跨线程调用 void TcpConnection::send(const void *data, size_t len) { if (state_ == kConnected) { if (loop_->isInLoopThread()) { sendInLoop(data, len); } else { string message(static_cast<const char *>(data), len); loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::sendInLoop,this,message)); } } } // 线程安全,可以跨线程调用 void TcpConnection::send(const StringPiece &message) { if (state_ == kConnected) { if (loop_->isInLoopThread()) { sendInLoop(message); } else { loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::sendInLoop,this,message.as_string())); //std::forward<string>(message))); } } } // 线程安全,可以跨线程调用 void TcpConnection::send(Buffer *buf) { if (state_ == kConnected) { if (loop_->isInLoopThread()) { sendInLoop(buf->peek(), buf->readableBytes()); buf->retrieveAll(); } else { loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::sendInLoop,this,buf->retrieveAllAsString())); //std::forward<string>(message))); } } } void TcpConnection::sendInLoop(const StringPiece &message) { sendInLoop(message.data(), message.size()); } //???这个函数和handlewrite函数都是向文件描述符中写入,有什么区别呢? void TcpConnection::sendInLoop(const void *data, size_t len) { /* loop_->assertInLoopThread(); sockets::write(channel_->fd(), data, len); */ loop_->assertInLoopThread(); ssize_t nwrote = 0; size_t remaining = len; bool error = false; if (state_ == kDisconnected) { LOG_WARN << "disconnected, give up writing"; return; } // if no thing in output queue, try writing directly // 通道没有关注可写事件并且发送缓冲区没有数据,直接write if (!channel_->isWriting() && outputBuffer_.readableBytes() == 0) { nwrote = sockets::write(channel_->fd(), data, len); if (nwrote >= 0) { remaining = len - nwrote; // 写完了,回调writeCompleteCallback_ if (remaining == 0 && writeCompleteCallback_) { loop_->queueInLoop(boost::bind(writeCompleteCallback_, shared_from_this())); } } else // nwrote < 0 { nwrote = 0; if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK) { LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::sendInLoop"; if (errno == EPIPE) // FIXME: any others? { error = true; } } } } assert(remaining <= len); // 没有错误,并且还有未写完的数据(说明内核发送缓冲区满,要将未写完的数据添加到output buffer中) if (!error && remaining > 0) { LOG_TRACE << "I am going to write more data"; size_t oldLen = outputBuffer_.readableBytes(); // 如果超过highWaterMark_(高水位标),回调highWaterMarkCallback_ if (oldLen + remaining >= highWaterMark_ && oldLen < highWaterMark_ && highWaterMarkCallback_) { loop_->queueInLoop(boost::bind(highWaterMarkCallback_, shared_from_this(), oldLen + remaining)); } outputBuffer_.append(static_cast<const char *>(data) + nwrote, remaining);//将剩余数据存入应用层发送缓冲区 if (!channel_->isWriting()) { channel_->enableWriting(); // 关注POLLOUT事件 } } } void TcpConnection::shutdown()//关闭连接 { // FIXME: use compare and swap if (state_ == kConnected) { setState(kDisconnecting); // FIXME: shared_from_this()? loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::shutdownInLoop, this)); } } void TcpConnection::shutdownInLoop()//在loop中关闭写半边,还是可以读数据 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); if (!channel_->isWriting()) { // we are not writing socket_->shutdownWrite(); } } void TcpConnection::setTcpNoDelay(bool on)//设置TCP延迟连接 { socket_->setTcpNoDelay(on); } void TcpConnection::connectEstablished()//这个建立连接是TcpConnection类中的channel加入到对应的比如Tcpclient或者Tcpserver类所属的eventloop中 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); assert(state_ == kConnecting);//设置正在连接状态 setState(kConnected); LOG_TRACE << "[3] usecount=" << shared_from_this().use_count(); channel_->tie(shared_from_this()); channel_->enableReading(); // TcpConnection所对应的通道加入到Poller关注 connectionCallback_(shared_from_this()); LOG_TRACE << "[4] usecount=" << shared_from_this().use_count(); } void TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()//取消连接,从对应的Eventloop上的epoll队列中去除 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); if (state_ == kConnected) { setState(kDisconnected); channel_->disableAll(); connectionCallback_(shared_from_this()); } channel_->remove();//将channel从epoll队列中移除 } void TcpConnection::handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime)//处理读事件的函数 { /* loop_->assertInLoopThread(); int savedErrno = 0; ssize_t n = inputBuffer_.readFd(channel_->fd(), &savedErrno); if (n > 0) { messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), &inputBuffer_, receiveTime); } else if (n == 0) { handleClose(); } else { errno = savedErrno; LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleRead"; handleError(); } */ /* loop_->assertInLoopThread(); int savedErrno = 0; char buf[65536]; ssize_t n = ::read(channel_->fd(), buf, sizeof buf); if (n > 0) { messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), buf, n); } else if (n == 0) { handleClose(); } else { errno = savedErrno; LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleRead"; handleError(); } */ loop_->assertInLoopThread(); int savedErrno = 0; ssize_t n = inputBuffer_.readFd(channel_->fd(), &savedErrno);//直接将数据读到inputBuffer_缓冲区 if (n > 0) { messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), &inputBuffer_, receiveTime); } else if (n == 0) { handleClose();//如果读到的数据为0,就自动退出 } else { errno = savedErrno; LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleRead"; handleError(); } } // 监听到写事件了,就调用这个函数,此时服务器已经把要写的内容写到outputBuffer_中去了,所以要写的内容从读指针处开始 void TcpConnection::handleWrite() { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); if (channel_->isWriting())//查看是否有写事件需要关注 { ssize_t n = sockets::write(channel_->fd(), outputBuffer_.peek(), outputBuffer_.readableBytes());//写到文件描述符中去 if (n > 0) { outputBuffer_.retrieve(n);//处理读写指针 if (outputBuffer_.readableBytes() == 0) // 发送缓冲区已清空 { channel_->disableWriting(); // 停止关注POLLOUT事件,以免出现busy loop if (writeCompleteCallback_) // 回调writeCompleteCallback_ { // 应用层发送缓冲区被清空,就回调用writeCompleteCallback_ // 发送给IO线程进行处理 loop_->queueInLoop(boost::bind(writeCompleteCallback_, shared_from_this())); } if (state_ == kDisconnecting) // 发送缓冲区已清空并且连接状态是kDisconnecting, 要关闭连接 { shutdownInLoop(); // 关闭写连接 } } else { LOG_TRACE << "I am going to write more data"; } } else { LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleWrite"; // if (state_ == kDisconnecting) // { // shutdownInLoop(); // } } } else { LOG_TRACE << "Connection fd = " << channel_->fd() << " is down, no more writing"; } } void TcpConnection::handleClose()//关闭事件处理,也是epoll如果发生关闭事件的回调函数 { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel_->fd() << " state = " << state_; assert(state_ == kConnected || state_ == kDisconnecting); // we don't close fd, leave it to dtor, so we can find leaks easily. setState(kDisconnected); channel_->disableAll(); TcpConnectionPtr guardThis(shared_from_this()); connectionCallback_(guardThis); // 在结束前,最后一次处理一下,这一行,可以不调用 LOG_TRACE << "[7] usecount=" << guardThis.use_count(); // must be the last line closeCallback_(guardThis); // 调用TcpServer::removeConnection LOG_TRACE << "[11] usecount=" << guardThis.use_count(); } void TcpConnection::handleError()//处理错误的函数,也是epoll如果发生错误事件的回调函数 { int err = sockets::getSocketError(channel_->fd()); LOG_ERROR << "TcpConnection::handleError [" << name_ << "] - SO_ERROR = " << err << " " << strerror_tl(err); }