议程
1.LINQ To SQL概述
2.LINQ To SQL对象模型
3.LINQ To SQL查询
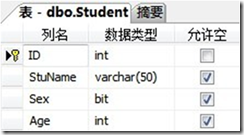
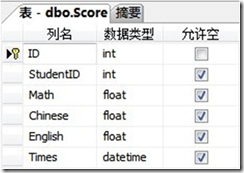
用到的数据库
SQL Server 2005,数据库名为Test。
两张表,分别为Student学生表和Score成绩表
LINQ To SQL概述
在 LINQ to SQL 中,关系数据库的数据模型映射到用开发人员所用的编程语言表示的对象模型。当应用程序运行时,LINQ to SQL 会将对象模型中的语言集成查询转换为 SQL,然后将它们发送到数据库进行执行。当数据库返回结果时,LINQ to SQL 会将它们转换回您可以用您自己的编程语言处理的对象。
LINQ To SQL对象模型
在 LINQ to SQL 中,用开发人员所用的编程语言表示的对象模型映射到关系数据库的数据模型。然后就会按照对象模型来执行对数据的操作。
在这种情况下,您无需向数据库发出数据库命令(例如,INSERT),而是在对象模型中更改值和执行方法。当您需要查询数据库或向其发送更改时,LINQ to SQL 会将您的请求转换成正确的 SQL 命令,然后将这些命令发送到数据库。
DataBase属性
DataBase属性用于在定义数据和对象之间的映射时指定数据库的名称。这个属性有一个Name特性,用来保存要为定义映射的数据库的名称。
class LinqToSql
{
static void Main()
{
TestDB td = new TestDB("server=.;uid=sa;pwd=sa;");
Console.WriteLine(td.DatabaseExists());//存在Test数据库
}
}
[Database(Name = "Test")]
class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constring)
: base(constring)
{
}
}
映射表
在 LINQ to SQL 中,数据库表由实体类表示。实体类与您可能创建的任何其他类相似,只不过对实体类进行批注的方法是使用将该类与数据库表关联的特殊信息。您需通过向类声明中添加自定义属性 (TableAttribute) 来进行这种批注。
只有声明为表的类(即实体类)的实例才能保存到数据库中。
[Table(Name = " Student ")]
public class Customerzz
{
}
映射列
除了将类与表关联以外,您还需指定字段或属性来表示数据库列。为此,LINQ to SQL 定义了 ColumnAttribute 属性。
只有映射到列的字段和属性才能持久保存到数据库中,从数据库中也只能检索这样的字段和属性。那些未声明为列的字段和属性被视为应用程序逻辑的瞬态部分。
[Table(Name = " Student ")]
public class Customerzz
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID
{ get; set; }
[Column]
public string StuName
{ get; set; }
[Column]
public bool Sex
{ get; set; }
[Column]
public int Age
{ get; set; }
}
下表介绍了此属性 (Attribute) 的属性 (Property)。
映射关系
在 LINQ to SQL 中,数据库关联(如外键到主键关系)是通过应用 AssociationAttribute 属性表示的。
可以在您的实体类中将始终相同的任何数据关系编码为属性引用。例如,在 Northwind 示例数据库中,由于客户通常会下订单,因此在模型中客户与其订单之间始终存在关系。
LINQ to SQL 定义了 AssociationAttribute 属性来帮助表示此类关系。此属性与 EntitySet <Tentity> 和 EntityRef<Tentity> 类型一起使用,来表示将作为数据库中的外键关系的内容。
EntitySet <Tentity>:为 LINQ to SQL 应用程序中的一对多关系和一对一关系的集合方提供延迟加载和关系维护。
EntityRef<Tentity>:为 LINQ to SQL 应用程序中的一对多关系的单一实例方提供延迟加载和关系维护。
大多数关系都是一对多关系,这一点在本主题后面部分的示例中会有所体现。您还可以按如下方式来表示一对一和多对多关系:
l一对一:通过向双方添加 EntitySet<(Of <(TEntity>)>) 来表示此类关系。
例如,假设有一个 Customer-SecurityCode 关系,创建此关系的目的是使得在 Customer 表中找不到客户的安全码,而只有得到授权的人才能访问此安全码。
l多对多:在多对多关系中,链接表(也称作联接表)的主键通常由来自其他两个表的外键组合而成。
例如,假设有一个通过使用链接表 EmployeeProject 构成的 Employee-Project 多对多关系。LINQ to SQL 要求使用以下三个类对这种关系进行模型化: Employee、Project 和 EmployeeProject。在这种情况下,更改 Employee 和 Project 之间的关系似乎需要更新主键 EmployeeProject。但是,这种情况最好的模型化处理方法是删除现有 EmployeeProject,然后创建新的 EmployeeProject。
映射关系Demo
EntytySet<Tentity>
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
private EntitySet<Score> _Scores;
[Association(Storage = "_Score", OtherKey = "StudentID")]
public EntitySet<Score> Scores
{
get { return this._Scores; }
set { this._Scores.Assign(value); }
}
}
[Table(Name = "Score")]
public class Score
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public int StudentID;
[Column]
public float Math;
[Column]
public float Chinese;
[Column]
public float English;
[Column]
public DateTime Times;
}
映射关系Demo
EntytySet<Tentity>
[Table(Name = "Score")]
public class Score
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public int StudentID;
[Column]
public float Math;
[Column]
public float Chinese;
[Column]
public float English;
[Column]
public DateTime Times;
private EntityRef<Student> _Student;
[Association(Storage = "_Student", ThisKey = "StudentID")]
public Student Student
{
get { return this._Student.Entity; }
set { this._Student.Entity = value; }
}
}
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
映射函数和存储过程
LINQ to SQL 支持存储过程和用户定义的函数。在 LINQ to SQL 中,您应将数据库定义的这些抽象映射到客户端对象,以便您可以从客户端代码中以强类型化方式访问它们。方法签名与数据库中定义的过程和函数的签名尽可能类似。
通过调用映射的过程返回的结果集为强类型化的集合。
LINQ to SQL 通过使用 FunctionAttribute 和 ParameterAttribute 属性将存储过程和函数映射到方法。表示存储过程的方法与表示用户定义的函数的方法通过 IsComposable 属性加以区分。如果此属性设置为 false(默认值),则此方法表示存储过程。如果它设置为 true,则此方法表示数据库函数。
[Function(Name = "GetScores")]
public ISingleResult<GetScores> getset([Parameter (DbType="int")] int stuid)
{
IExecuteResult result = this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, ((MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod())),stuid);
return ((ISingleResult<GetScores>)(result.ReturnValue));
}
LINQ to SQL 是 ADO.NET 系列技术的一部分。它基于由 ADO.NET 提供程序模型提供的服务。因此,您可以将 LINQ to SQL 代码与现有的 ADO.NET 应用程序混合在一起,将当前 ADO.NET 解决方案迁移到 LINQ to SQL。
DataContext 类
表示 LINQ to SQL 框架的主入口点。
DataContext 是轻量的,创建它不需要很大的开销。典型的 LINQ to SQL 应用程序在方法范围内创建 DataContext 实例,或将这些实例创建为生存期较短的类(这些类表示相关数据库操作的逻辑集合)的成员。
DataContext 是用来连接到数据库、从中检索对象以及将更改提交回数据库的主要渠道。使用 DataContext 时就像使用 ADO.NET SqlConnection 一样。事实上,DataContext 是用您提供的连接或连接字符串初始化的。
DataContext 的用途是将您对对象的请求转换成要对数据库执行的 SQL 查询,然后将查询结果汇编成对象。DataContext 通过实现与标准查询运算符(如 Where 和 Select)相同的运算符模式来实现 语言集成查询 (LINQ)。
//实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//查询
DataContext DC = new DataContext(constr);
Table<Student> stus = DC.GetTable<Student>();
var stu = from student in stus
select student;
foreach (var st in stu)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},性名:{1},年龄:{2},性别:{3}",st.ID ,st.StuName ,st.Sex ,st.Age);
}
每个数据库表表示为一个可借助 GetTable 方法(通过使用实体类来标识它)使用的 Table 集合。
最佳的做法是声明一个强类型化的 DataContext,而不是依靠基本 DataContext 类和 GetTable 方法。强类型化的 DataContext 将所有 Table 集合声明为上下文的成员,如下例中所示。
强类型DataContext
//实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//强类型DataContext
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Scores> Scores;
}
//调用
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
var stu = from student in Test.Student
select student;
foreach (var st in stu)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},性名:{1},年龄:{2},性别:{3}",st.ID ,st.StuName ,st.Sex ,st.Age);
}
强类型DataContext添加
//实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//强类型DataContext
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Scores> Scores;
}
///添加
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
Student student = new Student();
student.StuName = "大张";
student.Sex = false;
student .Age =34;
Test.Student.InsertOnSubmit(student);
Test.SubmitChanges();
强类型DataContext修改
//实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//强类型DataContext
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Scores> Scores;
}
//修改
var stud = Test.Student.Single(c => c.ID == 4);
Stud.StuName=“桂”;
//批量修改
//var stud = Test.Student.Where(c => c.ID >1);
//foreach (var st in stud )
//{
// st.StuName = "桂";
//}
Test.SubmitChanges();
强类型DataContext删除
//实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//强类型DataContext
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Scores> Scores;
}
//删除
//var stud = Test.Student.Where(c => c.ID >3);
//Test.Student.DeleteAllOnSubmit(stud);//批量删除
var stud = Test.Student.Single(c => c.ID == 4);
Test.Student.DeleteOnSubmit(stud);//单个删除
Test.SubmitChanges();
存储过程-根据一个参数查询一个集合
//存储过程
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetScores]
( @stuid int )
AS
SELECT id,studentid,math,chinese,english,times
FROM score
WHERE studentid=@stuid
//成绩实体类
[Table(Name = "Scores")]
public class Scores
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int StudentID;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Math;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Chinese;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float English;
[Column(DbType = "Datetime")]
public DateTime Times;
}
//定义执行存储过程方法
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
[Function(Name = "GetScores")]
public ISingleResult<Scores> getset([Parameter(DbType = "int")] int stuid)
{
IExecuteResult result = this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, ((MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod())), stuid);
return ((ISingleResult<Scores>)(result.ReturnValue));
}
}
//执行存储过程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
ISingleResult<Scores> retValue = Test.getset(2);
foreach (Scores value in retValue)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},语文:{1},数学:{2},考试时间:{3}",value .ID ,value .Chinese ,value .Math , value.Times);
}
存储过程-出参的实现
//存储过程
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetMaxMath]
@maxMath int output
AS
BEGIN
select @maxMath= max(math) from score
END
//定义执行存储过程方法
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
//实现存储过程
[Function(Name = "GetMaxMath")]
public int GetMaxMath([Parameter(DbType = "int")] ref int maxMath)
{
IExecuteResult result = this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, ((MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod())), maxMath);
maxMath = (int)result.GetParameterValue(0);
return (int)result.ReturnValue;
}
}
//执行存储过程
static string constr = "server=.;database=test;uid=sa;pwd=sa;";
static void Main()
{
//调用存储课程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
int value = 0;
Test.GetMaxMath(ref value);
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
存储过程-返回多个集合
//存储过程
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetStudentScore]
AS
BEGIN
select * from student
select * from score
END
//Scores实体类
[Table(Name = "Scores")]
public class Scores
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int StudentID;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Math;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Chinese;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float English;
[Column(DbType = "Datetime")]
public DateTime Times;
}
//Student实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true)]
public int ID;
[Column]
public string StuName;
[Column]
public bool Sex;
[Column]
public int Age;
}
//定义执行存储过程方法
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
//实现存储过程
[Function(Name = "GetStudentScore")]
[ResultType(typeof(Student))]
[ResultType(typeof(Scores))]
public IMultipleResults GetSutdentScore()
{
IExecuteResult result = this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, ((MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod())));
return (IMultipleResults)result.ReturnValue;
}
}
//执行存储过程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
IMultipleResults Result = Test.GetSutdentScore ();
foreach (Student student in Result.GetResult<Student>())
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},姓名:{1},年龄:{2},性别:{3}",student.ID,student .StuName,student .Age ,student .Sex );
}
Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------------------------");
foreach (Scores scores in Result.GetResult<Scores>())
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},学生编号:{1},语文:{2},英语:{3},数学{4},时间:{5}",scores.ID,scores.StudentID ,scores .Chinese ,scores .English ,scores .Math ,scores.Times );
}
自定议函数
//定义执行自定义函数的方法
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
//实现自定义函数
[Function(Name = "GetStudent", IsComposable = true)]
public IQueryable<Student> GetStudentById(int id)
{
return (IQueryable<Student>)this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, (MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod()), id).ReturnValue;
}
}
//执行自定义函数
static string constr = "server=.;database=test;uid=sa;pwd=sa;";
static void Main()
{
//调用存储课程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
foreach (var student in Test.GetStudentById(3))
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},姓名:{1},年龄:{2},性别:{3}", student.ID, student.StuName, student.Age, student.Sex);
}
}
表间关系查询
EnitySet类型为一对多关系中的“多”方的结果提供集合。与[Association]属性结合使用来定义并表示一个关系。OtherKey特性,指定在关联的另一端上作为键值的、目标实体类的一个或多个成员。
EnitityRef与EntitySet相反,用于一对多关系中的“一”方。与[Association]属性结合使用来定义并表示一个关系。ThisKey表示关联的此端上的键值的此实体类成员。
表间关系查询-EntitySet
//Student实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "varchar(50)")]
public string StuName;
[Column(DbType = "bit")]
public bool Sex;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int Age;
private EntitySet<Score> _scores;
[Association(Storage = "_scores", OtherKey = "StudentID")]
public EntitySet<Score> Score
{
get { return this._scores; }
set { this._scores.Assign(value); }
}
}
//Scores实体类
[Table(Name = "Score")]
public class Score
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int StudentID;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Math;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Chinese;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float English;
[Column(DbType = "Datetime")]
public DateTime Times;
}
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Score> Scores;
}
static string constr = "server=.;database=test;uid=sa;pwd=sa;";
static void Main()
{
//调用存储课程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
IQueryable<Student> s = from stu in Test.Student
select stu;
foreach (var v in s)
{
Console.WriteLine(v.StuName);
foreach (var o in v.Score)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},学生姓名:{1},学生年龄:{2},语文成绩:{3},考试时间:{4}", v.ID, v.StuName, v.Age, o.Chinese, o.Times.ToString("yyyy年MM月dd日"));
}
}
}
表间关系查询-EntytyRef
//Student实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "varchar(50)")]
public string StuName;
[Column(DbType = "bit")]
public bool Sex;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int Age;
}
//Scores实体类
[Table(Name = "Score")]
public class Score
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int StudentID;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Math;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Chinese;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float English;
[Column(DbType = "Datetime")]
public DateTime Times;
private EntityRef<Student> _Student;
[Association(Storage = "_Student", ThisKey = "StudentID")]
public Student Student
{
get { return this._Student.Entity; }
set { this._Student.Entity = value; }
}
}
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Score> Scores;
}
static string constr = "server=.;database=test;uid=sa;pwd=sa;";
static void Main()
{
//调用存储课程
TestDB Test = new TestDB(constr);
var query = from sco in Test.Scores
select sco;
foreach (var s in query)
{
Console.WriteLine("编号:{0},学生姓名:{1},学生年龄:{2},语文成绩:{3},考试时间:{4}", s.StudentID ,s.Student.StuName, s.Student.Age,s.Chinese, s.Times.ToString("yyyy年MM月dd日"));
}
}
事务-隐式事务
//数据库类
public class TestDB : DataContext
{
public TestDB(string constr)
: base(constr)
{ }
public Table<Student> Student;
public Table<Score> Scores;
}
//Student实体类
[Table(Name = "Student")]
public class Student
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated=true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "varchar(50)")]
public string StuName;
[Column(DbType = "bit")]
public bool Sex;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int Age;
}
//Scores实体类
[Table(Name = "Score")]
public class Score
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated =true, DbType = "int")]
public int ID;
[Column(DbType = "int")]
public int StudentID;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Math;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float Chinese;
[Column(DbType = "float")]
public float English;
[Column(DbType = "Datetime")]
public DateTime Times;
}
static string constr = "server=.;database=test;uid=sa;pwd=sa;";
static void Main()
{
TestDB test = new TestDB(constr);
using (TransactionScope tran = new TransactionScope())
{
Student student = new Student();
student.StuName = "桂素伟";
student.Sex = false;
student.Age = 20;
test.Student.InsertOnSubmit(student);
Score score = new Score();
score.StudentID =3;
score.Chinese = 90f;
score.English = 80f;
score.Math = 80f;
score.Times = DateTime.Now;
test.Scores.InsertOnSubmit(score);
test.SubmitChanges();
tran.Complete();
tran.Dispose();
}
}
事务-显式事务
TestDB test = new TestDB(constr);
test.Connection.Open();
test.Transaction = test.Connection.BeginTransaction();
try
{
Student student = new Student();
student.StuName = "桂素伟";
student.Sex = false;
student.Age = 20;
test.Student.InsertOnSubmit(student);
Score score = new Score();
score.StudentID = 3;
score.Chinese = 90f;
score.English = 80f;
score.Math = 80f;
score.Times = DateTime.Now;
test.Scores.InsertOnSubmit(score);
test.SubmitChanges();
test.Transaction.Commit();
}
catch
{
test.Transaction.Rollback();
}
finally
{
test.Transaction.Dispose();
test.Connection.Close();
}
文章摘录自:http://www.cnblogs.com/axzxs2001/archive/2009/08/29/1556363.html
![I176%5LA`G]I(TB1YQ`L423 I176%5LA`G]I(TB1YQ`L423](https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/axzxs2001/WindowsLiveWriter/LINQToSQL_EE32/I176%255LA%60G%5DI(TB1YQ%60L423_thumb.jpg)
![788R@7V$WTP4@KQ2()_`U99[4] 788R@7V$WTP4@KQ2()_`U99[4]](https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/axzxs2001/WindowsLiveWriter/LINQToSQL_EE32/788R@7V$WTP4@KQ2()_%60U99%5B4%5D_thumb_1.jpg)
