在测试过程中,参数化是必不可少的功能,本文就讨论下pytest的几种参数化方法
@pytest.mark.parametrize:参数化测试函数
1.内置的pytest.mark.parametrize装饰器支持测试函数的参数化基本用法
例如:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input,expect",[("3+5",8),("5+5",9),("4+9",12),("10+21",31)])
def test_param(input,expect):
assert eval(input)==expect
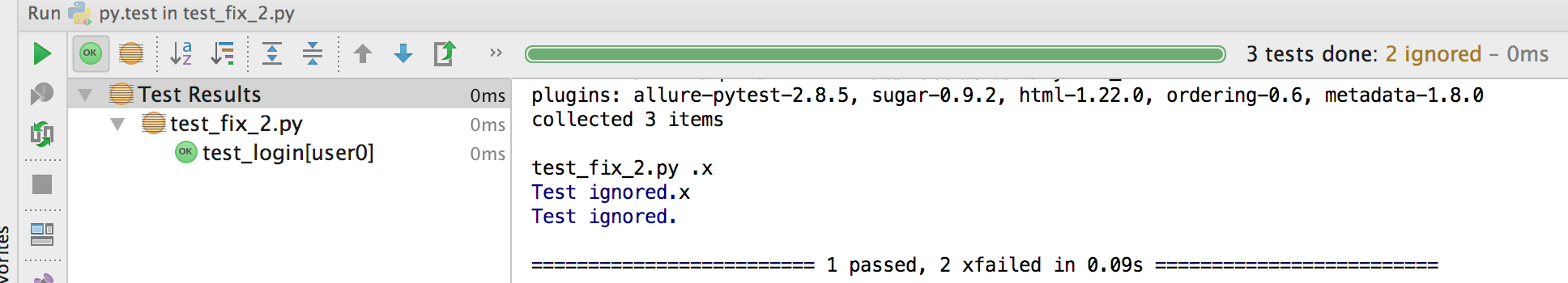
结果:成功2个失败2个.
2.它也可以标记单个测试实例在参数化,例如使用内置的mark.xfail
@pytest.mark.parametrize("input,expect",[("3+5",8),("5+5",9),("4+9",12),pytest.param("10+21",31,marks=pytest.mark.xfail)])
def test_param(input,expect):
assert eval(input)==expect
3.参数组合测试:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("x",[1,2,3,4])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("y",[3,4])
def test_param(x,y):
print("参数组合%s,******,%s"%(x,y))
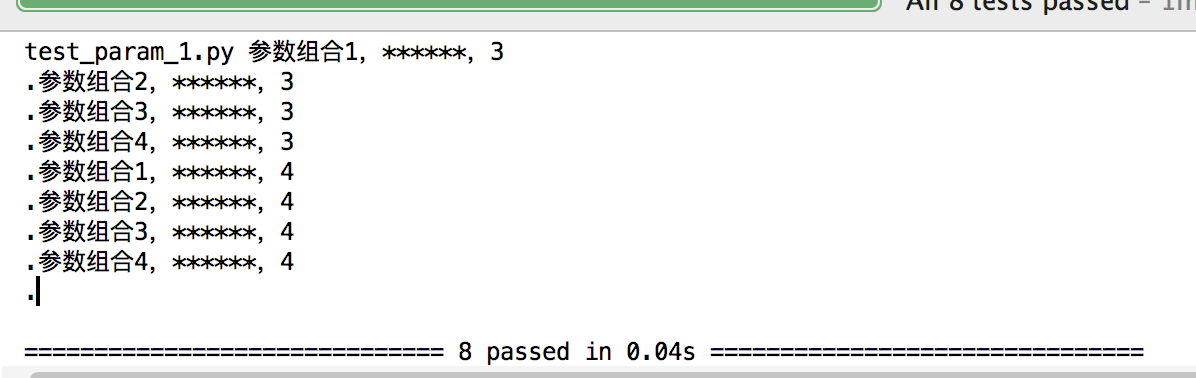
结果会测试8次组合结果,如图:
fixture参数化
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=[1,2,3,4,'abd']) ---可以是列表、也可以是元祖
def user(request): --- request是固定写法
return request.param --request也是固定写法
def test_login(user):
print("user:%s"%user)
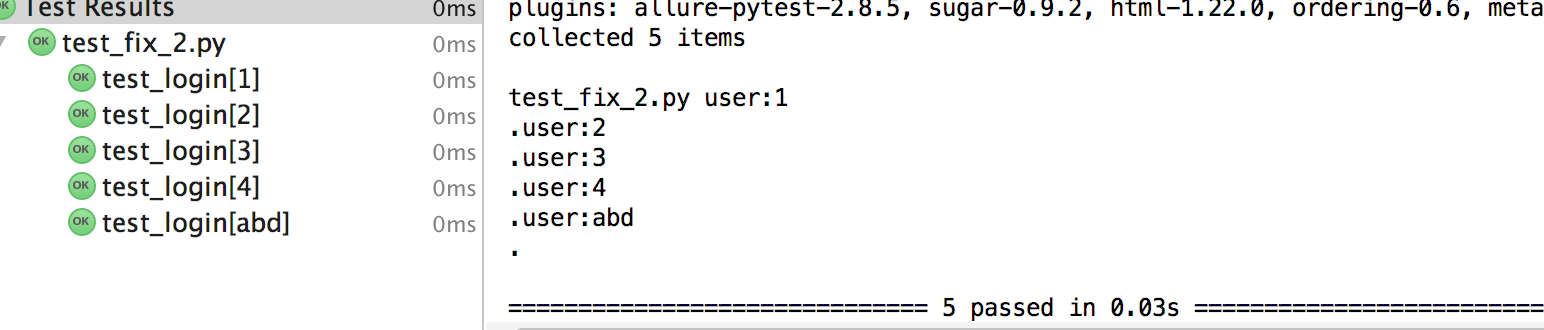
输出结果:
列表内包含字典数据格式参数化
例如有个登录窗口,分别验证用户名、密码正确,用户名、密码正确,用户名为空、密码为空等情况,并有个预期结果验证。
参数组成:
users =[
{"username":"test","password":"test","expect":"login success"},
{"username":"test1","password":"test1","expect":"login Fail"},
{"username":"","password":"test","expect":"username not empty"}
]
代码示例:
@pytest.fixture(params=users)
def user(request):
return request.param
def test_login(user):
username=user["username"]
password=user["password"]
if username=="test" and password=='test':
assert "login success" == user["expect"]
else:
pytest.xfail(reason="Fail")
输出结果: