1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class base{ //基类 4 public: 5 void a(void) 6 { 7 cout<<"base::a called "; 8 } 9 virtual void b(void) //虚函数 10 { 11 cout<<"base::b called "; 12 } 13 virtual void c(void) //虚函数 14 { 15 cout<<"base::c called "; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 class derived:public base{ //派生类 20 public: 21 void a(void) {cout<<"derived::a called ";} //派生类自定义的成员函数a 和 b,c继承于基类 22 void b(void) {cout<<"derived::b called ";} 23 }; 24 25 void do_base(base &a_base) // 基类作为变量,只在基类找成员函数 26 { 27 cout<<"call function in the base class "; 28 a_base.a(); //base::a called 29 a_base.b(); //derived::b called 虚函数作用 30 a_base.c(); //base::c called 31 } 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 derived a_derived; //定义derived对象 36 cout<<"calling function in the derived class "; 37 38 a_derived.a(); //调用a时,查看派生类,derived::a called 39 a_derived.b(); //derived::b called 40 a_derived.c(); //base::c called 派生类寻找失败,基类寻找 41 42 do_base(a_derived); 43 system("pause"); 44 return (0); 45 }
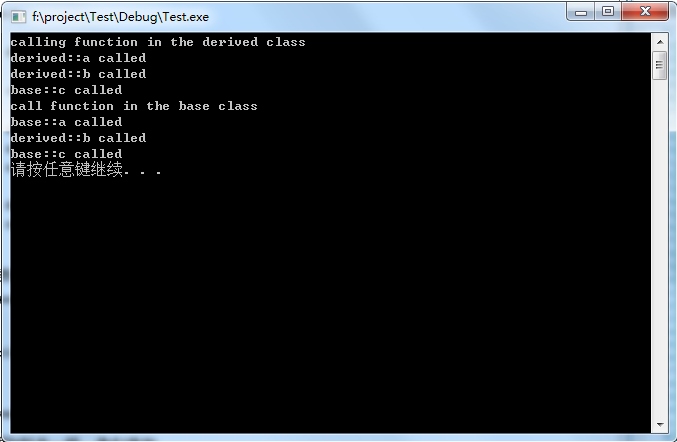
base为基类 derived为派生类
派生类有三个成员函数,其中两个是自定的:a和b,第三个c是继承于基类的,当调用a时,先查看派生类是否有a的定义:base::a called
b同理得::base::b called
但是当调用c时,派生类中没有定义这个成员函数,所以转到基类中寻找,即得到:base::c called
do_base函数,带有一个基类作为它的变量,所以C++只在基类中寻找成员函数
将输出:
base::a called
当调用成员函数b时,因为基类中b函数是一个虚函数,C++首先在派生类中寻找有没有成员函数b,然后在基类寻找,所以调用b输出:
derived::b called
当调用成员函数c时,先在派生类中寻找函数,但c并没有在派生类中定义,所以再去基类寻找,所以调用c输出:
base::c called
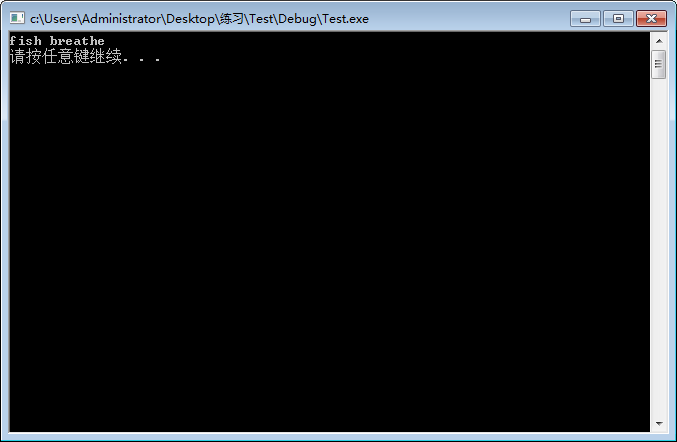
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class animal 4 { 5 public: 6 void eat() 7 { 8 cout<<"animal eat"<<endl; 9 } 10 virtual void breathe() 11 { 12 cout<<"animal breathe"<<endl; 13 } 14 }; 15 class fish:public animal 16 { 17 public: 18 void breathe() 19 { 20 cout<<"fish breathe"<<endl; 21 } 22 }; 23 void fn(animal * pAn) //指向animal类的指针作为全局函数fn()的参数 将基类作为参数,若有虚函数,调用派生类中的函数实现 24 { 25 pAn->breathe(); 26 } 27 void main() 28 { //指针表示一个地址 29 animal *pAn; //定义指向animal类的指针 pAn表示地址 *pAn表示该地址的值 30 fish fh; //实例化fish对象 31 pAn=&fh; //将fh的地址传给pAn 因为fish对象也是animal对象,将fish转换成animal类型不需要强制类型转换,C++编译器会自动转换 32 fn(pAn); //执行fn函数 ,如果animal中breathe为虚函数,C++就会采取迟绑定技术 33 system("pause"); 34 //多态性:在基类的函数前加virtual关键字,在派生类中重写该函数,运行时就会根据对象的实际类型来调用相应函数 35 }