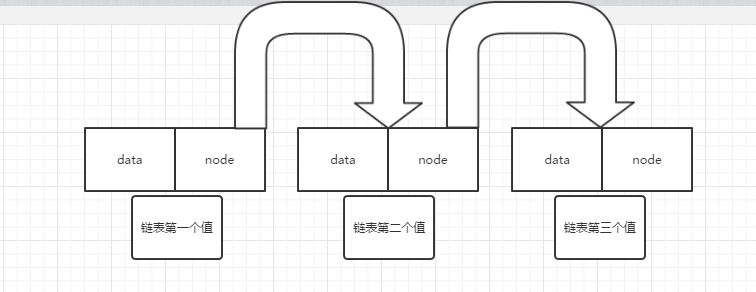
链表的实现原理
存储结构:
data为链表存储的数据,node则是向下一个元素的对象,若node为null,则表示该元素为该个链表的最后一个元素
java实现
package com.study; /** * 链表实体 * * @author qiutianyou * */ class Linked { public int count;//统计新增次数 public Node root;// 根节点 /** * 新增 * @param data */ public void add(String data) { Node newNode = new Node(data);//生成新节点 if (this.root == null) {//如果根节点不存在 this.root = newNode; } else { this.root.addNode(newNode); } count++; } /** * 输出 */ public void print() { if (this.root != null) { this.root.printNode(); } } /** * 链表的长度 * @return */ public int size() { return count; } /** * 私有的节点实体类 * * @author qiutianyou * */ private class Node { String data; Node next; public Node(String data) { this.data = data; } public void addNode(Node newNode) { if (this.next == null) { this.next = newNode; } else { this.next.addNode(newNode); } } /** * 递归调用printNode,输出;链表存储的data */ public void printNode() { System.out.println(this.data);//第一次 this=root,第二次调用时 this=root.next,第三次调用时 this=root.next.next if (this.next != null) { this.next.printNode(); } } } }