从一个比较有意思的题开始说起,最近要找工作无意间看到一个关于unix/linux中fork()的面试题:
1 1 #include<sys/types.h> 2 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 3 #include<unistd.h> 4 4 int main(void) 5 5 { 6 6 int i; 7 7 int buf[100]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; 8 8 for(i=0;i<2;i++) 9 9 { 10 10 fork(); 11 11 printf("+"); 12 12 //write("/home/pi/code/test_fork/test_fork.txt",buf,8); 13 13 write(STDOUT_FILENO,"-",1); 14 14 } 15 15 return 0; 16 16 17 17 }
题目要求是从上面的代码中确定输出的“+”的数量,我后面加了一个“-”,再确定输出“-”的数量。
先给答案:“+”8次,“-”6次
1 ---++--++-++++
上面的这段代码很简单,包含的内容却有很多,有进程产生、系统调用、不带缓冲I/O、标准I/O。
linux中产生一个进程的调用函数过程如下:
fork()---------->sys_fork()-------------->do_fork()---------->copy_process()
fork()、vfork()、_clone()库函数都根据各自需要的参数标志去调用clone(),然后由clone()去调用do_fork()。do_fork()完成了创建中的大部分工作,该函数调用copy_process()函数,
从用户空间调用fork()函数到执行系统调用产生软件中断陷入内核空间,在内核空间执行do_fork()函数,主要是复制父进程的页表、内核栈等,如果要执行子进程代码还要调用exac()函数拷贝硬盘上的代码到位内存上,由于刚创建的子进程没有申请内存,目前和父进程共用父进程的代码段、数据段等,没有存放子进程自己代码段数据段的内存,此时会产生一个缺页异常,为子进程申请内存,同时定制自己的全局描述GDT、局部描述符LDT、任务状态描述符TSS,下面从代码中分析这个过程然后在回答上面为什么“+”是8次,“-”6次。
调用fork()函数执行到了unistd.h中的宏函数syscall0
1 /* XXX - _foo needs to be __foo, while __NR_bar could be _NR_bar. */ 2 /* 3 * Don't remove the .ifnc tests; they are an insurance against 4 * any hard-to-spot gcc register allocation bugs. 5 */ 6 #define _syscall0(type,name) 7 type name(void) 8 { 9 register long __a __asm__ ("r10"); 10 register long __n_ __asm__ ("r9") = (__NR_##name); 11 __asm__ __volatile__ (".ifnc %0%1,$r10$r9 " 12 ".err " 13 ".endif " 14 "break 13" 15 : "=r" (__a) 16 : "r" (__n_)); 17 if (__a >= 0) 18 return (type) __a; 19 errno = -__a; 20 return (type) -1; 21 }
将宏函数展开后变为
1 /* XXX - _foo needs to be __foo, while __NR_bar could be _NR_bar. */ 2 /* 3 * Don't remove the .ifnc tests; they are an insurance against 4 * any hard-to-spot gcc register allocation bugs. 5 */ 7 int fork(void) 8 { 9 register long __a __asm__ ("r10"); 10 register long __n_ __asm__ ("r9") = (__NR_##name); 11 __asm__ __volatile__ (".ifnc %0%1,$r10$r9 " 12 ".err " 13 ".endif " 14 "break 13" 15 : "=r" (__a) 16 : "r" (__n_)); 17 if (__a >= 0) 18 return (type) __a; 19 errno = -__a; 20 return (type) -1; 21 }
##的意思就是宏中的字符直接替换
如果name = fork,那么在宏中__NR_##name就替换成了__NR_fork了。
__NR_##name是系统调用号,##指的是两次宏展开.即用实际的系统调用名字代替"name",然后再把__NR_...展开.如name == ioctl,则为__NR_ioctl。
上面的汇编目前还是没有怎么弄懂-------
int $0x80 是所有系统调用函数的总入口,fork()是其中之一,“0”(_NR_fork) 意思是将fork在sys_call_table[]中对应的函数编号_NR_fork也就是2,将2传给eax寄存器。这个编号就是sys_fork()函数在sys_call_table中的偏移值,其他的系统调用在sys_call_table均存在偏移值()。
int $0x80 中断返回后,将执行return (type) -1----->展开就是return (int) __a;产生int $0x80软件中断,CPU从3级特权的进程跳到0特权级内核代码中执行。中断使CPU硬件自动将SS、ESP、EFLAGGS、CS、EIP这五个寄存器的值按照这个顺序压人父进程的内核栈,这些压栈的数据将在后续的copy_process()函数中用来初始化进程1的任务状态描述符TSS
CPU自动压栈完成后,跳转到system_call.s中的_system_call处执行,继续将DS、ES、FS、EDX、ECX、EBX压栈(这些压栈仍旧是为了初始化子进程中的任务状态描述符TSS做准备)。最终内核通过刚刚设置的eax的偏移值“2”查询sys_call_table[],知道此次系统调用对应的函数是sys_fork()。跳转到_sys_fork处执行。
注意:一个函数的参数不是由函数定义的,而是由函数定义以外的程序通过压栈的方式“做”出来的,是操作系统底层代码与应用程序代码写作手法的差异之一。我们知道在C语言中函数运行时参数是存在栈中的,根据这个原理操作系统设计者可以将前面程序强行压栈的值作为函数的参数,当调用这个函数时这些值就是函数的参数。
sys_fork函数
1 asmlinkage int sys_fork(void) 2 { 3 #ifndef CONFIG_MMU 4 /* fork almost works, enough to trick you into looking elsewhere:-( */ 5 return -EINVAL; 6 #else 7 return do_fork(SIGCHLD, user_stack(__frame), __frame, 0, NULL, NULL); 8 #endif 9 }
do_fork函数
1 /* 2 * Ok, this is the main fork-routine. 3 * 4 * It copies the process, and if successful kick-starts 5 * it and waits for it to finish using the VM if required. 6 */ 7 long do_fork(unsigned long clone_flags, 8 unsigned long stack_start, 9 struct pt_regs *regs, 10 unsigned long stack_size, 11 int __user *parent_tidptr, 12 int __user *child_tidptr) 13 { 14 struct task_struct *p; 15 int trace = 0; 16 struct pid *pid = alloc_pid(); 17 long nr; 18 19 if (!pid) 20 return -EAGAIN; 21 nr = pid->nr; 22 if (unlikely(current->ptrace)) { 23 trace = fork_traceflag (clone_flags); 24 if (trace) 25 clone_flags |= CLONE_PTRACE; 26 } 27 dup_task_struct 28 p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, regs, stack_size, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, pid); 29 /* 30 * Do this prior waking up the new thread - the thread pointer 31 * might get invalid after that point, if the thread exits quickly. 32 */ 33 if (!IS_ERR(p)) { 34 struct completion vfork; 35 36 if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) { 37 p->vfork_done = &vfork; 38 init_completion(&vfork); 39 } 40 41 if ((p->ptrace & PT_PTRACED) || (clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED)) { 42 /* 43 * We'll start up with an immediate SIGSTOP. 44 */ 45 sigaddset(&p->pending.signal, SIGSTOP); 46 set_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_SIGPENDING); 47 } 48 49 if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED)) 50 wake_up_new_task(p, clone_flags); 51 else 52 p->state = TASK_STOPPED; 53 54 if (unlikely (trace)) { 55 current->ptrace_message = nr; 56 ptrace_notify ((trace << 8) | SIGTRAP); 57 } 58 59 if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) { 60 freezer_do_not_count(); 61 wait_for_completion(&vfork); 62 freezer_count(); 63 if (unlikely (current->ptrace & PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE)) { 64 current->ptrace_message = nr; 65 ptrace_notify ((PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE << 8) | SIGTRAP); 66 } 67 } 68 } else { 69 free_pid(pid); 70 nr = PTR_ERR(p); 71 } 72 return nr; 73 }
copy_process函数
1 /* 2 * This creates a new process as a copy of the old one, 3 * but does not actually start it yet. 4 * 5 * It copies the registers, and all the appropriate 6 * parts of the process environment (as per the clone 7 * flags). The actual kick-off is left to the caller. 8 */ 9 static struct task_struct *copy_process(unsigned long clone_flags, 10 unsigned long stack_start, 11 struct pt_regs *regs, 12 unsigned long stack_size, 13 int __user *parent_tidptr, 14 int __user *child_tidptr, 15 struct pid *pid) 16 { 17 int retval; 18 struct task_struct *p = NULL; 19 20 if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) 21 return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); 22 23 /* 24 * Thread groups must share signals as well, and detached threads 25 * can only be started up within the thread group. 26 */ 27 if ((clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND)) 28 return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); 29 30 /* 31 * Shared signal handlers imply shared VM. By way of the above, 32 * thread groups also imply shared VM. Blocking this case allows 33 * for various simplifications in other code. 34 */ 35 if ((clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_VM)) 36 return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); 37 38 retval = security_task_create(clone_flags); 39 if (retval) 40 goto fork_out; 41 42 retval = -ENOMEM; 43 p = dup_task_struct(current); 44 if (!p) 45 goto fork_out; 46 sys_fork 47 rt_mutex_init_task(p); 48 49 #ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS 50 DEBUG_LOCKS_WARN_ON(!p->hardirqs_enabled); 51 DEBUG_LOCKS_WARN_ON(!p->softirqs_enabled); 52 #endif 53 retval = -EAGAIN; 54 if (atomic_read(&p->user->processes) >= 55 p->signal->rlim[RLIMIT_NPROC].rlim_cur) { 56 if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN) && !capable(CAP_SYS_RESOURCE) && 57 p->user != &root_user) 58 goto bad_fork_free; 59 } 60 61 atomic_inc(&p->user->__count); 62 atomic_inc(&p->user->processes); 63 get_group_info(p->group_info); 64 65 /* 66 * If multiple threads are within copy_process(), then this check 67 * triggers too late. This doesn't hurt, the check is only there 68 * to stop root fork bombs. 69 */ 70 if (nr_threads >= max_threads) 71 goto bad_fork_cleanup_count; 72 73 if (!try_module_get(task_thread_info(p)->exec_domain->module)) 74 goto bad_fork_cleanup_count; 75 76 if (p->binfmt && !try_module_get(p->binfmt->module)) 77 goto bad_fork_cleanup_put_domain; 78 79 p->did_exec = 0; 80 delayacct_tsk_init(p); /* Must remain after dup_task_struct() */ 81 copy_flags(clone_flags, p); 82 p->pid = pid_nr(pid); 83 retval = -EFAULT; 84 if (clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT_SETTID) 85 if (put_user(p->pid, parent_tidptr)) 86 goto bad_fork_cleanup_delays_binfmt; 87 88 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->children); 89 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->sibling); 90 p->vfork_done = NULL; 91 spin_lock_init(&p->alloc_lock); 92 93 clear_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_SIGPENDING); 94 init_sigpending(&p->pending); 95 96 p->utime = cputime_zero; 97 p->stime = cputime_zero; 98 p->sched_time = 0; 99 #ifdef CONFIG_TASK_XACCT 100 p->rchar = 0; /* I/O counter: bytes read */ 101 p->wchar = 0; /* I/O counter: bytes written */ 102 p->syscr = 0; /* I/O counter: read syscalls */ 103 p->syscw = 0; /* I/O counter: write syscalls */ 104 #endif 105 task_io_accounting_init(p); 106 acct_clear_integrals(p); 107 108 p->it_virt_expires = cputime_zero; 109 p->it_prof_expires = cputime_zero; 110 p->it_sched_expires = 0; 111 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->cpu_timers[0]); 112 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->cpu_timers[1]); 113 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->cpu_timers[2]); 114 115 p->lock_depth = -1; /* -1 = no lock */ 116 do_posix_clock_monotonic_gettime(&p->start_time); 117 p->security = NULL; 118 p->io_context = NULL; 119 p->io_wait = NULL; 120 p->audit_context = NULL; 121 cpuset_fork(p); 122 #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA 123 p->mempolicy = mpol_copy(p->mempolicy); 124 if (IS_ERR(p->mempolicy)) { 125 retval = PTR_ERR(p->mempolicy); 126 p->mempolicy = NULL; 127 goto bad_fork_cleanup_cpuset; 128 } 129 mpol_fix_fork_child_flag(p); 130 #endif 131 #ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS 132 p->irq_events = 0; 133 #ifdef __ARCH_WANT_INTERRUPTS_ON_CTXSW 134 p->hardirqs_enabled = 1; 135 #else 136 p->hardirqs_enabled = 0; 137 #endif 138 p->hardirq_enable_ip = 0; 139 p->hardirq_enable_event = 0; 140 p->hardirq_disable_ip = _THIS_IP_; 141 p->hardirq_disable_event = 0; 142 p->softirqs_enabled = 1; 143 p->softirq_enable_ip = _THIS_IP_; 144 p->softirq_enable_event = 0; 145 p->softirq_disable_ip = 0; 146 p->softirq_disable_event = 0; 147 p->hardirq_context = 0; 148 p->softirq_context = 0; 149 #endif 150 #ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP 151 p->lockdep_depth = 0; /* no locks held yet */ 152 p->curr_chain_key = 0; 153 p->lockdep_recursion = 0; 154 #endif 155 156 #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES 157 p->blocked_on = NULL; /* not blocked yet */ 158 #endif 159 160 p->tgid = p->pid; 161 if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) 162 p->tgid = current->tgid; 163 164 if ((retval = security_task_alloc(p))) 165 goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy; 166 if ((retval = audit_alloc(p))) 167 goto bad_fork_cleanup_security; 168 /* copy all the process information */ 169 if ((retval = copy_semundo(clone_flags, p))) 170 goto bad_fork_cleanup_audit; 171 if ((retval = copy_files(clone_flags, p))) 172 goto bad_fork_cleanup_semundo; 173 if ((retval = copy_fs(clone_flags, p))) 174 goto bad_fork_cleanup_files; 175 if ((retval = copy_sighand(clone_flags, p))) 176 goto bad_fork_cleanup_fs; 177 if ((retval = copy_signal(clone_flags, p))) 178 goto bad_fork_cleanup_sighand; 179 if ((retval = copy_mm(clone_flags, p))) 180 goto bad_fork_cleanup_signal; 181 if ((retval = copy_keys(clone_flags, p))) 182 goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm; 183 if ((retval = copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p))) 184 goto bad_fork_cleanup_keys; 185 retval = copy_thread(0, clone_flags, stack_start, stack_size, p, regs); 186 if (retval) 187 goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces; 188 189 p->set_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_SETTID) ? child_tidptr : NULL; 190 /* 191 * Clear TID on mm_release()? 192 */ 193 p->clear_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID) ? child_tidptr: NULL; 194 p->robust_list = NULL; 195 #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT 196 p->compat_robust_list = NULL; 197 #endif 198 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->pi_state_list); 199 p->pi_state_cache = NULL; 200 201 /* 202 * sigaltstack should be cleared when sharing the same VM 203 */ 204 if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_VM|CLONE_VFORK)) == CLONE_VM) 205 p->sas_ss_sp = p->sas_ss_size = 0; 206 207 /* 208 * Syscall tracing should be turned off in the child regardless 209 * of CLONE_PTRACE. 210 */ 211 clear_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_SYSCALL_TRACE); 212 #ifdef TIF_SYSCALL_EMU 213 clear_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_SYSCALL_EMU); 214 #endif 215 216 /* Our parent execution domain becomes current domain 217 These must match for thread signalling to apply */ 218 p->parent_exec_id = p->self_exec_id; 219 220 /* ok, now we should be set up.. */ 221 p->exit_signal = (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) ? -1 : (clone_flags & CSIGNAL); 222 p->pdeath_signal = 0; 223 p->exit_state = 0; 224 225 /* 226 * Ok, make it visible to the rest of the system. 227 * We dont wake it up yet. 228 */ 229 p->group_leader = p; 230 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->thread_group); 231 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->ptrace_children); 232 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->ptrace_list); 233 234 /* Perform scheduler related setup. Assign this task to a CPU. */ 235 sched_fork(p, clone_flags); 236 237 /* Need tasklist lock for parent etc handling! */ 238 write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock); 239 240 /* for sys_ioprio_set(IOPRIO_WHO_PGRP) */ 241 p->ioprio = current->ioprio; 242 243 /* 244 * The task hasn't been attached yet, so its cpus_allowed mask will 245 * not be changed, nor will its assigned CPU. 246 * 247 * The cpus_allowed mask of the parent may have changed after it was 248 * copied first time - so re-copy it here, then check the child's CPU 249 * to ensure it is on a valid CPU (and if not, just force it back to 250 * parent's CPU). This avoids alot of nasty races. 251 */ 252 p->cpus_allowed = current->cpus_allowed; 253 if (unlikely(!cpu_isset(task_cpu(p), p->cpus_allowed) || 254 !cpu_online(task_cpu(p)))) 255 set_task_cpu(p, smp_processor_id()); 256 257 /* CLONE_PARENT re-uses the old parent */ 258 if (clone_flags & (CLONE_PARENT|CLONE_THREAD)) 259 p->real_parent = current->real_parent; 260 else 261 p->real_parent = current; 262 p->parent = p->real_parent; 263 264 spin_lock(¤t->sighand->siglock); 265 266 /* 267 * Process group and session signals need to be delivered to just the 268 * parent before the fork or both the parent and the child after the 269 * fork. Restart if a signal comes in before we add the new process to 270 * it's process group. 271 * A fatal signal pending means that current will exit, so the new 272 * thread can't slip out of an OOM kill (or normal SIGKILL). 273 */ 274 recalc_sigpending(); 275 if (signal_pending(current)) { 276 spin_unlock(¤t->sighand->siglock); 277 write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock); 278 retval = -ERESTARTNOINTR; 279 goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces; 280 } 281 282 if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) { 283 p->group_leader = current->group_leader; 284 list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group, &p->group_leader->thread_group); 285 286 if (!cputime_eq(current->signal->it_virt_expires, 287 cputime_zero) || 288 !cputime_eq(current->signal->it_prof_expires, 289 cputime_zero) || 290 current->signal->rlim[RLIMIT_CPU].rlim_cur != RLIM_INFINITY || 291 !list_empty(¤t->signal->cpu_timers[0]) || 292 !list_empty(¤t->signal->cpu_timers[1]) || 293 !list_empty(¤t->signal->cpu_timers[2])) { 294 /* 295 * Have child wake up on its first tick to check 296 * for process CPU timers. 297 */ 298 p->it_prof_expires = jiffies_to_cputime(1); 299 } 300 } 301 302 if (likely(p->pid)) { 303 add_parent(p); 304 if (unlikely(p->ptrace & PT_PTRACED)) 305 __ptrace_link(p, current->parent); 306 307 if (thread_group_leader(p)) { 308 p->signal->tty = current->signal->tty; 309 p->signal->pgrp = process_group(current); 310 set_signal_session(p->signal, process_session(current)); 311 attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PGID, task_pgrp(current)); 312 attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_SID, task_session(current)); 313 314 list_add_tail_rcu(&p->tasks, &init_task.tasks); 315 __get_cpu_var(process_counts)++; 316 } 317 attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID, pid); 318 nr_threads++; 319 } 320 321 total_forks++; 322 spin_unlock(¤t->sighand->siglock); 323 write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock); 324 proc_fork_connector(p); 325 return p; 326 327 bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces: 328 exit_task_namespaces(p); 329 bad_fork_cleanup_keys: 330 exit_keys(p); 331 bad_fork_cleanup_mm: 332 if (p->mm) 333 mmput(p->mm); 334 bad_fork_cleanup_signal: 335 cleanup_signal(p); 336 bad_fork_cleanup_sighand: 337 __cleanup_sighand(p->sighand); 338 bad_fork_cleanup_fs: 339 exit_fs(p); /* blocking */ 340 bad_fork_cleanup_files: 341 exit_files(p); /* blocking */ 342 bad_fork_cleanup_semundo: 343 exit_sem(p); 344 bad_fork_cleanup_audit: 345 audit_free(p); 346 bad_fork_cleanup_security: 347 security_task_free(p); 348 bad_fork_cleanup_policy: 349 #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA 350 mpol_free(p->mempolicy); 351 bad_fork_cleanup_cpuset: 352 #endif 353 cpuset_exit(p); 354 bad_fork_cleanup_delays_binfmt: 355 delayacct_tsk_free(p); 356 if (p->binfmt) 357 module_put(p->binfmt->module); 358 bad_fork_cleanup_put_domain: 359 module_put(task_thread_info(p)->exec_domain->module); 360 bad_fork_cleanup_count: 361 put_group_info(p->group_info); 362 atomic_dec(&p->user->processes); 363 free_uid(p->user); 364 bad_fork_free: 365 free_task(p); 366 fork_out: 367 return ERR_PTR(retval); 368 }
dup_task_struct函数,tsk = alloc_task_struct();dup_task_struct()函数主要是为子进程创建一个内核栈,主要赋值语句setup_thread_stack(tsk, orig);
在函数中调用alloc_task_struct()进行内存分配,alloc_task_struct()函数获取内存的方式内核里面有几种:
1、# define alloc_task_struct() kmem_cache_alloc(task_struct_cachep, GFP_KERNEL)
2、
1 struct task_struct *alloc_task_struct(void) 2 { 3 struct task_struct *p = kmalloc(THREAD_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL); 4 if (p) 5 atomic_set((atomic_t *)(p+1), 1); 6 return p; 7 }
3、#define alloc_task_struct() ((struct task_struct *)__get_free_pages(GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_COMP, KERNEL_STACK_SIZE_ORDER))
以上3中申请内存的方式最后一种是最底层的,直接分配页,第二种利用了页高速缓存,相当于是对第3中方式进行了封装,第1种在第2中的方式上进行分配,相当于调用了第2种页高速缓存的API进行内存分配的。
1 static struct task_struct *dup_task_struct(struct task_struct *orig) 2 { 3 struct task_struct *tsk; 4 struct thread_info *ti; 5 6 prepare_to_copy(orig); 7 8 tsk = alloc_task_struct(); 9 if (!tsk) 10 return NULL; 11 12 ti = alloc_thread_info(tsk); 13 if (!ti) { 14 free_task_struct(tsk); 15 return NULL; 16 } 17 18 *tsk = *orig; 19 tsk->stack = ti; 20 setup_thread_stack(tsk, orig); //主要赋值语句将父进程的进程的thread_info赋值给子进程 21 22 #ifdef CONFIG_CC_STACKPROTECTOR 23 tsk->stack_canary = get_random_int(); 24 #endif 25 26 /* One for us, one for whoever does the "release_task()" (usually parent) */ 27 atomic_set(&tsk->usage,2); 28 atomic_set(&tsk->fs_excl, 0); 29 #ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IO_TRACE 30 tsk->btrace_seq = 0; 31 #endif 32 tsk->splice_pipe = NULL; 33 return tsk; 34 }
现在我们主要分析copy_process函数,此函数中做了非常重要的,体现linux中父子进程创建机制的工作。
1、调用dup_task_struct()为子进程创建一个内核栈、thread_info结构和task_struct,这些值与当前进程的值相同。此时子进程和父进程的描述符是完全相同的。
p = dup_task_struct(current)---->(struct task_struct *tsk---------->tsk = alloc_task_struct()从slab层分配了一个关于进程描述符的slab)
2、检查并确保新创建这个子进程后,当前用户所拥有的进程数目没有超出给它分配的资源的限制。
3、子进程着手使自己与父进程区别开来,为进程的task_struct、tss做个性化设置,进程描述符内的许多成员都要被清0或设置为初始值。那些不是继承而来的进程描述符成员,主要是统计信息。task_struct中的大多数数据都依然未被修改。
4、为子进程创建第一个页表,将进程0的页表项内容赋给这个页表。
copy_process()————>copy_fs(),_copy_fs_struct(current->fs)中current指针表示当前进程也就是父进程的
copy_fs()函数为子进程复制父进程的页目录项
1 static inline int copy_fs(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct * tsk) 2 { 3 if (clone_flags & CLONE_FS) { 4 atomic_inc(¤t->fs->count); 5 return 0; 6 } 7 tsk->fs = __copy_fs_struct(current->fs); 8 if (!tsk->fs) 9 return -ENOMEM; 10 return 0; 11 }
_copy_fs_struct()
1 static inline struct fs_struct *__copy_fs_struct(struct fs_struct *old) 2 { 3 struct fs_struct *fs = kmem_cache_alloc(fs_cachep, GFP_KERNEL); 4 /* We don't need to lock fs - think why ;-) */ 5 if (fs) { 6 atomic_set(&fs->count, 1); 7 rwlock_init(&fs->lock); 8 fs->umask = old->umask; 9 read_lock(&old->lock); //进行加锁不能被打断 10 fs->rootmnt = mntget(old->rootmnt); 11 fs->root = dget(old->root); 12 fs->pwdmnt = mntget(old->pwdmnt); 13 fs->pwd = dget(old->pwd); 14 if (old->altroot) { 15 fs->altrootmnt = mntget(old->altrootmnt); 16 fs->altroot = dget(old->altroot); 17 } else { 18 fs->altrootmnt = NULL; 19 fs->altroot = NULL; 20 } 21 read_unlock(&old->lock); 22 } 23 return fs; 24 }
fs_struct数据结构,这个数据结构将VFS层里面的描述页目录对象的结构体进行了实例化,这样就可以为子进程创建一个页目录项,同时这个fs_strcut结构体和为子进程分配内核栈一样都是通过页高速缓存实现的:struct fs_struct *fs = kmem_cache_alloc(fs_cachep, GFP_KERNEL);
1 struct fs_struct { 2 atomic_t count; 3 rwlock_t lock; 4 int umask; 5 struct dentry * root, * pwd, * altroot; //struct denty 页目录项结构体 6 struct vfsmount * rootmnt, * pwdmnt, * altrootmnt; 7 };
copy_files()函数,为子进程复制父进程的页表,共享父进程的文件
1 static int copy_files(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct * tsk) 2 { 3 struct files_struct *oldf, *newf; 4 int error = 0; 5 6 /* 7 * A background process may not have any files ... 8 */ 9 oldf = current->files; //将父进程的页表 10 if (!oldf) 11 goto out; 12 13 if (clone_flags & CLONE_FILES) { 14 atomic_inc(&oldf->count); 15 goto out; 16 } 17 18 /* 19 * Note: we may be using current for both targets (See exec.c) 20 * This works because we cache current->files (old) as oldf. Don't 21 * break this. 22 */ 23 tsk->files = NULL; 24 newf = dup_fd(oldf, &error); 25 if (!newf) 26 goto out; 27 28 tsk->files = newf; 29 error = 0; 30 out: 31 return error; 32 }
dup_fd()
1 /* 2 * Allocate a new files structure and copy contents from the 3 * passed in files structure. 4 * errorp will be valid only when the returned files_struct is NULL. 5 */ 6 files_struct 7 static struct files_struct *dup_fd(struct files_struct *oldf, int *errorp) 8 { 9 struct files_struct *newf; 10 struct file **old_fds, **new_fds; 11 int open_files, size, i; 12 struct fdtable *old_fdt, *new_fdt; 13 14 *errorp = -ENOMEM; 15 newf = alloc_files(); 16 if (!newf) 17 goto out; 18 19 spin_lock(&oldf->file_lock); 20 old_fdt = files_fdtable(oldf); 21 new_fdt = files_fdtable(newf); 22 open_files = count_open_files(old_fdt); 23 24 /* 25 * Check whether we need to allocate a larger fd array and fd set. 26 * Note: we're not a clone task, so the open count won't change. 27 */ 28 if (open_files > new_fdt->max_fds) { 29 new_fdt->max_fds = 0; 30 spin_unlock(&oldf->file_lock); 31 spin_lock(&newf->file_lock); 32 *errorp = expand_files(newf, open_files-1); 33 spin_unlock(&newf->file_lock); 34 if (*errorp < 0) 35 goto out_release; 36 new_fdt = files_fdtable(newf); 37 /* 38 * Reacquire the oldf lock and a pointer to its fd table 39 * who knows it may have a new bigger fd table. We need 40 * the latest pointer. 41 */ 42 spin_lock(&oldf->file_lock); 43 old_fdt = files_fdtable(oldf); 44 } 45 46 old_fds = old_fdt->fd; 47 new_fds = new_fdt->fd; 48 49 memcpy(new_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits, 50 old_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits, open_files/8); 51 memcpy(new_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits, 52 old_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits, open_files/8); 53 54 for (i = open_files; i != 0; i--) { 55 struct file *f = *old_fds++; 56 if (f) { 57 get_file(f); 58 } else { 59 /* 60 * The fd may be claimed in the fd bitmap but not yet 61 * instantiated in the files array if a sibling thread 62 * is partway through open(). So make sure that this 63 * fd is available to the new process. 64 */ 65 FD_CLR(open_files - i, new_fdt->open_fds); 66 } 67 rcu_assign_pointer(*new_fds++, f); 68 } 69 spin_unlock(&oldf->file_lock); 70 71 /* compute the remainder to be cleared */ 72 size = (new_fdt->max_fds - open_files) * sizeof(struct file *); 73 74 /* This is long word aligned thus could use a optimized version */ 75 memset(new_fds, 0, size); 76 77 if (new_fdt->max_fds > open_files) { 78 int left = (new_fdt->max_fds-open_files)/8; 79 int start = open_files / (8 * sizeof(unsigned long)); 80 81 memset(&new_fdt->open_fds->fds_bits[start], 0, left); 82 memset(&new_fdt->close_on_exec->fds_bits[start], 0, left); 83 } 84 85 return newf; 86 87 out_release: 88 kmem_cache_free(files_cachep, newf); 89 out: 90 return NULL; 91 }
files_struct结构体,files_struct结构保存了进程打开的所有文件表数据,描述一个正被打开的文件。
1 struct files_struct { 2 atomic_t count; //自动增量 3 struct fdtable *fdt; 4 struct fdtable fdtab; 5 fd_set close_on_exec_init; //执行exec时 6 需要关闭的文件描述符初值集合 7 fd_set open_fds_init; //当前打开文件 8 的文件描述符屏蔽字 9 struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT]; 10 spinlock_t file_lock; /* Protects concurrent 11 writers. Nests inside tsk->alloc_lock */ 12 };
alloc_files()函数
1 static struct files_struct *alloc_files(void) 2 { 3 struct files_struct *newf; 4 struct fdtable *fdt; 5 6 newf = kmem_cache_alloc(files_cachep, GFP_KERNEL); 7 if (!newf) 8 goto out; 9 10 atomic_set(&newf->count, 1); 11 12 spin_lock_init(&newf->file_lock); 13 newf->next_fd = 0; 14 fdt = &newf->fdtab; 15 fdt->max_fds = NR_OPEN_DEFAULT; 16 fdt->close_on_exec = (fd_set *)&newf->close_on_exec_init; 17 fdt->open_fds = (fd_set *)&newf->open_fds_init; 18 fdt->fd = &newf->fd_array[0]; 19 INIT_RCU_HEAD(&fdt->rcu); 20 fdt->next = NULL; 21 rcu_assign_pointer(newf->fdt, fdt); 22 out: 23 return newf; 24 }
4、子进程的状态被设置为TASK_UNINTERRUPTEIBLE,保证子进程不会投入运行。
。。。。。。前面对于子进程个性化设置没有分析得很清楚,后面自己弄懂了再来补充。
先总结一下fork()的执行流程然后在来解决文章刚开始的问题。
从上面的分析可以看出fork()的流程大概是:
1、p = dup_task_struct(current); 为新进程创建一个内核栈、thread_iofo和task_struct,这里完全copy父进程的内容,所以到目前为止,父进程和子进程是没有任何区别的。
2、为新进程在其内存上建立内核堆栈
3、对子进程task_struct任务结构体中部分变量进行初始化设置,检查所有的进程数目是否已经超出了系统规定的最大进程数,如果没有的话,那么就开始设置进程描诉符中的初始值,从这开始,父进程和子进程就开始区别开了。
4、把父进程的有关信息复制给子进程,建立共享关系
5、设置子进程的状态为不可被TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE,从而保证这个进程现在不能被投入运行,因为还有很多的标志位、数据等没有被设置
6、复制标志位(falgs成员)以及权限位(PE_SUPERPRIV)和其他的一些标志
7、调用get_pid()给子进程获取一个有效的并且是唯一的进程标识符PID
8、return ret_from_fork;返回一个指向子进程的指针,开始执行
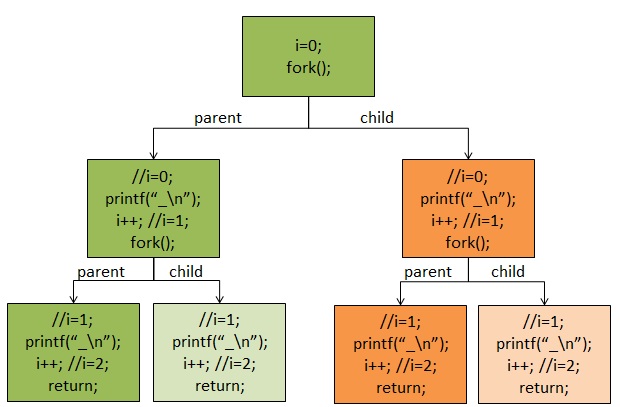
关于文章开始提出的问题,我们可以从前面的分析知道,子进程的产生是从父进程那儿复制的内核栈、页表项以及与父进程共享文件(对于父进程的文件只能读不能写),所以子进程如果没有执行exac()函数载入自己的可执行代码,他和父进程将共享数据即代码段数据段,这就是为什么fork()一次感觉执行了两次printf()函数,至于为什么不是6次“+”这个和标准I/O里面的缓冲有关系,所以后面我用了一个不带缓冲的I/O函数进行了测试输出是6次“-”,在子进程复制父进程的内核栈、页表项、页表的时候页把缓存复制到了子进程中,所以多了两次。
可以从下面的图中看明白
注:本文参考了《linux 内核设计与实现》、《深入理解linux内核》
参考博文:http://blog.csdn.net/Always2015/article/details/45008785
http://www.oschina.net/question/195301_62902?sort=default&p=1#answers
总结
linux创建一个新的进程是从复制父进程内核栈、页表项开始的,在系统内核里首先是将父进程的进程描述符进行拷贝,然后再根据自己的情况修改相应的参数,获取自己的进程号,再开始执行。
后续关于线程
在前面我们讲的是在linux中创建一个进程,其实在其中创建线程也和上面的流程一样,只是我们需要设置标志位让子进程与父进程共享数据。linux实现线程的机制非常独特,从内核的角度讲,linux没有线程这个说法,linux把所有的线程都当做进程来实现。内核没有准备特别的调度算法或者是定义特别的数据结构来表征线程。相反,线程仅仅被视为一个与其它进程共享某些资源的进程。每个线程都拥有唯一隶属于自己的task_struct,所以在内核中看起来像一个普通的进程只是线程和其它进程共享某些资源,如地址空间。
所以linux里面实现线程的方法和windows或者sun solaris等操作系统实现差异非常大。这些操作系统在内核里面专门提供了支持线程的机制。对于linux来说线程只是一种共享资源的手段。
线程创建时和普通的进程类似,只不过在调用clone()的时候需要传递一些参数标志来指明需要共享的资源。如:
CLONE_FILES:父子进程共享打开的文件
CLONE_FS:父子进程共享打开的文件系统信息
。。。。
后续关于进程终结
一般来说进程的析构是自身引起的。它发生在进程调用exit()系统调用时,既可以显示的调用这个系统调用,也可以隐式的从某个函数返回,C语言编译器会在main函数的返回点后面放置调用exit()的代码。当进程接收到它既不能处理也不能忽略的信号或者异常时,它还能被动的终结。调用do_exit()函数完成进程的终结。进程的终结就是一个释放进程占有的资源的过程。