第二期 Pandas数据处理
21.读取本地EXCEL数据
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel('pandas120.xlsx')
22.查看df数据前5行

23.将salary列数据转换为最大值与最小值的平均值
#备注,在某些版本pandas中.ix方法可能失效,可使用.iloc,参考https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5xJ-VLaHCV9qX2AMNOLRtw
#为什么不能直接使用max,min函数,因为我们的数据中是20k-35k这种字符串,所以需要先用正则表达式提取数字
import re
# 方法一:apply + 自定义函数
def func(df):
lst = df['salary'].split('-')
smin = int(lst[0].strip('k'))
smax = int(lst[1].strip('k'))
df['salary'] = int((smin + smax) / 2 * 1000)
return df
df = df.apply(func,axis=1)
# 方法二:iterrows + 正则
import re
for index,row in df.iterrows():
nums = re.findall('d+',row[2])
df.iloc[index,2] = int(eval(f'({nums[0]} + {nums[1]}) / 2 * 1000'))
24.将数据根据学历进行分组并计算平均薪资
print(df.groupby('education').mean())

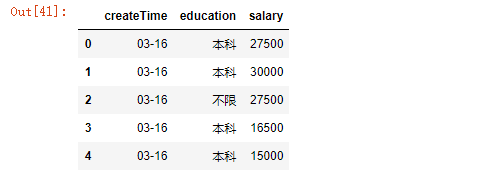
25.将createTime列时间转换为月-日
#备注,在某些版本pandas中.ix方法可能失效,可使用.iloc,参考https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5xJ-VLaHCV9qX2AMNOLRtw
for i in range(len(df)):
df.ix[i,0] = df.ix[i,0].to_pydatetime().strftime("%m-%d")
df.head()
26.查看索引、数据类型和内存信息

27.查看数值型列的汇总统计

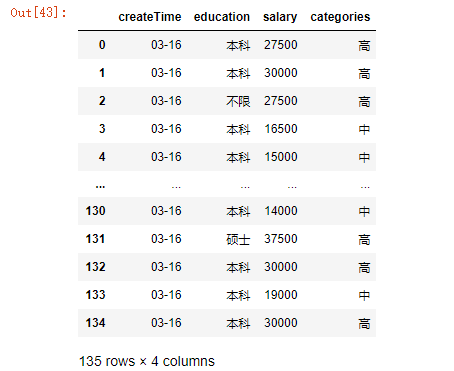
28.新增一列根据salary将数据分为三组
bins = [0,5000, 20000, 50000]
group_names = ['低', '中', '高']
df['categories'] = pd.cut(df['salary'], bins, labels=group_names)
df
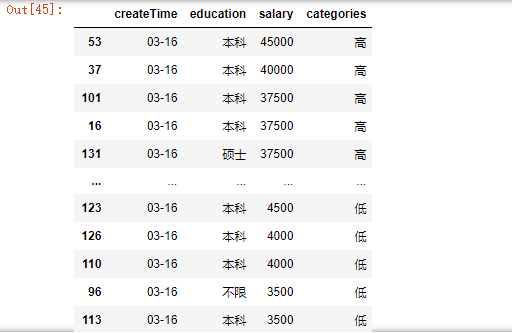
29.按照salary列对数据降序排列
df.sort_values('salary', ascending=False)
30.取出第33行数据

31.计算salary列的中位数

32.绘制薪资水平频率分布直方图
#执行两次
df.salary.plot(kind='hist')

33.绘制薪资水平密度曲线
df.salary.plot(kind='kde',xlim=(0,80000))

34.删除最后一列categories
del df['categories']
# 等价于
df.drop(columns=['categories'], inplace=True)

35.将df的第一列与第二列合并为新的一列
df['test'] = df['education']+df['createTime']
df

36.将education列与salary列合并为新的一列
#备注:salary为int类型,操作与35题有所不同
df["test1"] = df["salary"].map(str) + df['education']
df

37.计算salary最大值与最小值之差
df[['salary']].apply(lambda x: x.max() - x.min())

38.将第一行与最后一行拼接
pd.concat([df[:1], df[-2:-1]])

39.将第8行数据添加至末尾
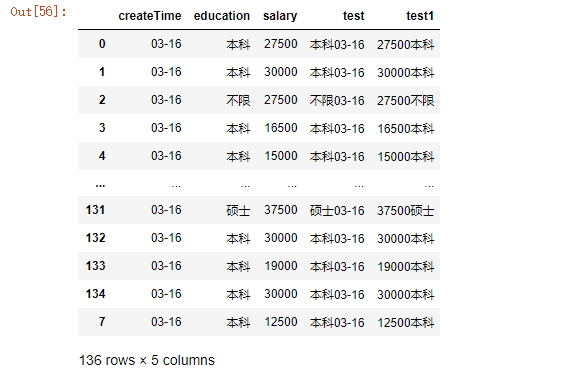
40.查看每列的数据类型

41.将createTime列设置为索引
df.set_index("createTime")

42.生成一个和df长度相同的随机数dataframe
df1 = pd.DataFrame(pd.Series(np.random.randint(1, 10, 135)))
df1

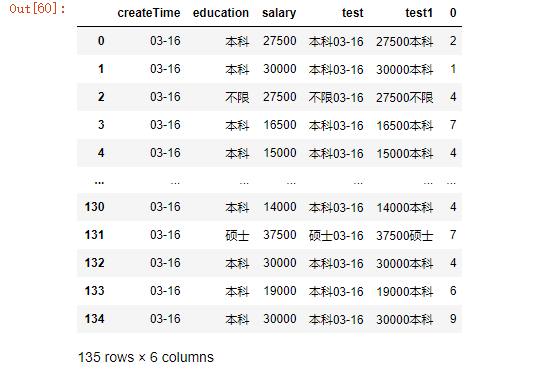
43.将上一题生成的dataframe与df合并
df= pd.concat([df,df1],axis=1)
df
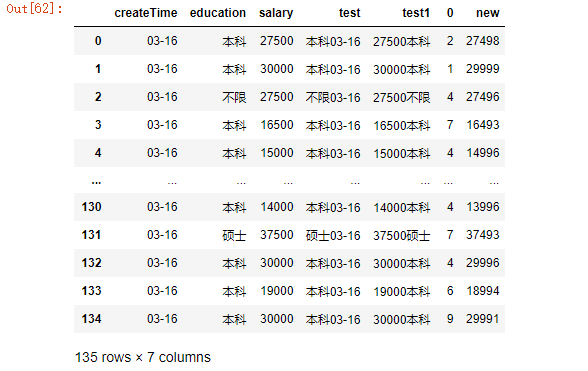
44.生成新的一列new为salary列减去之前生成随机数列
df["new"] = df["salary"] - df[0]
df
45.检查数据中是否含有任何缺失值

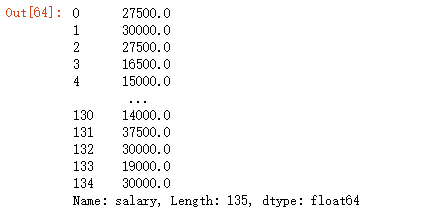
46.将salary列类型转换为浮点数
df['salary'].astype(np.float64)
47.计算salary大于10000的次数
len(df[df['salary']>10000])

48.查看每种学历出现的次数
df.education.value_counts()
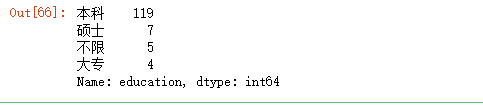
49.查看education列共有几种学历
df['education'].nunique()

50.提取salary与new列的和大于60000的最后3行
df1 = df[['salary','new']]
rowsums = df1.apply(np.sum, axis=1)
res = df.iloc[np.where(rowsums > 60000)[0][-3:], :]
res





























