https://datawhalechina.github.io/pms50/#/chapter10/chapter10
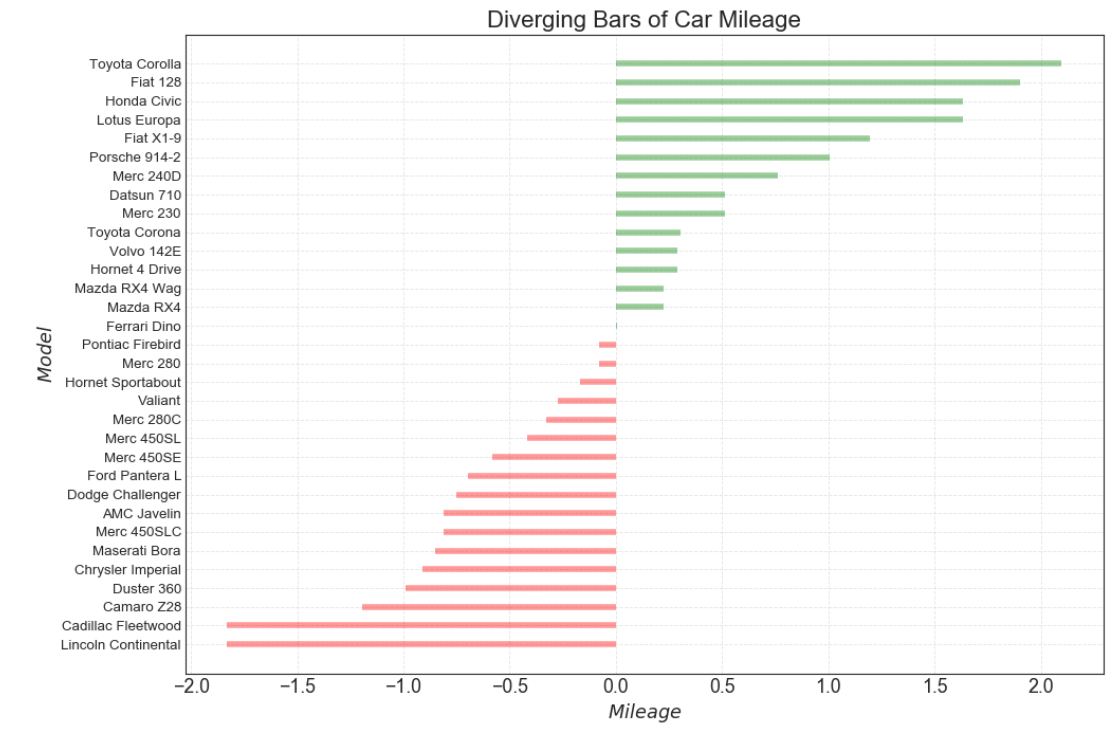
如果您想根据单个指标查看项目的变化情况,并可视化此差异的顺序和数量,那么散型条形图 (Diverging Bars) 是一个很好的工具。
它有助于快速区分数据中组的性能,并且非常直观,并且可以立即传达这一点。
导入所需要的库
import numpy as np # 导入numpy库 import pandas as pd # 导入pandas库 import matplotlib as mpl # 导入matplotlib库 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns # 导入seaborn库
设定图像各种属性
large = 22; med = 16; small = 12 params = {'axes.titlesize': large, # 设置子图上的标题字体 'legend.fontsize': med, # 设置图例的字体 'figure.figsize': (16, 10), # 设置图像的画布 'axes.labelsize': med, # 设置标签的字体 'xtick.labelsize': med, # 设置x轴上的标尺的字体 'ytick.labelsize': med, # 设置整个画布的标题字体 'figure.titlesize': large} #plt.rcParams.update(params) # 更新默认属性 plt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid') # 设定整体风格 sns.set_style("white") # 设定整体背景风格
程序代码
# step1:导入数据
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv") x = df.loc[:, 'mpg'] # 获取mpg这一列数据 # z-score 标准化(正太标准化):将数据按期属性(按列进行)减去其均值,并处以其方差。得到的结果是,对于每个属性/每列来说所有数据都聚集在0附近,方差为1。 df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean()) / x.std() # 列表推导式 # 小于0__红色,大于0__绿色 df['colors'] = ['red' if x <0 else 'green' for x in df['mpg_z']] # 颜色标签 df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace = True) # 对'mpg_z这一列数据进行排序 df.reset_index(inplace = True) # 对排序后的数据重置索引
# step2:绘制发散条形图
# 画布 plt.figure(figsize = (14, 10), # 画布尺寸_(14, 10) dpi = 80) # 分辨率__80 # 发散条形图 plt.hlines(df.index, # 将y下标作为绘制直线的位置 xmin = 0, # 每一行的开头 xmax = df.mpg_z, # 每一行的结尾 colors = df.colors, # 颜色,默认为'k'(黑色) alpha = 0.4, # 色彩饱和度 linewidth = 5) # 线宽
# step3:装饰图像
# x,y轴的标题 plt.gca().set(ylabel='$Model$', xlabel='$Mileage$') # 获取当前子图,若没有子图则创建一个子图,并设置横, 纵坐标的名称 # y轴标签 plt.yticks(df.index, # 放置刻度的位置列表 df.cars, # 放置给定位置列表的标签列表 fontsize = 12) # 字体尺寸 plt.title('Diverging Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20}) # 设置图像标题 # 设置网格线 plt.grid(linestyle = '--', # 网格线类型 alpha = 0.5) # 透明度 plt.show() # 显示图像
博文总结
matplotlib.pyplot.hlines()
matplotlib.pyplot.hlines(y, xmin, xmax, colors='k', linestyles='solid', label='', *, data=None, **kwargs)
Plot horizontal lines at each y from xmin to xmax.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: |
|
| Other Parameters: |
|