RGB颜色空间
最常用的用途就是显示器系统,通过RGB数字驱动RGB电子枪发射电子,并激发显示屏上的荧光粉发出不同亮度的光线,并通过混合产生各种颜色。在RGB颜色空间中,任意色光F都可以用R、G、B三色不同分量的相加混合而成
YUV编码系统
YUV是一种彩色编码系统,相比于RGB颜色空间(用红绿蓝三基色描述),设计YUV的目的就是为了编码、传输的方便,减少带宽占用。
Y表示亮度luma, UV其实是指CbCr,表示色度(chroma)。YUV编码将亮度和色度分离,如果只有Y分量,那么图像就是黑白的,其实当时YUV的设计初衷就是为了使彩色电视能够兼容黑白电视。
人眼的视觉特点是对亮度更敏感,对位置、色彩相对来说不敏感。一个像素如果有YUV三个分量,每个分量用8bit来表示,那么一个像素就需占用3*8 = 24bit = 3byte的大小。为了降低带宽,我们可以保存更多的亮度信息Y,保存较少的色度信息UV,这叫做色度二次采样。原则:1、每个图形像素都要包含亮度Y信息;2、几个图形像素个共用一个CbCr值,一般是2、4、8个像素。
通常有YUV444,YUV422,YUV420等编码格式,对于YUV后面的数字要如何理解,我们可以通过一张图来表示(来源:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/85620611)
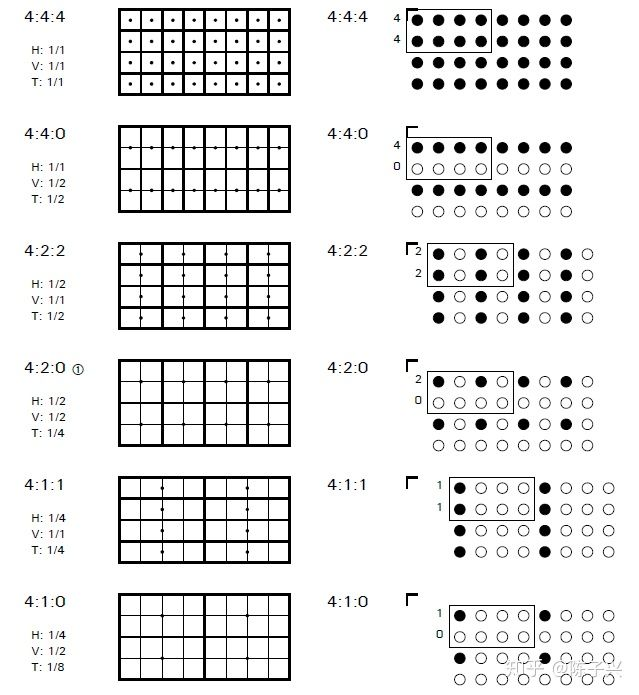
上图中,左侧一列,每一个小矩形表示图形像素,小黑点是表示色度像素值(Cb+Cr),表示图形像素和色度像素在水平和垂直方向的比例关系。我们一般用4*2的像素区域来表示其中的比例关系,比如:
4:4:0 水平方向是1/1,垂直方向是1/2,在4*2像素框中一个色度像素对应了两个图形像素
4:2:2 水平方向是1/2,垂直方向是1/1,表示一个色度像素对应了两个图形像素。
4:2:0 水平方向是1/2,垂直方向是1/2,表示一个色度像素对应了四个图形像素。
右侧一列是二次采样模式记号表示, 是 J:a:b 模式,实心黑色圆圈表示包含色度像素(Cb+Cr),空心圆圈表示不包含色度像素。对于 J:a:b 模式,主要是围绕参考块的概念定义的,这个参考块是一个 J x 2 的矩形,J 通常是 4。这样,此参考块就是宽度有 4 个像素、高度有 2 个像素的矩形。a 表示参考块的第一行包含的色度像素样本数,b 表示在参考块的第二行包含的色度像素样本数。
4:4:0 参考块第一行包含四个色度样本,第二行没有包含色度样本。
4:2:2 参考块第一行包含两个色度样本,第二行也包含两个色度样本,他们是交替出现。
4:2:0 参考块第一行包含两个色度样本,第二行没有包含色度样本。(代表每四个图形像素共用一个色度像素)。
现在我们发现 yuv444,yuv422,yuv420 yuv 等像素格式的本质是:每个图形像素都会包含亮度值,但是某几个图形像素会共用一个色度值,这个比例关系就是通过 4 x 2 的矩形参考块来定的。这样很容易理解类似 yuv440,yuv420 这样的格式了
存储方式
平面格式
平面格式是指用三个不同的数组来表示 YCbCr 的三个 Component,每一个 Component 都是通过不同的平面表示。为此,每一个 Component 会对应一个 plane
YUV420表示的width*High的图片大小计算
每个分量用8bit二进制表示,我们把8bit成为位深度,图片大小 = (w* h)*(1 + 1/4 + 1/4) = w * h * 3/2,上述1/4表示的是4个像素点共用一个色度分量u,所以只有(w*h)*1/4个u分量,以及4个像素点共用一个色度分量v。
压缩格式
压缩格式是指用一个数组表示 YCbCr,每一个 component 是交替出现的。
常见的存储格式:(来源https://www.cnblogs.com/daner1257/p/10767570.html)
YU12/I420
该格式属于4:2:0类型,存储方式上面已经说过,就是先存储把全部的Y分量存完,再存U分量,最后存V分量,从网上找了一张很形象的图:
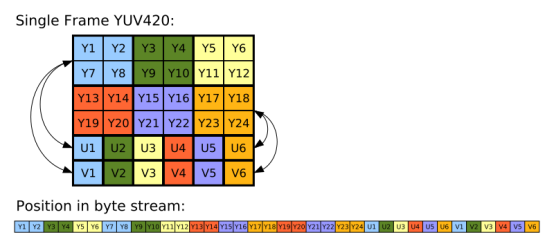
可以看到,第一行的Y1Y2和第二行的Y7Y8共同使用一组UV分量U1V1。
YV12
该格式与YU12基本一样,唯一的区别是先存储V分量再存储U分量,对应到上图把第五行和第六行位置互换一下就是了。
以上两种格式我们可以看到都是4:2:0的,因为都是planar方式存储,简称420p。
除了上面两种,还有两种4:2:0,NV12和NV21,这两种是比较特殊的存储格式,是planar和packed混合存储的,分别看下
NV12
该格式是先存储全部的Y分量,然后UV分量交叉存储,用图像表示下:
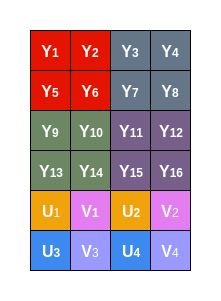
很直观,不多说了。
NV21
该格式与NV21的区别和上面YU12/YV12一样,唯一的区别只是UV分量交叉的顺序不同,NV12是U排前面,NV21是V排前面,用图像表示如下:
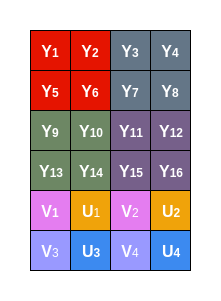
上面两种虽然也是4:2:0类型,但是并不是完全的planar格式,所以又称为420sp,与420p进行区分。
上面说的都是4:2:0类型的,下面说几个4:2:2类型较常见的
YUV422P
名字中带P表示是planar格式存储,该格式存储方式与I420是一样的,唯一的区别是UV分量的数量不同,I420中四个Y共用一组UV,而该格式中两个Y共用一组UV,也就是说UV分量相对于I420在数量上多了一倍,从网上找了一张图,如下:

如上图,在渲染时Y00与Y01会共用U00和V00.
YUYV/YUY2
该格式属于4:2:2类型,且是用packed形式存储的,上面也简单的说过,存储方式如下图:

可以看到,每两个Y分量共用一组UV分量,存储顺序是YUYV。
YVYU
该格式与YUYV相似,只是存储时UV分量顺序不同而已,为YVYU。
UYVY
该格式也是4:2:2类型,与上面两种方式并无大的不同,从网上找了一张图如下:
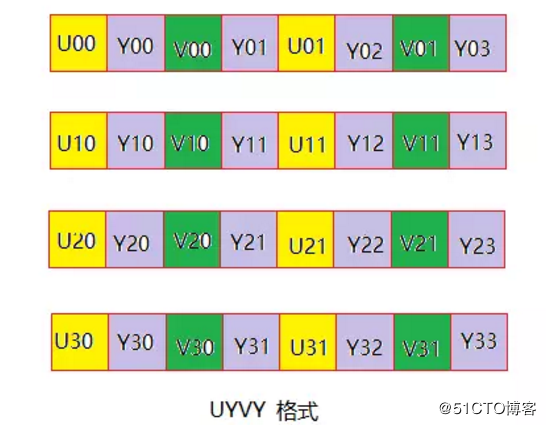
可以看到存储时YUV分量的顺序如名字所示:UYVY。
YUV图像基本处理
以下内容转载自:一文掌握 YUV 图像的基本处理 - 云+社区 - 腾讯云 (tencent.com)
YUV 图
可以通过FFmpeg来将jpeg图片转换为YUV格式图片。
1. YUV 的由来
YUV 是一种色彩编码模型,也叫做 YCbCr,其中 “Y” 表示明亮度(Luminance),“U” 和 “V” 分别表示色度(Chrominance)和浓度(Chroma)。
YUV 色彩编码模型,其设计初衷为了解决彩色电视机与黑白电视的兼容问题,利用了人类眼睛的生理特性(对亮度敏感,对色度不敏感),允许降低色度的带宽,降低了传输带宽。
在计算机系统中应用尤为广泛,利用 YUV 色彩编码模型可以降低图片数据的内存占用,提高数据处理效率。
另外,YUV 编码模型的图像数据一般不能直接用于显示,还需要将其转换为 RGB(RGBA) 编码模型,才能够正常显示。
2. YUV 几种常见采样方式
YUV 图像主流的采样方式有三种:
- YUV 4:4:4,每一个 Y 分量对于一对 UV 分量,每像素占用3 字节 (Y + U + V = 8 + 8 + 8 = 24bits);
- YUV 4:2:2,每两个 Y 分量共用一对 UV 分量,每像素占用 2 字节 (Y + 0.5U + 0.5V = 8 + 4 + 4 = 16bits);
- YUV 4:2:0,每四个 Y 分量共用一对 UV 分量,每像素占用1.5 字节 (Y + 0.25U + 0.25V = 8 + 2 + 2 = 12bits);
其中最常用的采样方式是 YUV422 和 YUV420 。 YUV 格式也可按照 YUV 三个分量的组织方式分为打包(Packed)格式和平面格式(Planar)。
- 打包(Packed)格式:每个像素点的 YUV 分量是连续交叉存储的,如 YUYV 格式;
- 平面格式(Planar):YUV 图像数据的三个分量分别存放在不同的矩阵中,这种格式适用于采样,如 YV12、YU12 格式。
3. YUV 几种常用的格式
下面以一幅分辨率为 4x4 的 YUV 图为例,说明在不同 YUV 格式下的存储方式(括号内范围表示内存地址索引范围,默认以下不同格式图片存储使用的都是连续内存)。
YUYV (YUV422 采样方式)
YUYV 格式的存储格式
(0 ~ 7) Y00 U00 Y01 V00 Y02 U01 Y03 V01
(8 ~ 15) Y10 U10 Y11 V10 Y12 U11 Y13 V11
(16 ~ 23) Y20 U20 Y21 V20 Y22 U21 Y23 V21
(24 ~ 31) Y30 U30 Y31 V30 Y32 U31 Y33 V31
YV12/YU12 (YUV420 采样方式)
YV12/YU12 也属于 YUV420P ,即 YUV420 采样方式的平面模式,YUV 三个分量分别存储于 3 个不同的矩阵(平面)。 YV12 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 17) V00 V01
(18 ~ 19) V10 V11
(20 ~ 21) U00 U01
(22 ~ 23) U10 U11
YU12(也称 I420) 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 17) U00 U01
(18 ~ 19) U10 U11
(20 ~ 21) V00 V01
(22 ~ 23) V10 V11
NV21/NV12 (YUV420 采样方式)
NV21/NV12 属于 YUV420SP ,YUV420SP 格式有 2 个平面,Y 分量存储于一个平面,UV 分量交错存储于另一个平面。
NV21 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 19) V00 U00 V01 U01
(20 ~ 23) V10 U10 V11 U11
NV12 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 19) U00 V00 U01 V01
(20 ~ 23) U10 V10 U11 V11
NV21 与 NV12 格式的区别仅在于 UV 分量排列的先后顺序不同。
4. YUV 图像的基本操作
下面以最常用的 NV21 图为例介绍其旋转、缩放和剪切的基本方法。
YUV 图片的定义、加载、保存及内存释放。
//YUV420SP NV21 or NV12
typedef struct
{
int width; // 图片宽
int height; // 图片高
unsigned char *yPlane; // Y 平面指针
unsigned char *uvPlane; // UV 平面指针
} YUVImage;
void LoadYUVImage(const char *filePath, YUVImage *pImage)
{
FILE *fpData = fopen(filePath, "rb+");
if (fpData != NULL)
{
fseek(fpData, 0, SEEK_END);
int len = ftell(fpData);
pImage->yPlane = malloc(len);
fseek(fpData, 0, SEEK_SET);
fread(pImage->yPlane, 1, len, fpData);
fclose(fpData);
fpData = NULL;
}
pImage->uvPlane = pImage->yPlane + pImage->width * pImage->height;
}
void SaveYUVImage(const char *filePath, YUVImage *pImage)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filePath, "wb+");
if (fp)
{
fwrite(pImage->yPlane, pImage->width * pImage->height, 1, fp);
fwrite(pImage->uvPlane, pImage->width * (pImage->height >> 1), 1, fp);
}
}
void ReleaseYUVImage(YUVImage *pImage)
{
if (pImage->yPlane)
{
free(pImage->yPlane);
pImage->yPlane = NULL;
pImage->uvPlane = NULL;
}
}
NV21 图片旋转
以顺时针旋转 90 度为例,Y 和 UV 两个平面分别从平面左下角进行纵向拷贝,需要注意的是每对 UV 分量作为一个整体进行拷贝。以此类比,顺时针旋转 180 度时从平面右下角进行横向拷贝,顺时针旋转 270 度时从平面右上角进行纵向拷贝。

Y 平面旋转

UV 平面旋转
Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03 Y30 Y20 Y10 Y00
Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13 旋转90度 Y31 Y21 Y11 Y01
Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23 -----> Y32 Y22 Y12 Y02
Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33 Y33 Y23 Y13 Y03
V00 U00 V01 U01 -----> V10 U10 V00 U00
V10 U10 V11 U11 V11 U11 V01 U01
代码实现:
//angle 90, 270, 180
void RotateYUVImage(YUVImage *pSrcImg, YUVImage *pDstImg, int angle)
{
int yIndex = 0;
int uvIndex = 0;
switch (angle)
{
case 90:
{
// y plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height; j++) {
*(pDstImg->yPlane + yIndex) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + (pSrcImg->height - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i);
yIndex++;
}
}
//uv plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i += 2) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height / 2; j++) {
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i);
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex + 1) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i + 1);
uvIndex += 2;
}
}
}
break;
case 180:
{
// y plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->width; j++) {
*(pDstImg->yPlane + yIndex) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + (pSrcImg->height - 1 - i) * pSrcImg->width + pSrcImg->width - 1 - j);
yIndex++;
}
}
//uv plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height / 2