JDK动态代理的实现原理
1、示例demo
- 计算接口
package com.zcqby.proxy.jdk;
public interface Calculator {
public int add(int i, int j);
public int sub(int i, int j);
public int mult(int i, int j);
public int div(int i, int j);
}
- 实现类
package com.zcqby.proxy.jdk;
public class MyCalculator implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int mult(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}
- 代理类
package com.zcqby.proxy.jdk;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class CalculatorProxy {
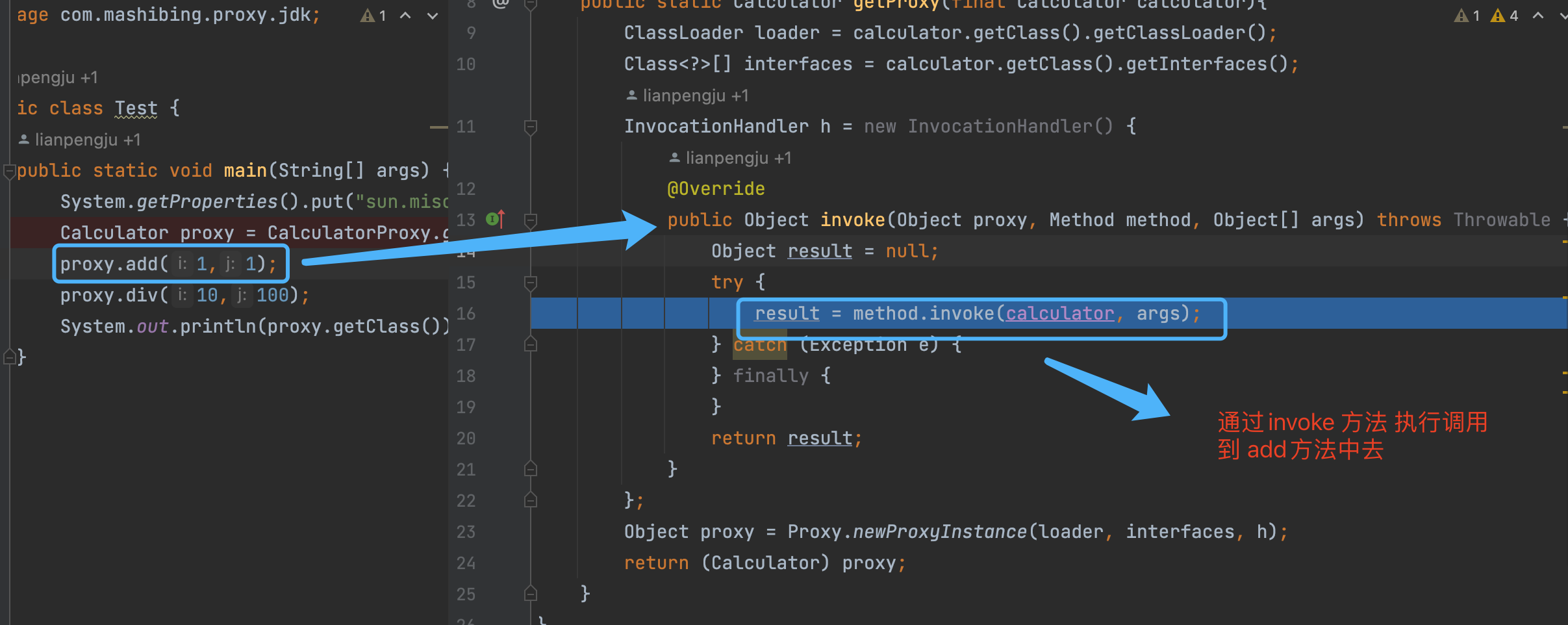
public static Calculator getProxy(final Calculator calculator){
ClassLoader loader = calculator.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = calculator.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
result = method.invoke(calculator, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
}
return result;
}
};
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return (Calculator) proxy;
}
}
- 测试类
package com.zcqby.proxy.jdk;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
Calculator proxy = CalculatorProxy.getProxy(new MyCalculator());
proxy.add(1,1);
proxy.div(10,100);
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
}
}
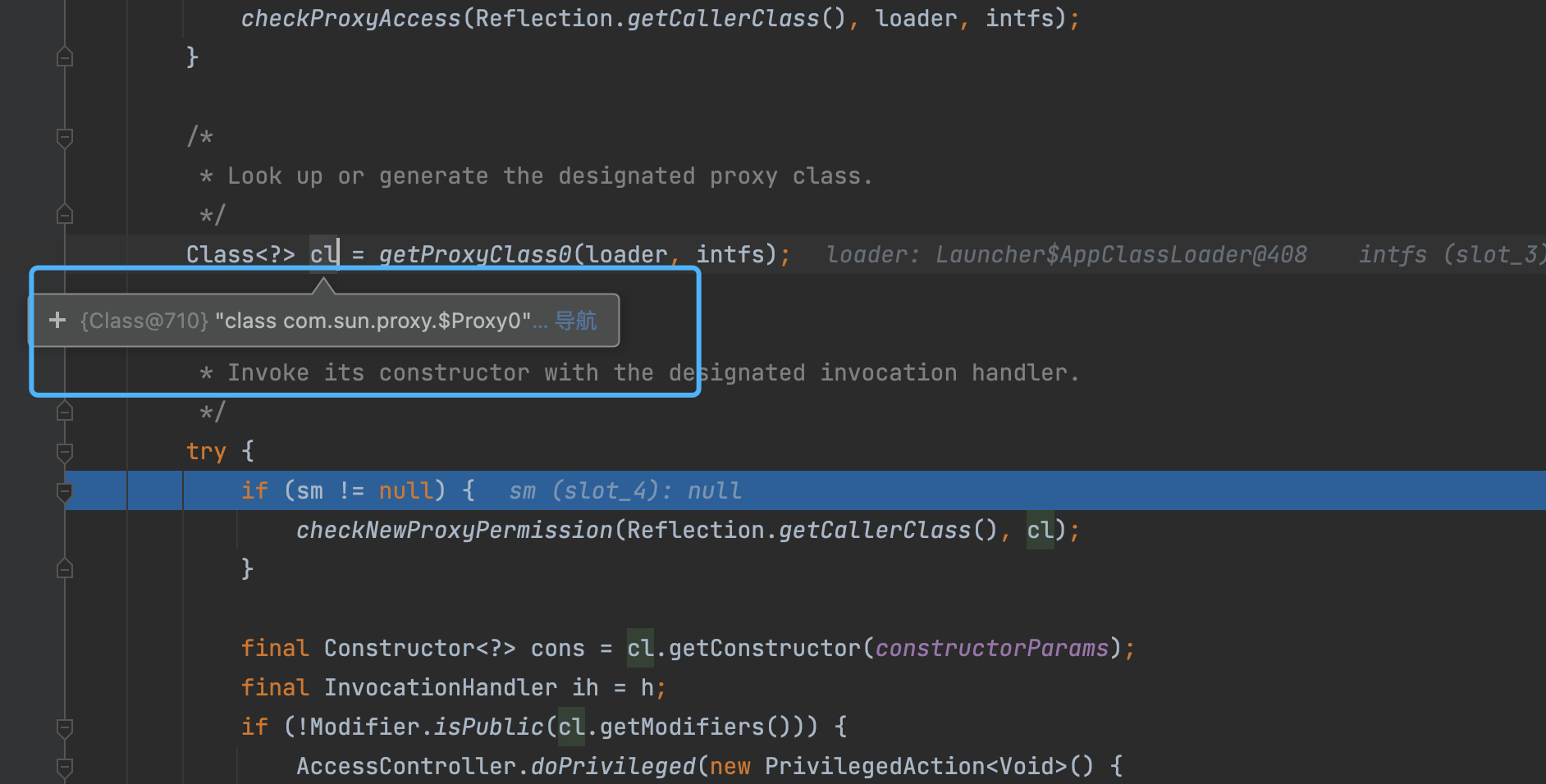
2、源码跟踪
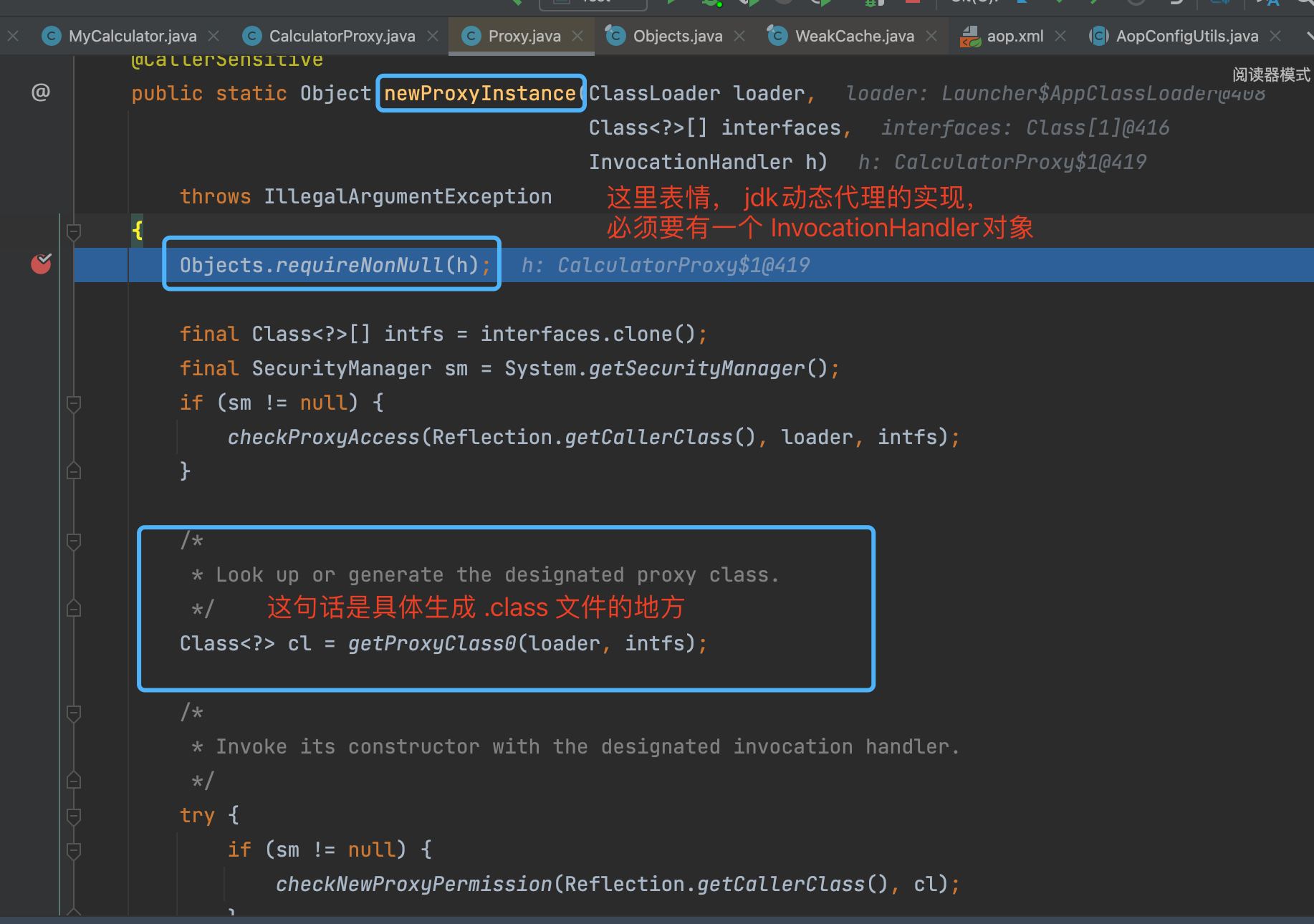

- 上图的注释部分, 我们可以大致知道, 就是 如果
proxyClassCache缓存中已经有了这个对象,那么我们就直接从缓存中获取对象; - 如果缓存中没有该对象, 则我们就需要通过
ProxyClassFactory代理类工厂去创建对象。
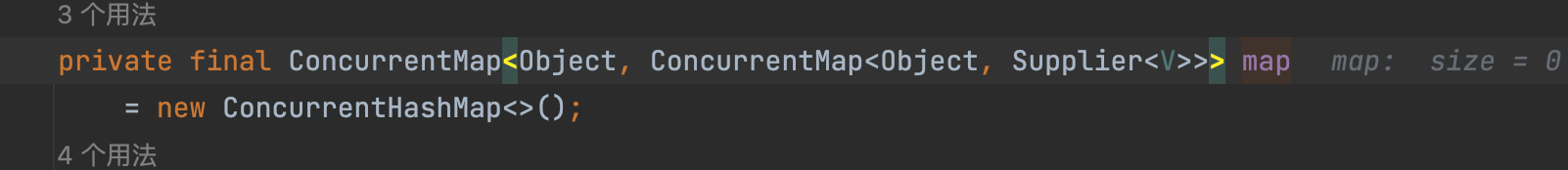
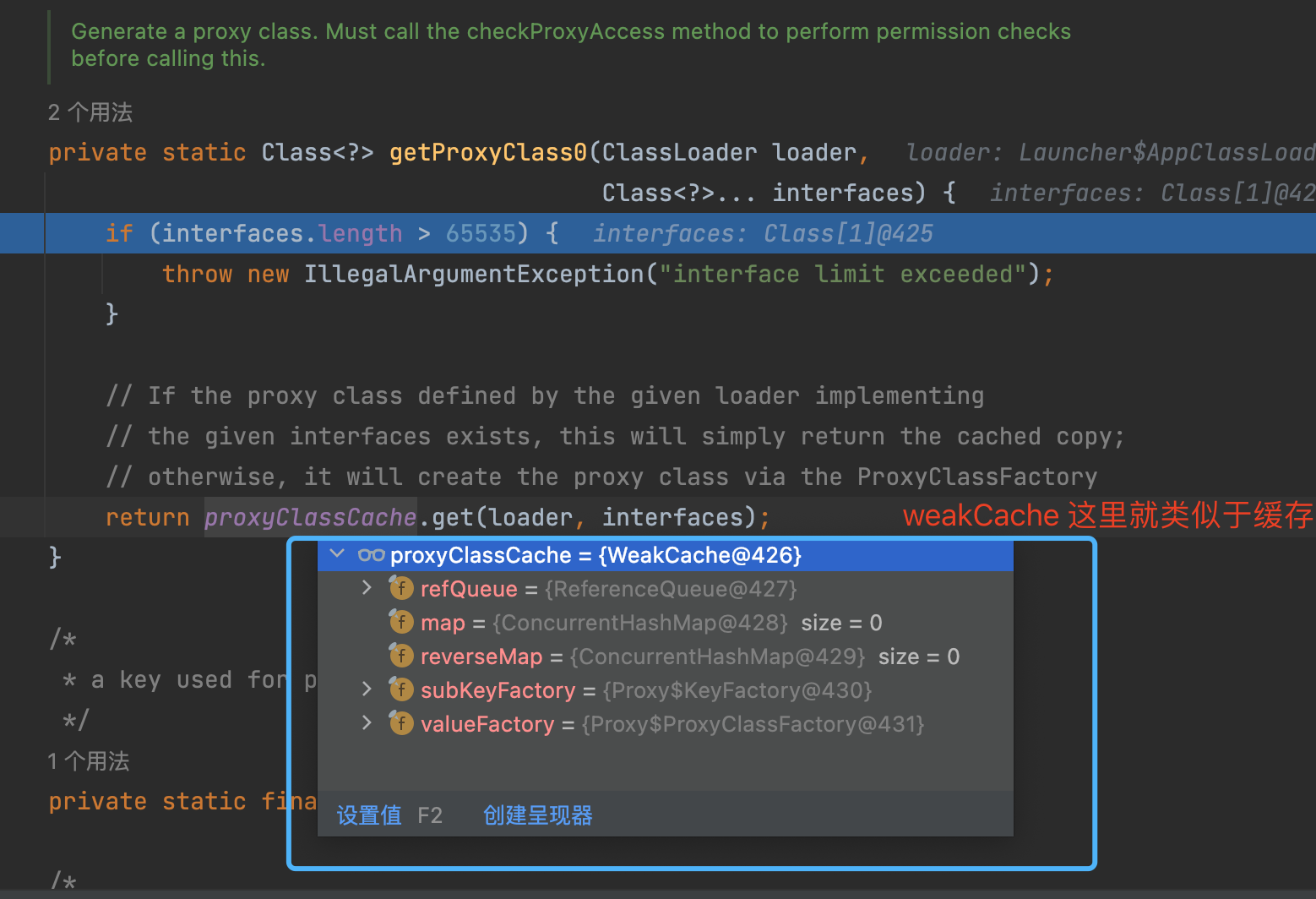
- 值得注意的是, 这边的 map 的数据结构是 是 map里面套map,并且使用的
ConcurrentMap
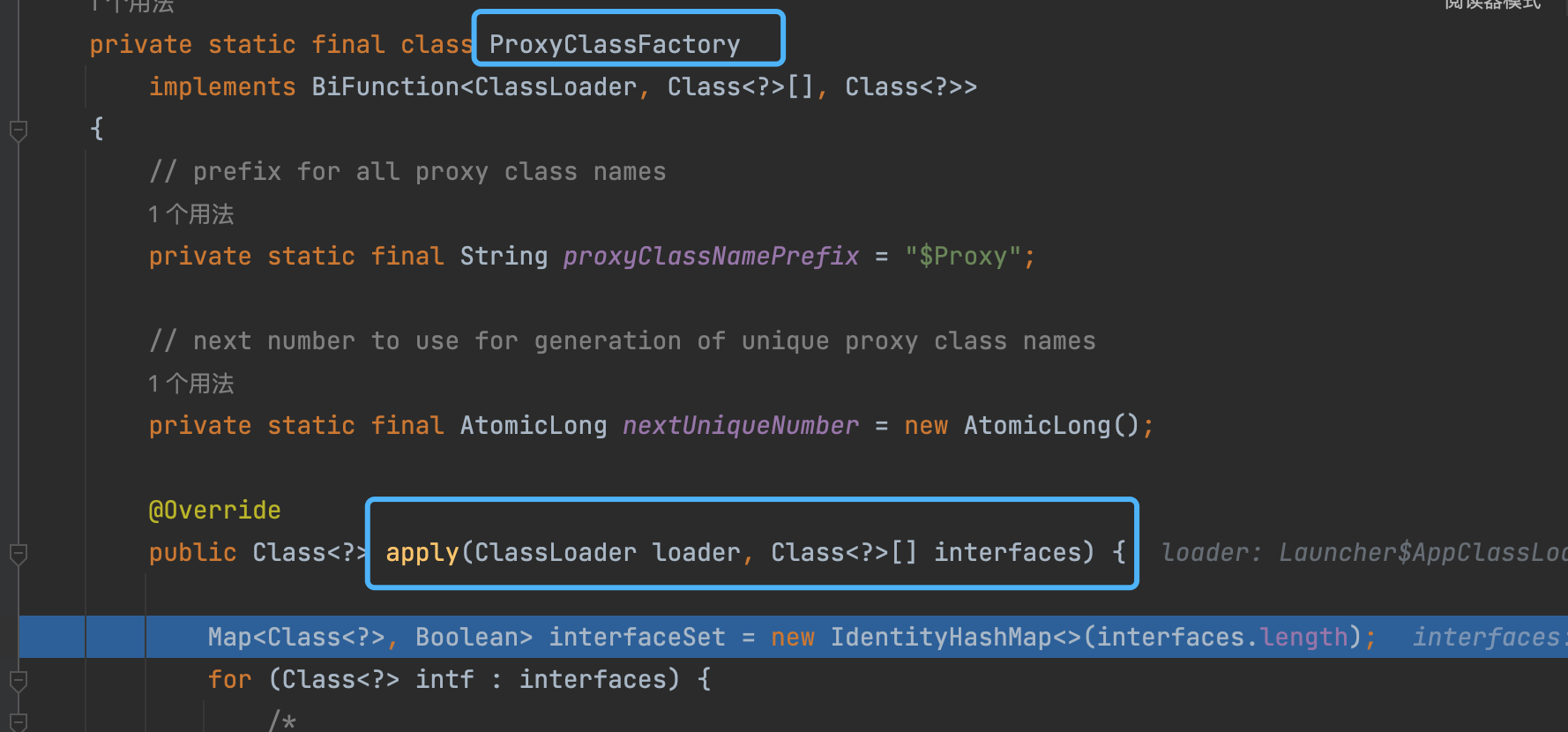
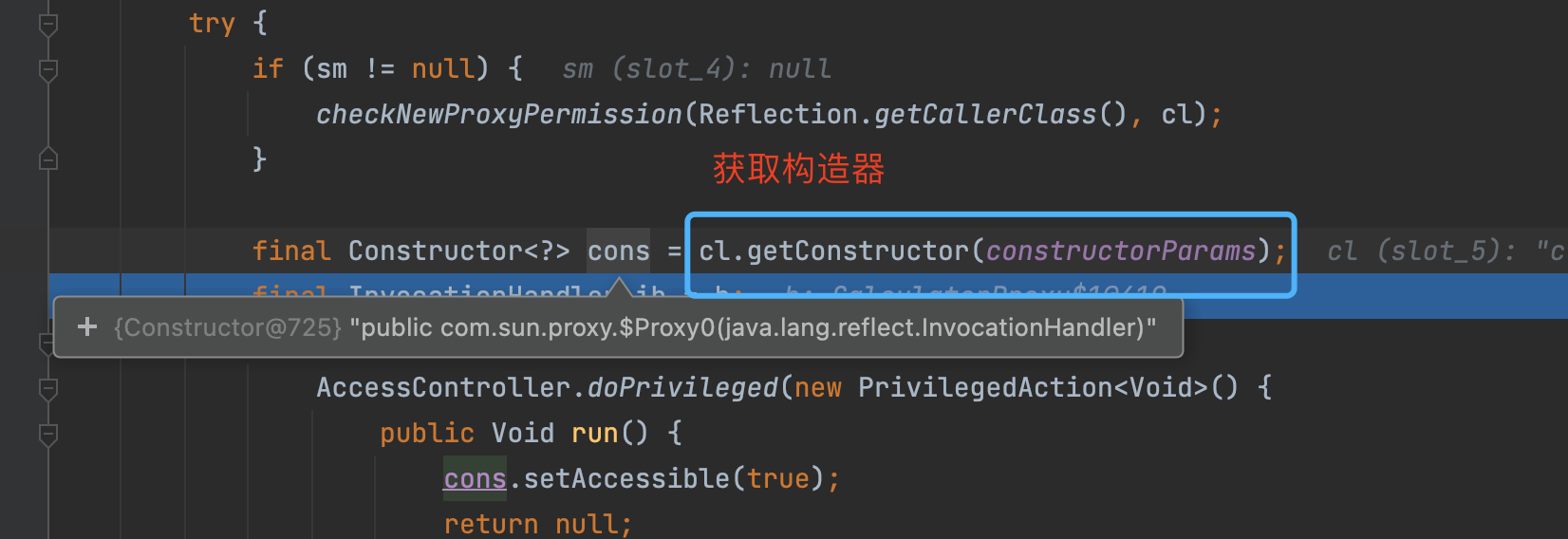
如上图所示, 动态代理的class文件生成的主要实现, 就是上图所示的ProxyClassFactory 中,这里就是真实的创建动态代理生成的class文件的地方。
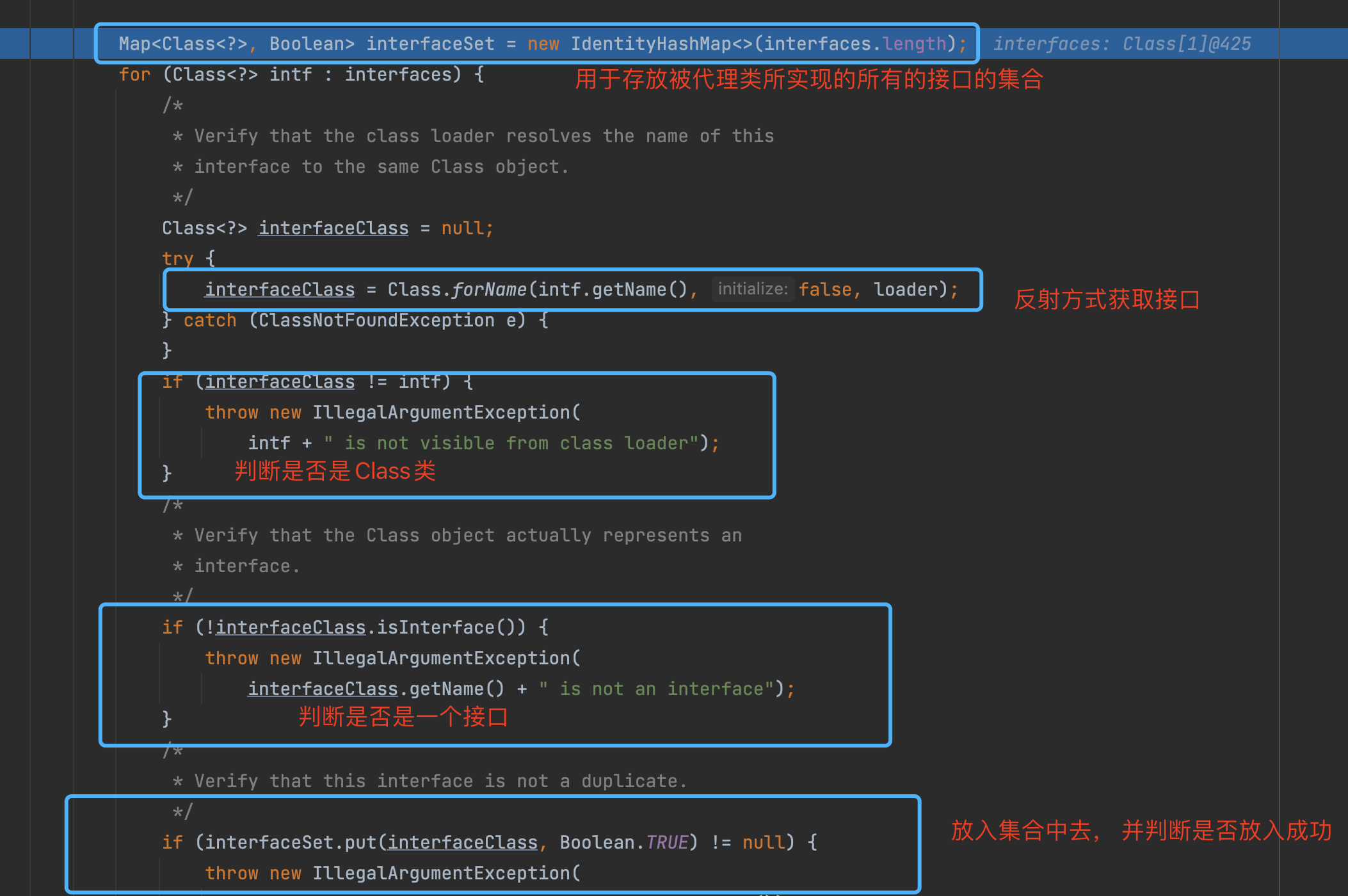
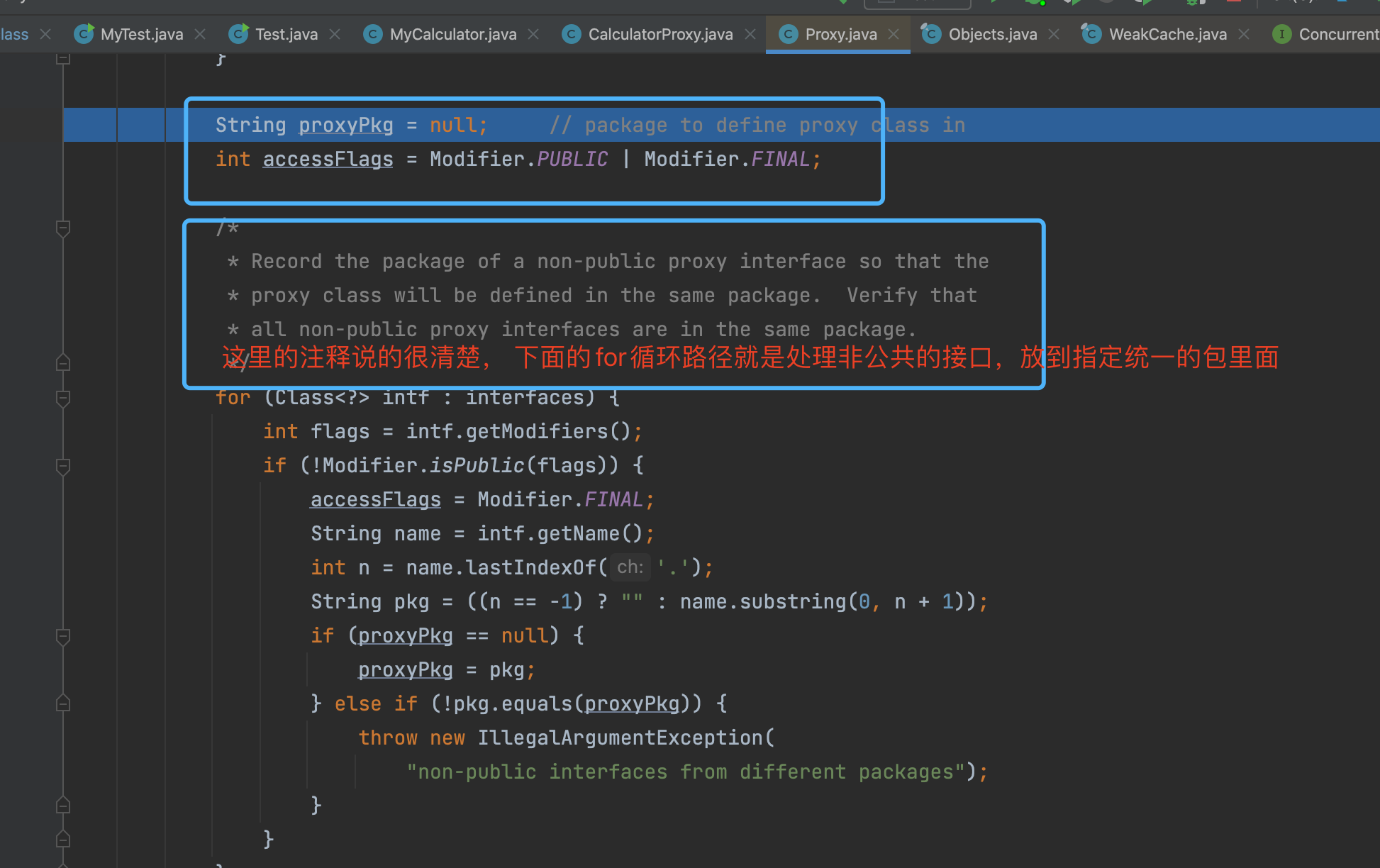
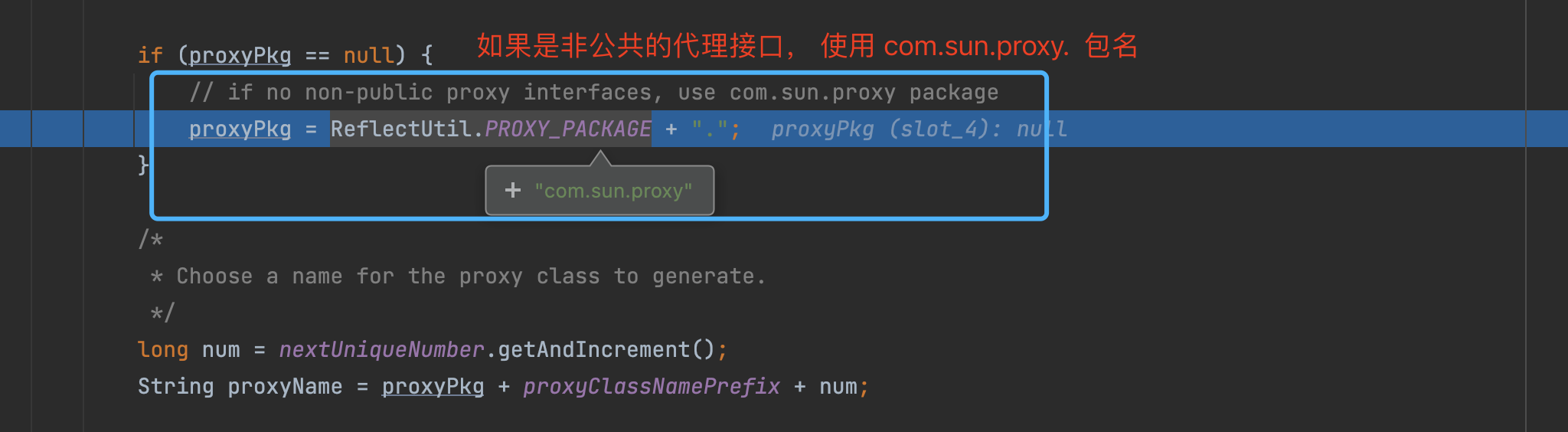
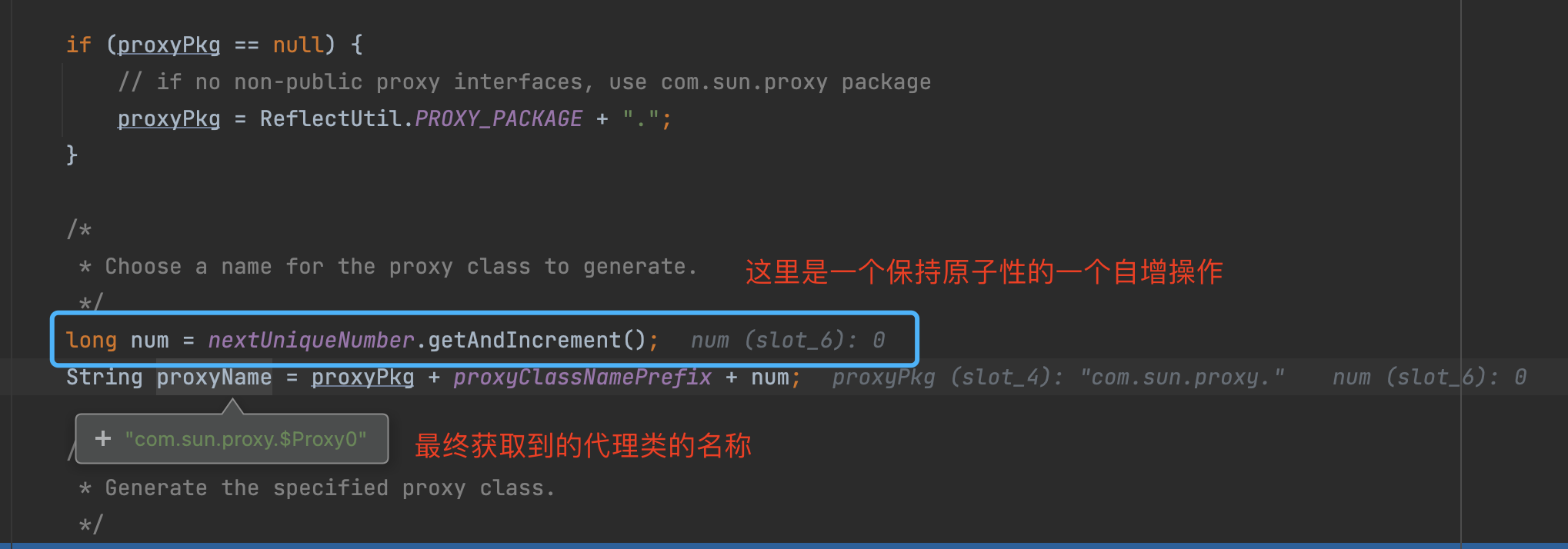
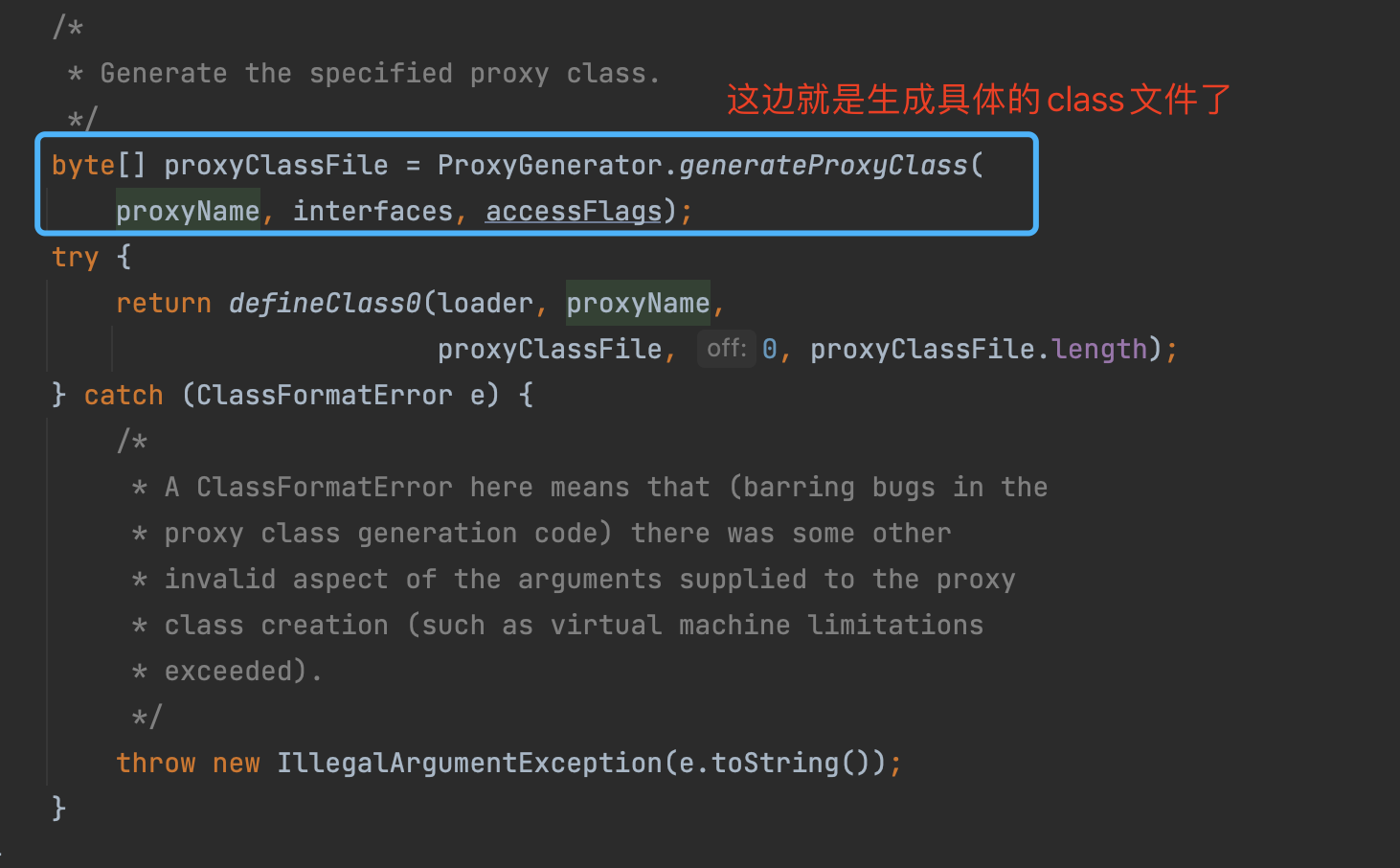
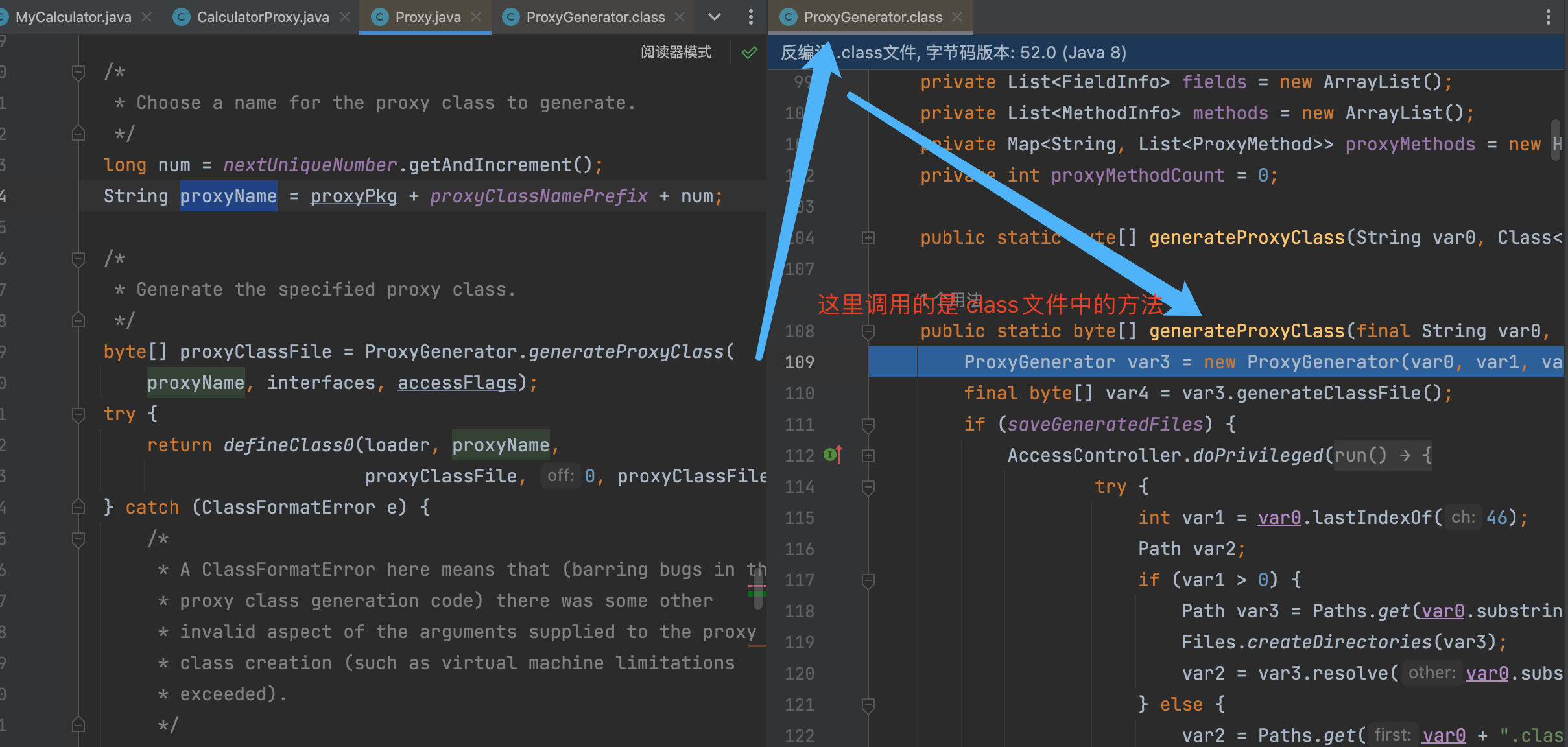
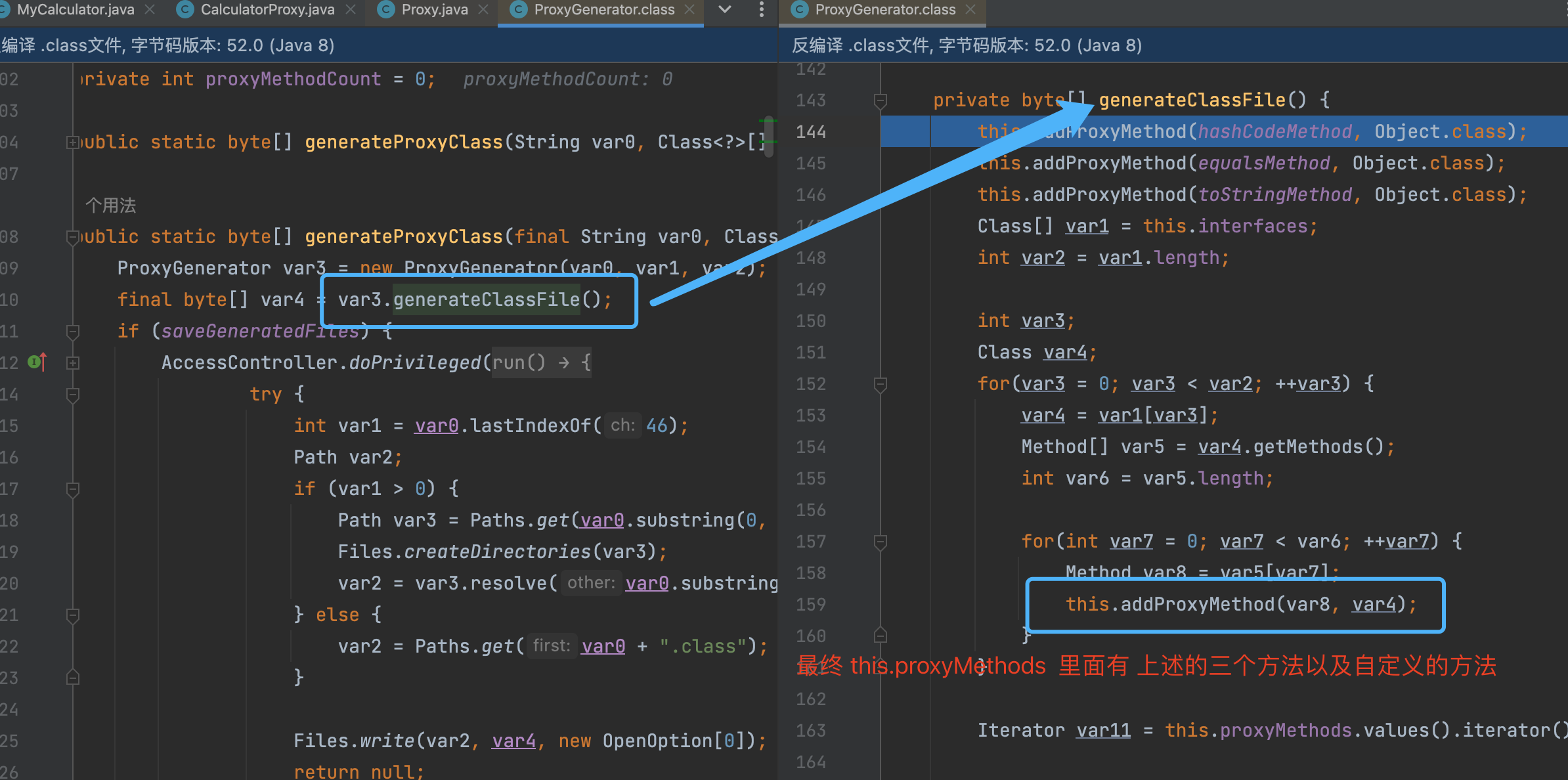
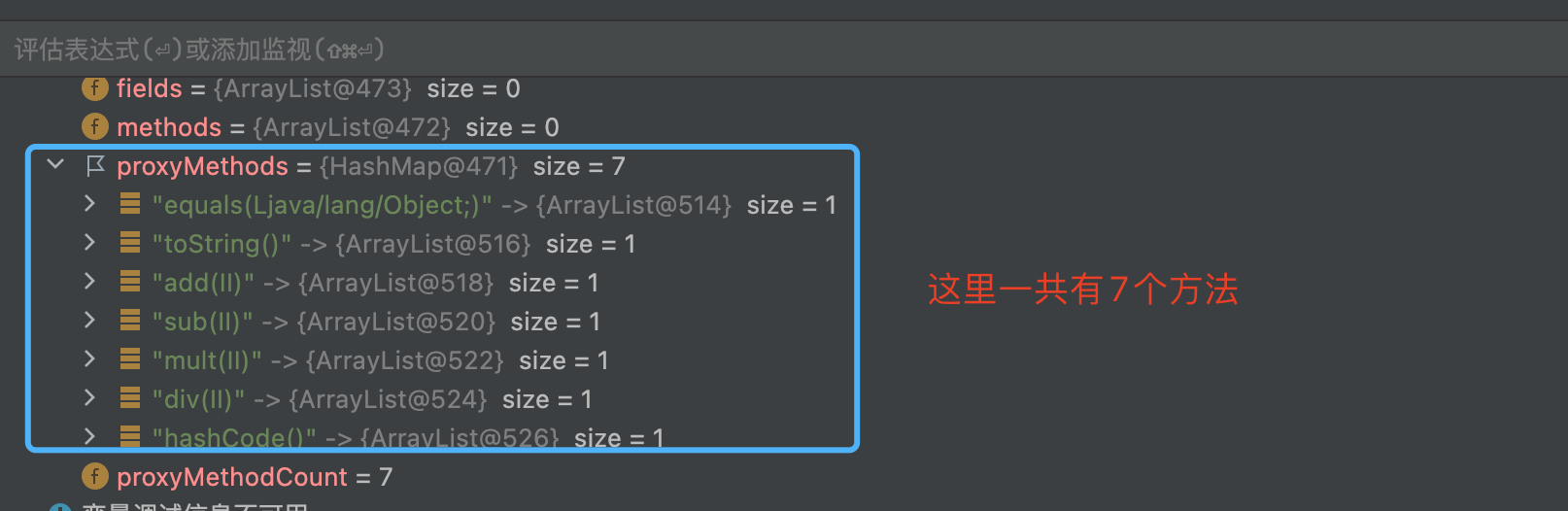
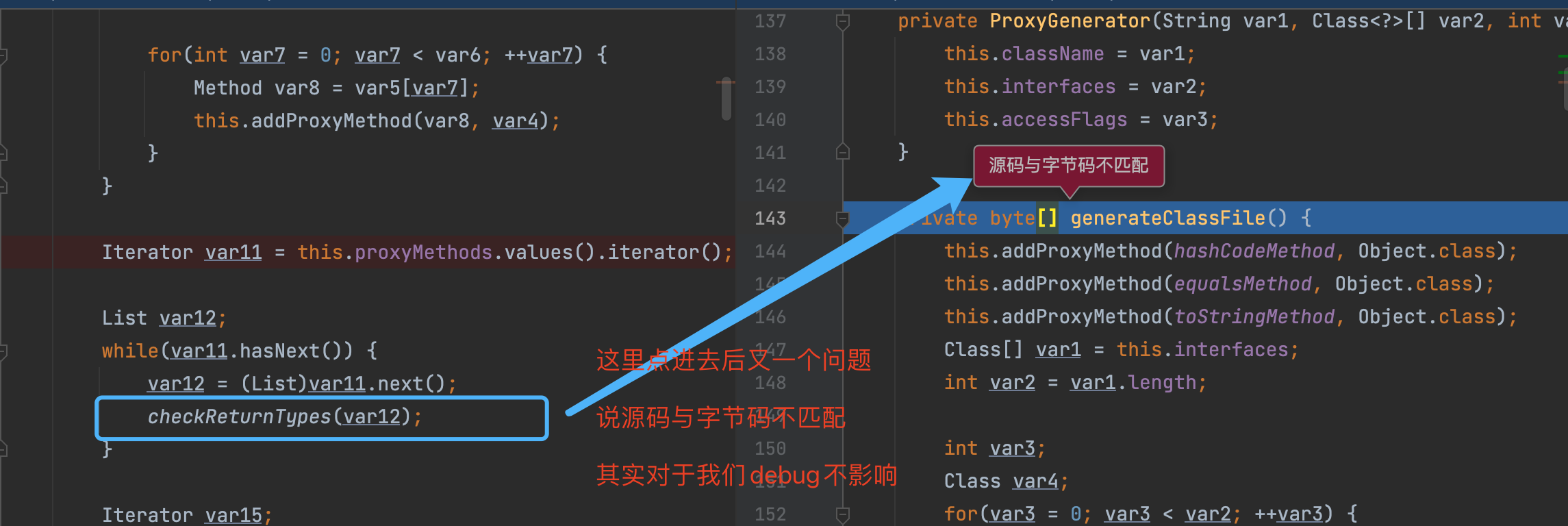
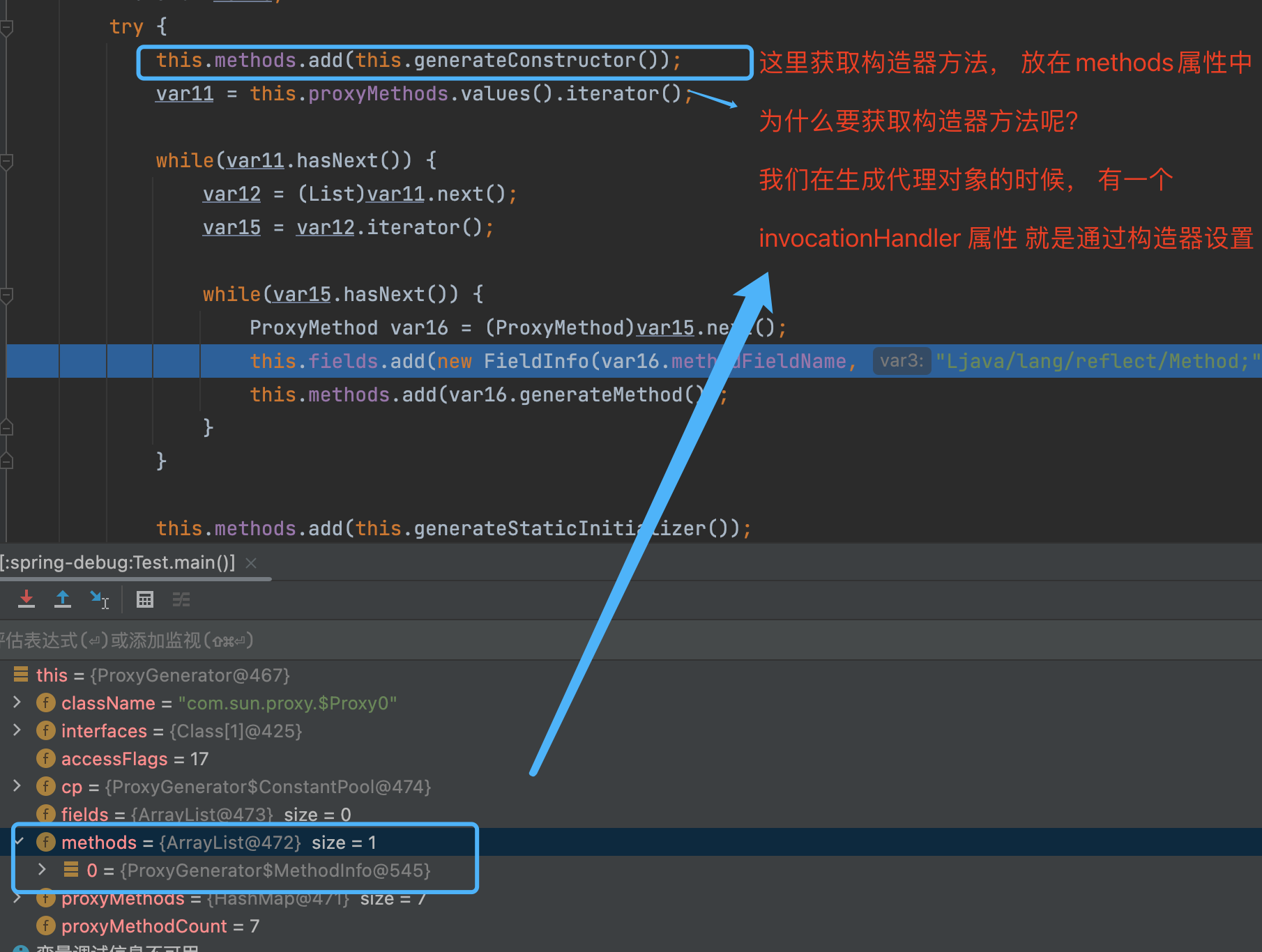
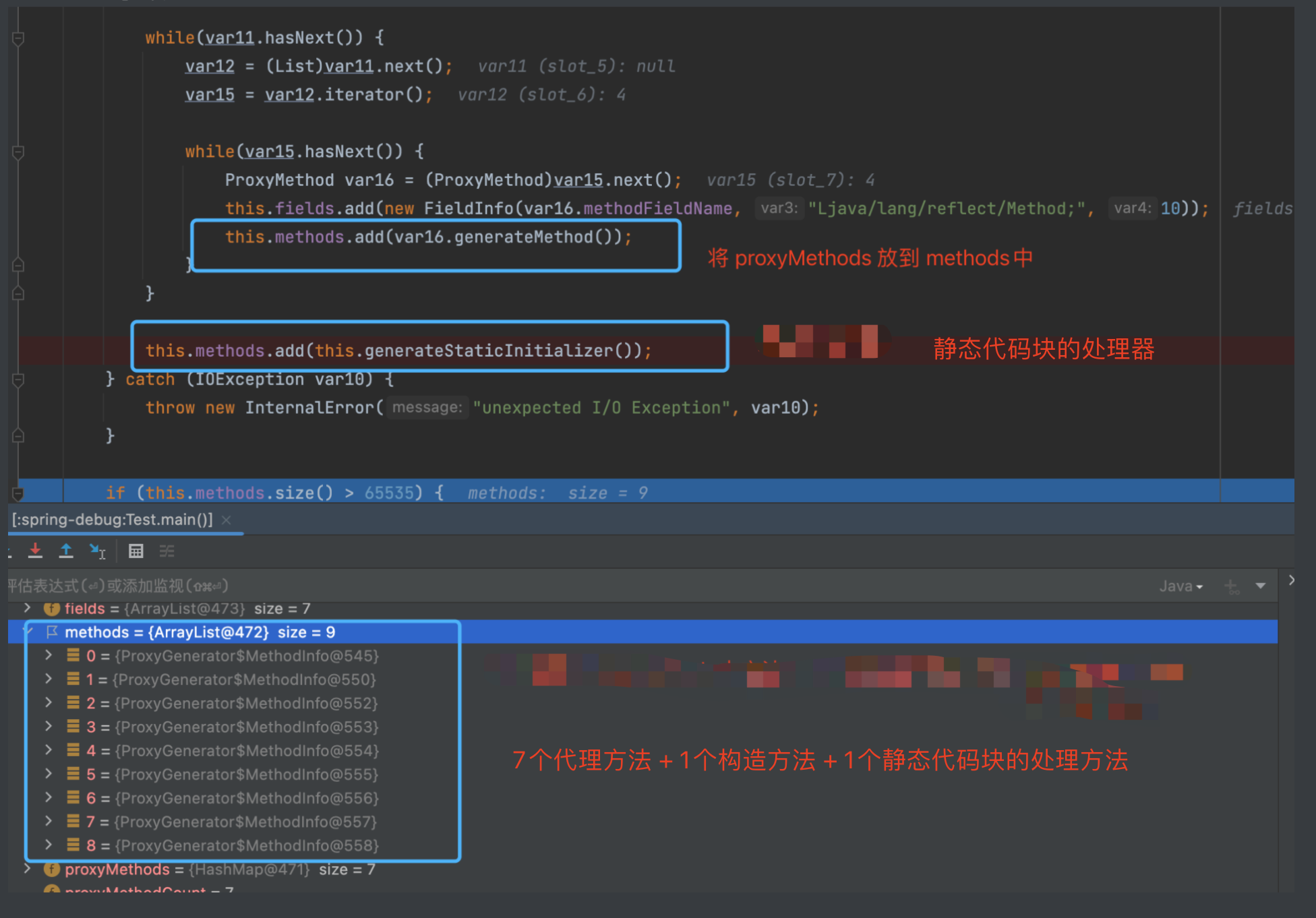
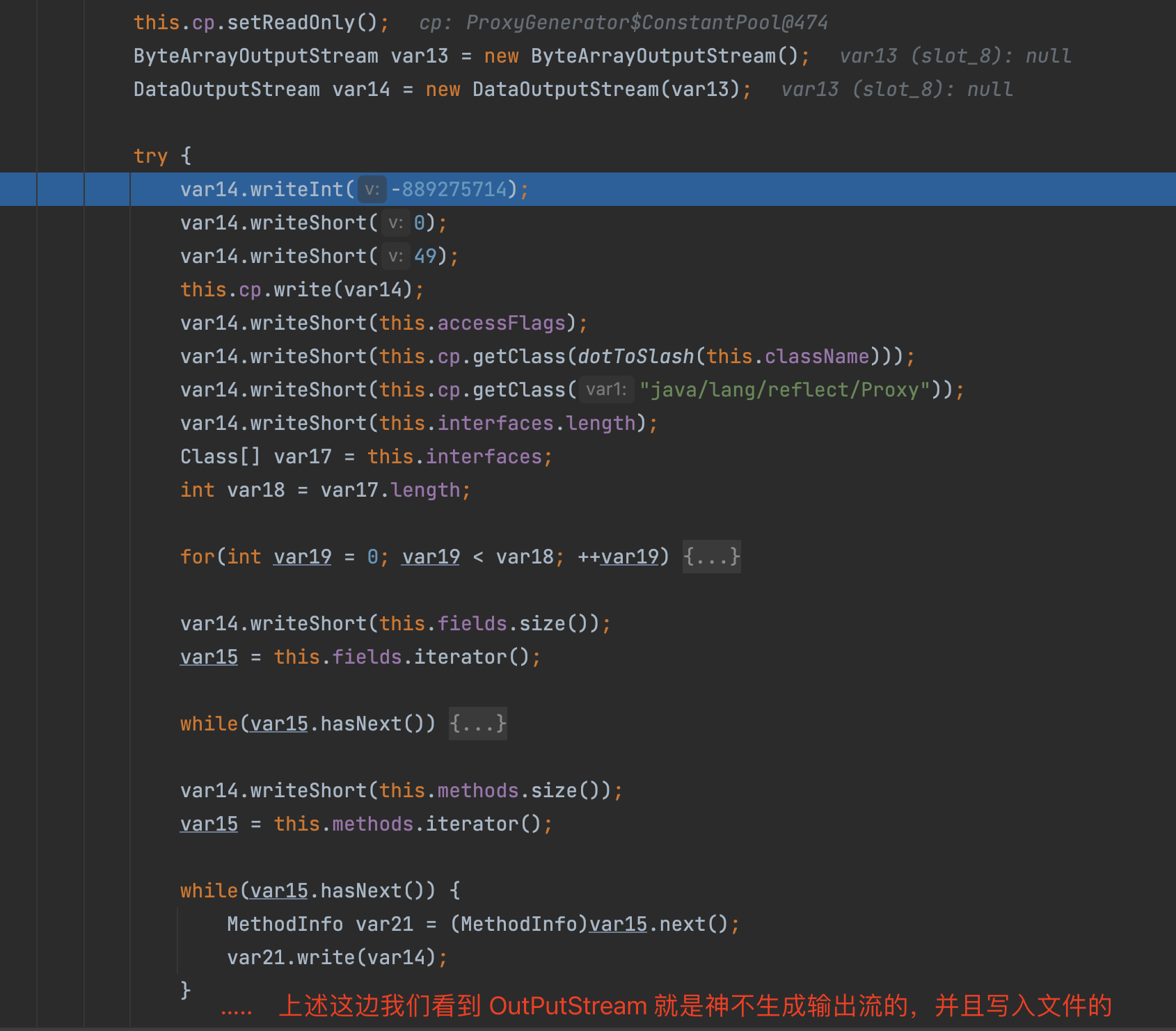
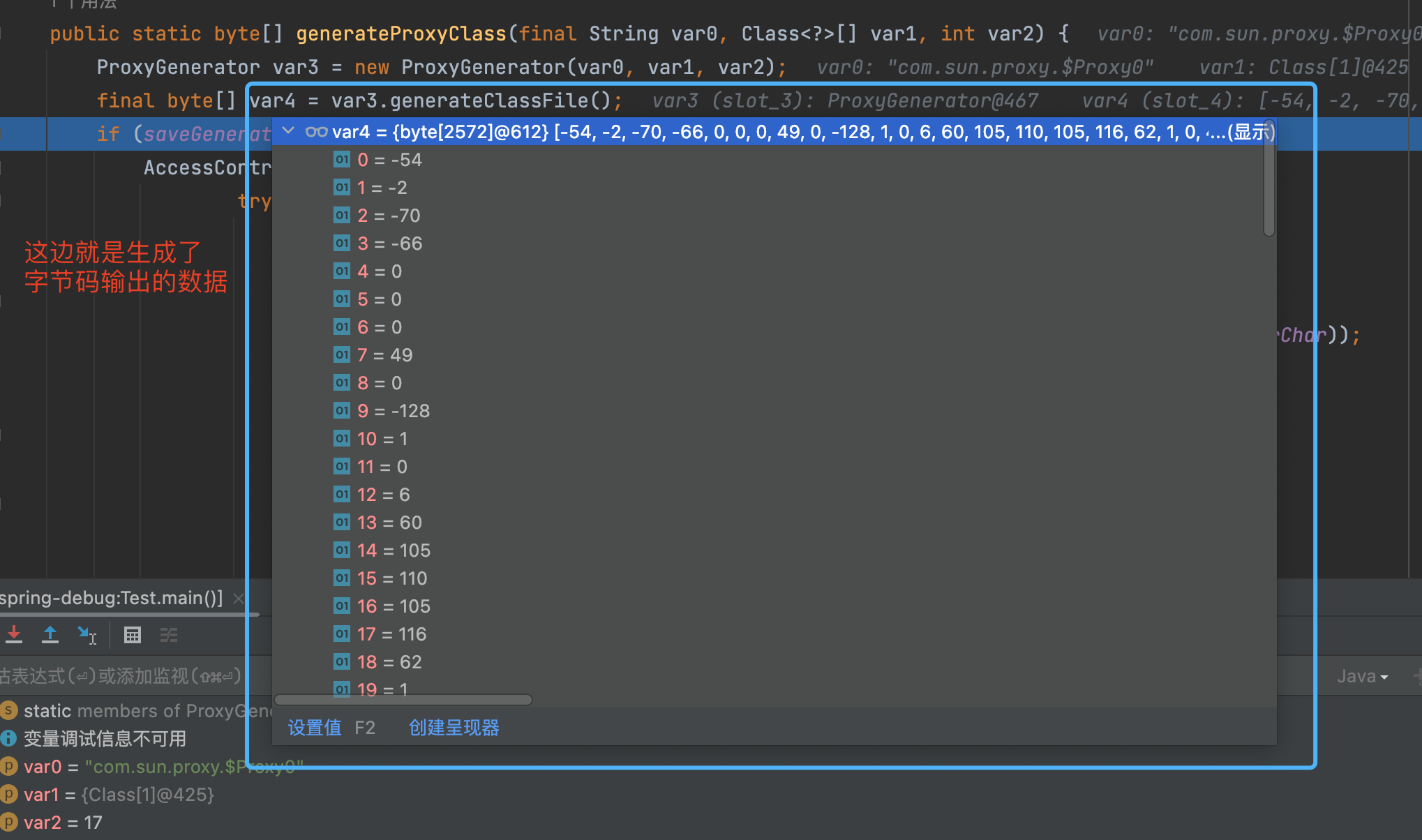
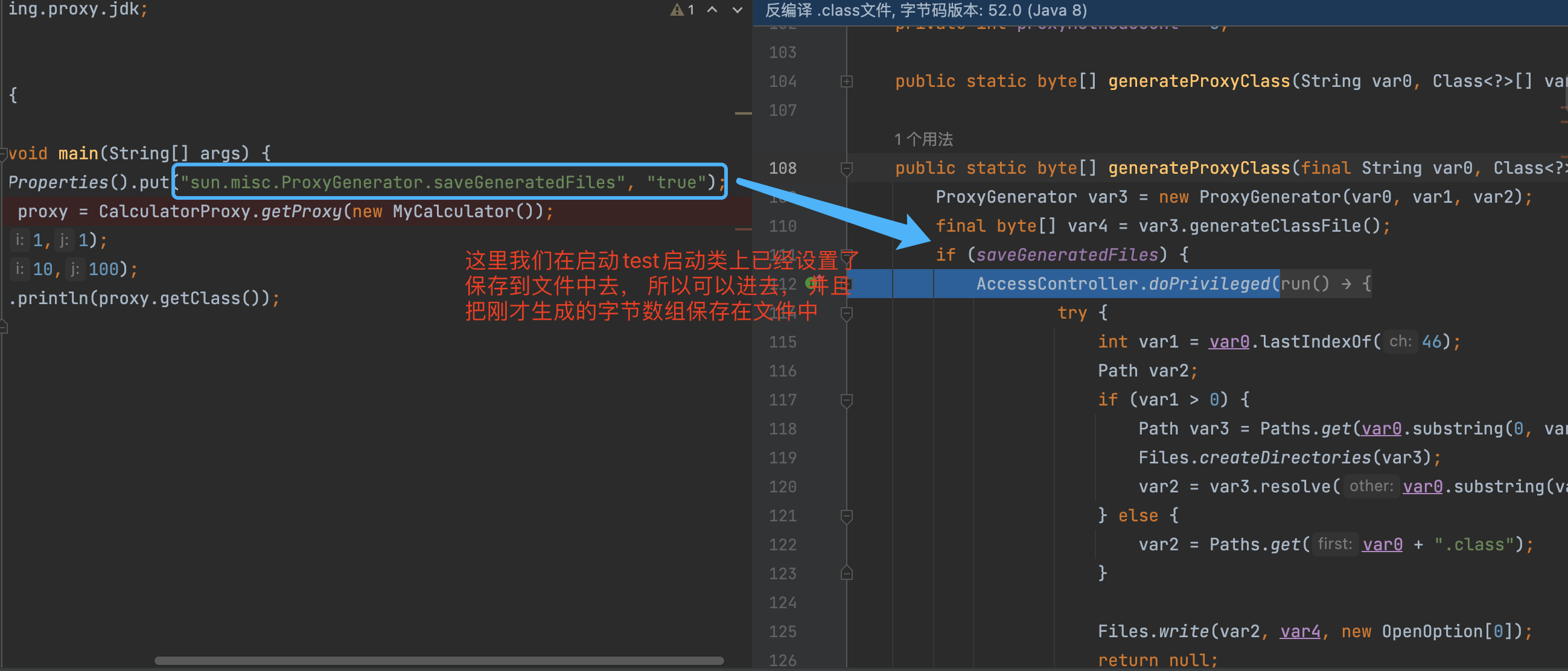
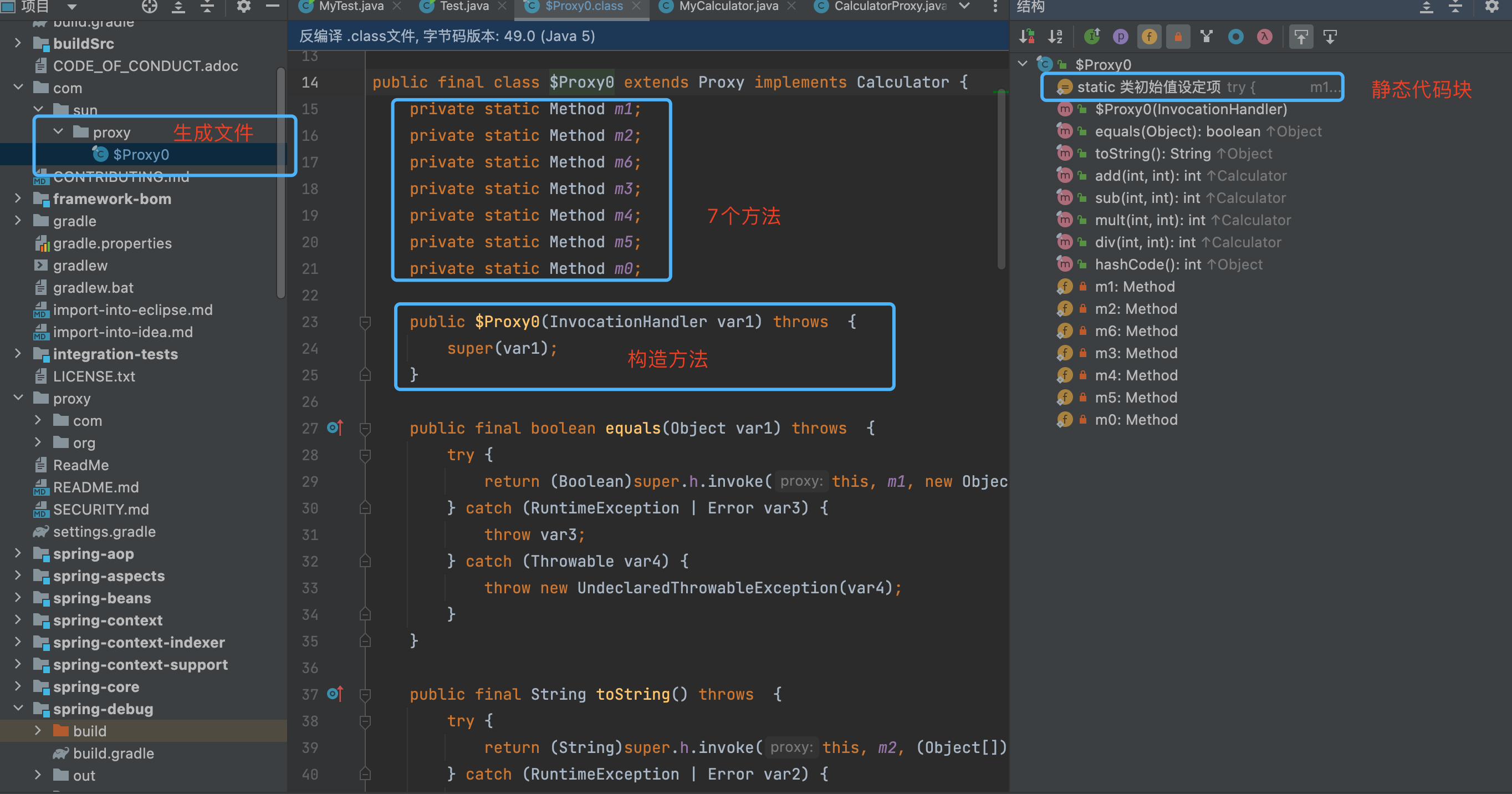
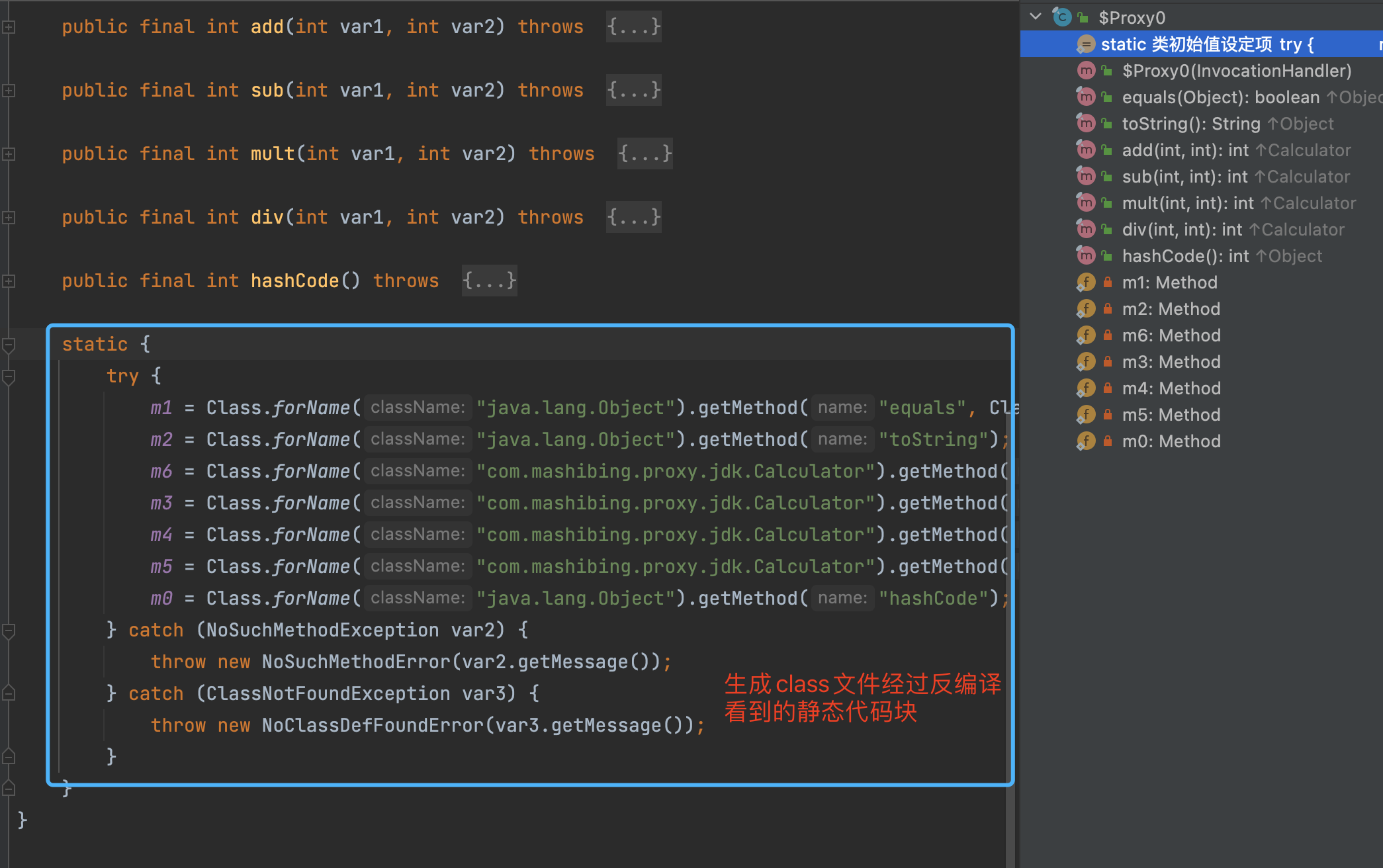
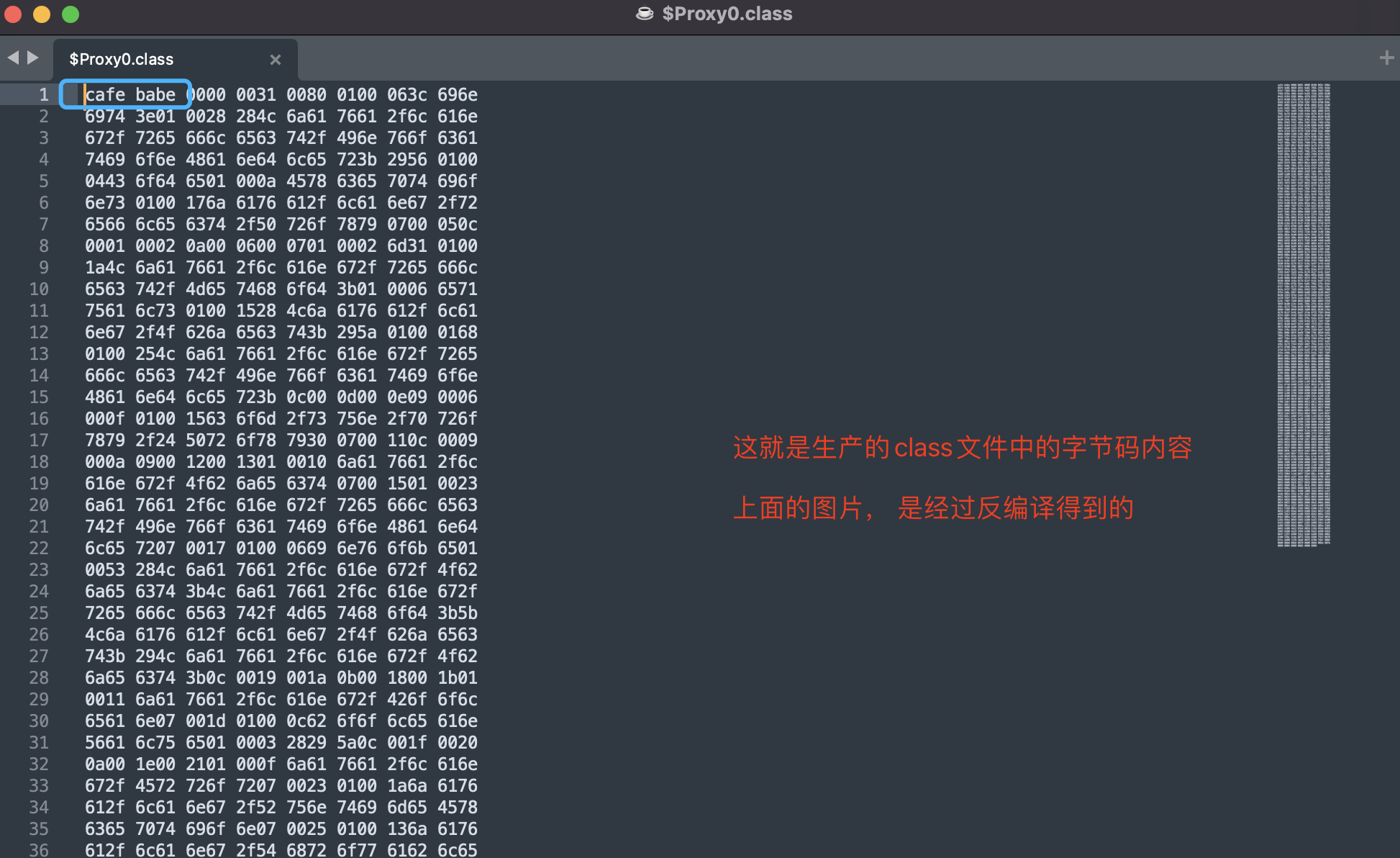
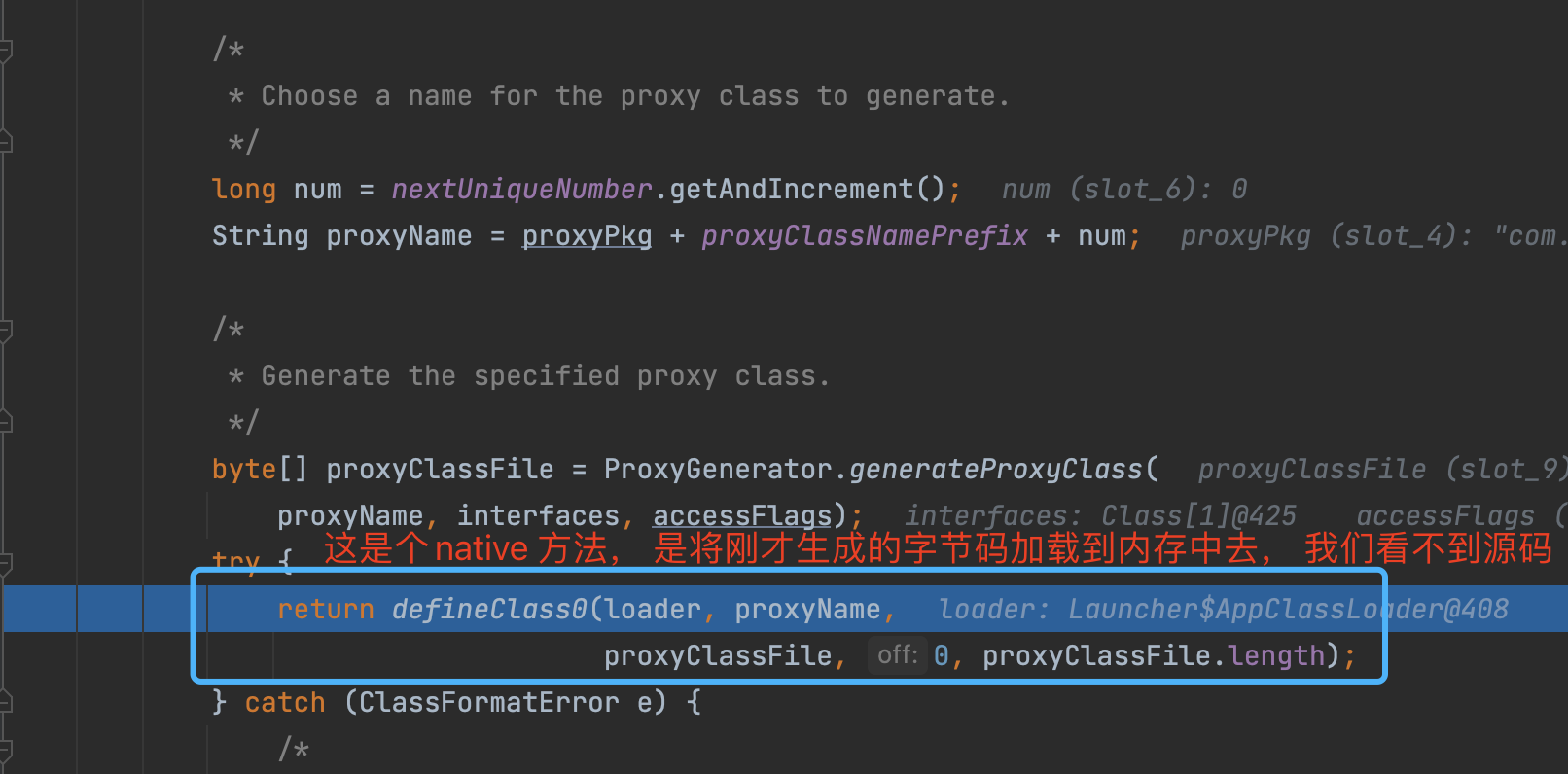
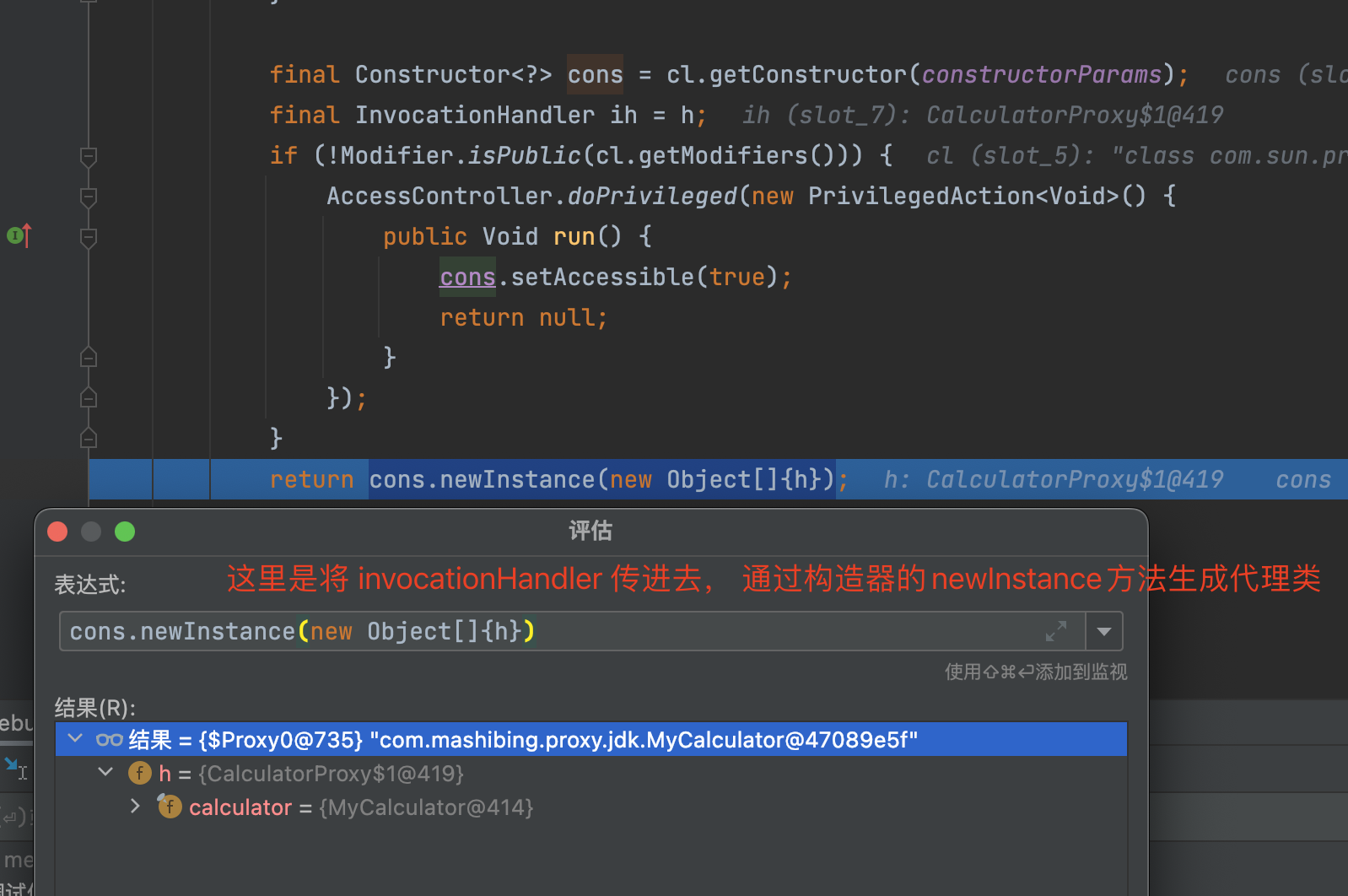
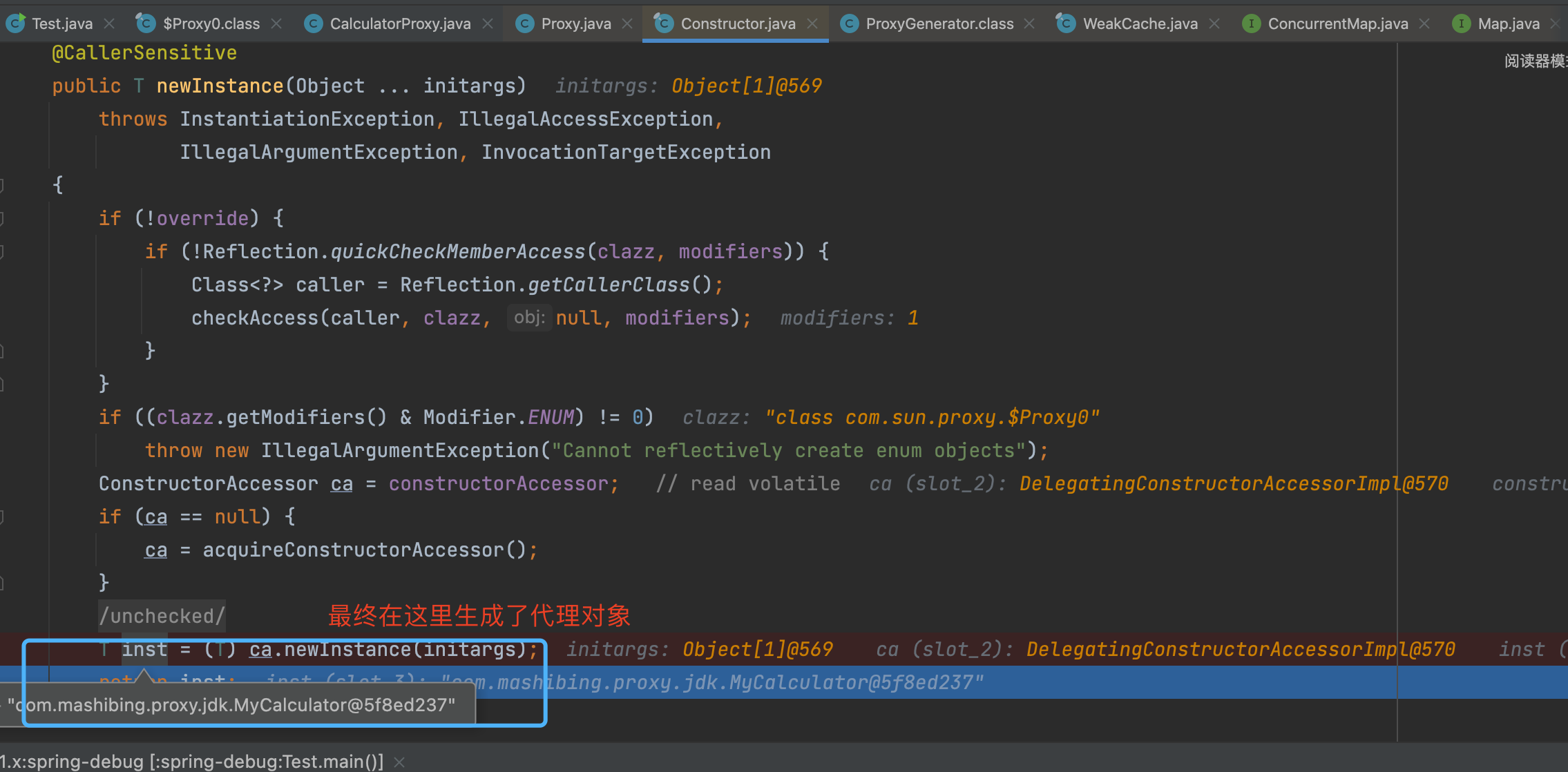
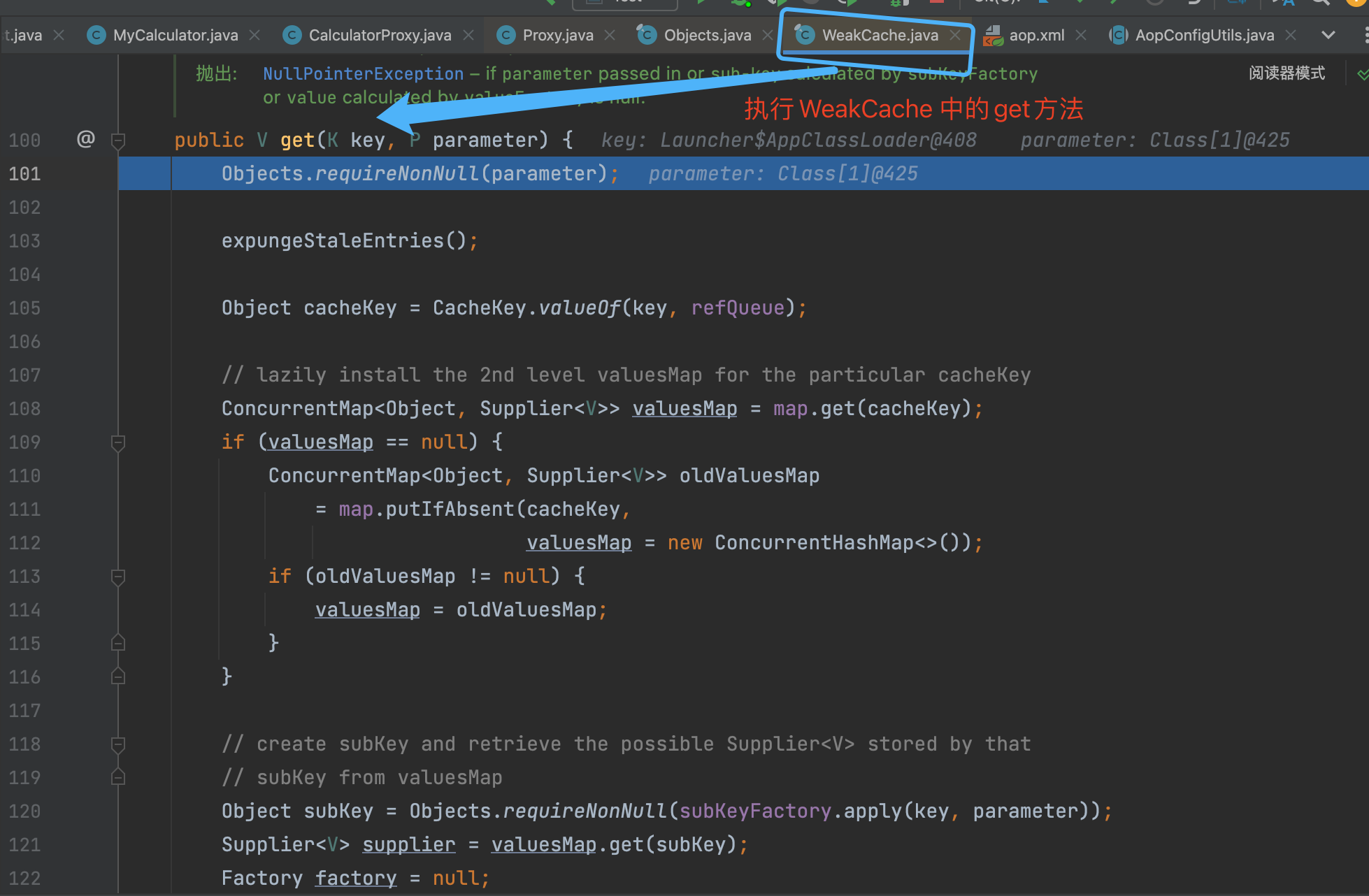
执行完上述逻辑后, 不断返回个上层调用者, 最终到如下图的位置的时候, 就有了代理类