1、方法定义中调用方法本身的现象
2、递归注意实现
1) 要有出口,否则就是死递归
2) 次数不能太多,否则就内存溢出
3) 构造方法不能递归使用
3、递归解决问题的思想和图解:
分解和合并【先分解后合并】
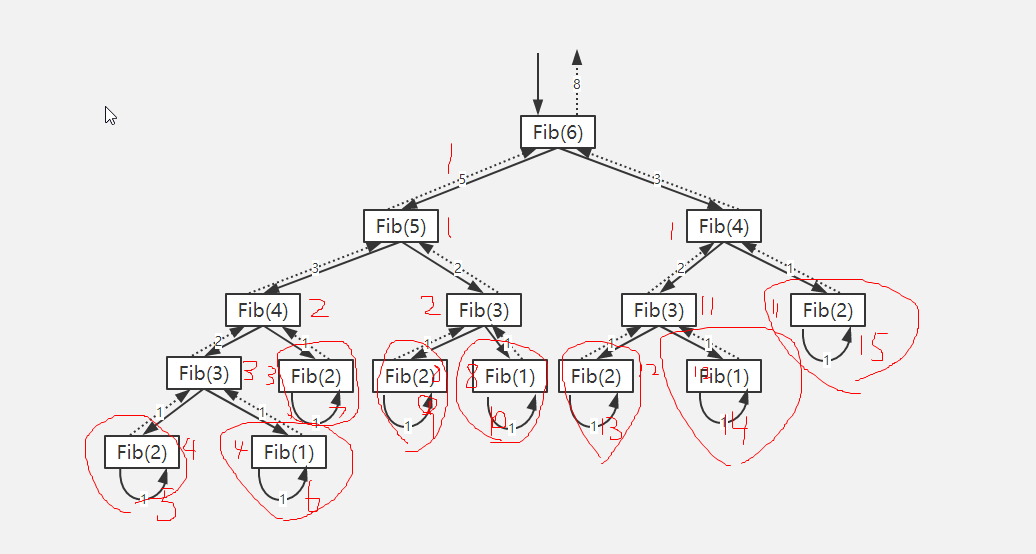
1. 常见的斐波那契数列
1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,...
特征: 从第三个数开始,每个数是前两个数的和。
int count = 0;
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果1" );
return 1;}
else
{
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 "+ "getFibo("+(i - 1)+")"+" + getFibo("+(i - 2)+")");
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
int value = getFibo(6);
System.out.println(value);
}


2. 阶乘
10!= 10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
9! = 9 * 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
8! = 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
特征:
9!=9* 8!
10! =10 * 9!
//阶乘
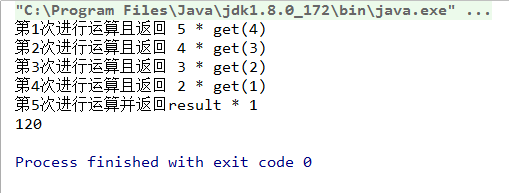
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果* 1" );
result = result * 1;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算" + "get(" +(i-1)+")" );
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result;
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
System.out.println(get(5));
}

3. 加法实现1+2+3+4+5+...+100=
//求和
private int fsum(int i){
if (i <= 0) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回0" );
return 0;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i +" + fsum(" +(i-1)+")" );
return (i + fsum(i-1));
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
System.out.println(fsum(10));
}
4. 实现打印乘法表
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//递归实现
public static void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10));
getByFor(8);
getByRecursion(9);
}
6. 汉诺塔游戏
三根木棒,n个依次增大的空心圈圈,每次移动一个圈圈到木棒上,且任何时候保证小的圈圈不能被大的圈圈压在下面。
2的n次方-1

//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count;
} else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10));
//getByFor(8);
//getByRecursion(9);
int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count);
}
代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test02 {
int count = 0;
//1. 斐波那契数列递归,用的时候请将count和输出System.Out去除
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果1" );
return 1;}
else
{
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 "+ "getFibo("+(i - 1)+")"+" + getFibo("+(i - 2)+")");
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
//2. 阶乘
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回result * 1" );
result = result * 1;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i+" * get(" +(i-1)+")" );
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result;
}
//3. 求和
private int fsum(int i){
if (i <= 0) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回0" );
return 0;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i +" + fsum(" +(i-1)+")" );
return (i + fsum(i-1));
}
}
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//4. 递归实现
public void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count;
} else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10));
//getByFor(8);
//getByRecursion(9);
int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count);
}
}
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test03 {
int count = 0;
//1. 斐波那契数列递归,用的时候请将count和输出System.Out去除
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
return 1;}
else
{
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
//2. 阶乘
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
result = result * 1;
}
else {
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result;
}
//3. 求和
private int fsum(int i){
if (i <= 0) {
return 0;
}
else {
return (i + fsum(i-1));
}
}
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//4. 递归实现
public void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count;
} else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
System.out.println(getFibo(6));
System.out.println(get(5));
System.out.println(fsum(10));
getByFor(8);
getByRecursion(8);
int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count);
}
}