https://medium.com/the-graphqlhub/your-first-graphql-server-3c766ab4f0a2#.n88wyan4e
0.问题来了
DT 时代,各种业务依赖强大的基础数据平台快速生长,如何高效地为各种业务提供数据支持,是所有人关心的问题。
现有的业务场景一般是这样的,业务方提出需求,然后寻找开发资源,由后端提供数据,让前端实现各种不同的业务视图。这样的做法存在很多的重复劳动,如果能够将其中通用的内容抽取出来提供给各个业务方反复使用,必然能够节省宝贵的开发时间和开发人力。
前端的解决方案是将视图组件化,各个业务线既可以是组件的使用者,也可以是组件的生产者。那么问题来了,前端通过组件实现了跨业务的复用,后端接口如何相应地提高开发效率呢?
我们假设某个业务需要以下数据内容 a:
{
|
对,这不是 JSON,但是我们仍然可以看懂它表示的是查询 id 为 3500401 用户的 id,name 和 isViewerFriend 信息。用户信息对于各个业务都是通用的,假设另外一个业务需要这样的用户信息 b:
{
|
对比一下,我们发现只是少了两个字段,多了一个字段而已。如果要实现我们的目标,即复用同一个接口来支持这两种业务的话,会有以下几种做法:
- 用同一个接口,这个接口提供了所有数据。这样做的好处是实现起来简单,但缺点是对业务做判断的逻辑会增多,而且对于业务来说,响应内容中有些数据根本用不到;
- 使用参数来区分不同的业务方并返回相应的数据。好处仍然是实现简单,虽然不会有用不到的数据返回,但是仍然需要增加业务逻辑判断,会造成以后维护的困难。
此外,这样还会造成不同业务之间的强依赖,每次发布都需要各个业务线一起测试和回归。不重用接口则没法提高开发效率,重用接口则会有这些问题,那么到底有没有“好一点”的解决方案呢?
这是我们在处理复杂的前后端分离中经常要面临的一个思考。
1.GraphQL,一种新的思路
我们知道,用户信息对应的数据模型是固定的,每次请求其实是对这些数据做了过滤和筛选。对应到数据库操作,就是数据的查询操作。如果客户端也能够像“查询”一样发送请求,那不就可以从后端接口这个大的“大数据库”去过滤筛选业务需要的数据了吗?
GraphQL 就是基于这样的思想来设计的。上面提到的(a)和(b)类型的数据结构就是 GraphQL 的查询内容。使用上面的查询,GraphQL 服务器会分别返回如下响应内容。
a 查询对应的响应:
{
|
b 查询对应的响应:
{
|
只需要改变查询内容,前端就能定制服务器返回的响应内容,这就是 GraphQL 的客户端指定查询(Client Specified Queries)。假如我们能够将基础数据平台做成一个 GraphQL 服务器,不就能为这个平台上的所有业务提供统一可复用的数据接口了吗?
了解了 GraphQL 的这些信息,我们一起来动手实践吧。
2.使用 Node.js 实现 GraphQL 服务器
我们先按照官方文档搭建一个 GraphQL 服务器:
$ mkdir graphql-intro && cd ./graphql-intro
|
index.js 的内容如下:
//index.js
|
server.js 的内容如下:
//server.js
|
然后执行代码: nodemon index.js:
如果没有安装 nodemon,需要先 npm install -g nodemon,也推荐使用 node-dev 模块。
测试是否有效:
curl -XPOST http://localhost:3000/graphql
|
接着编写 GraphQL Schema
接下来是添加 GraphQL Schema(Schema 是 GraphQL 请求的入口,用户的 GraphQL 请求会对应到具体的 Schema),首先回忆一下 GraphQL 请求是这样的:
query getHightScore { score }
|
上面的请求是获取 getHightScore 的 score 值。也可以加上查询条件,例如:
query getHightScore(limit: 10) { score }
|
这样的请求格式就是 GraphQL 中的 schema。通过 schema 可以定义服务器的响应内容。
接下来我们在项目中使用 graphql:
npm install graphql --save
|
使用 body-parser 来处理请求内容:npm install body-parser --save。 而 graphql 这个 npm 包会负责组装服务器 schema 并处理 GraphQL 请求。
创建 schema:touch ./schema.js。
//schema.js
|
这段代码创建了一个 GraphQLSchema 实例。这个 schema 的顶级查询对象会返回一个 RootQueryType 对象,这个 RootQueryType 对象有一个整数类型的 count 域。GraphQL 除了支持整数( Interger ),还支持字符串( String )、列表( List )等多种类型的数据。
连接 schema
下面是将 GraphQL schema 和服务器连接起来,我们需要修改 server.js 为如下所示:
//server.js
|
验证下效果:
curl -v -XPOST -H "Content-Type:application/graphql" -d 'query RootQueryType { count }' http://localhost:3000/graphql
|
结果如下图所示:
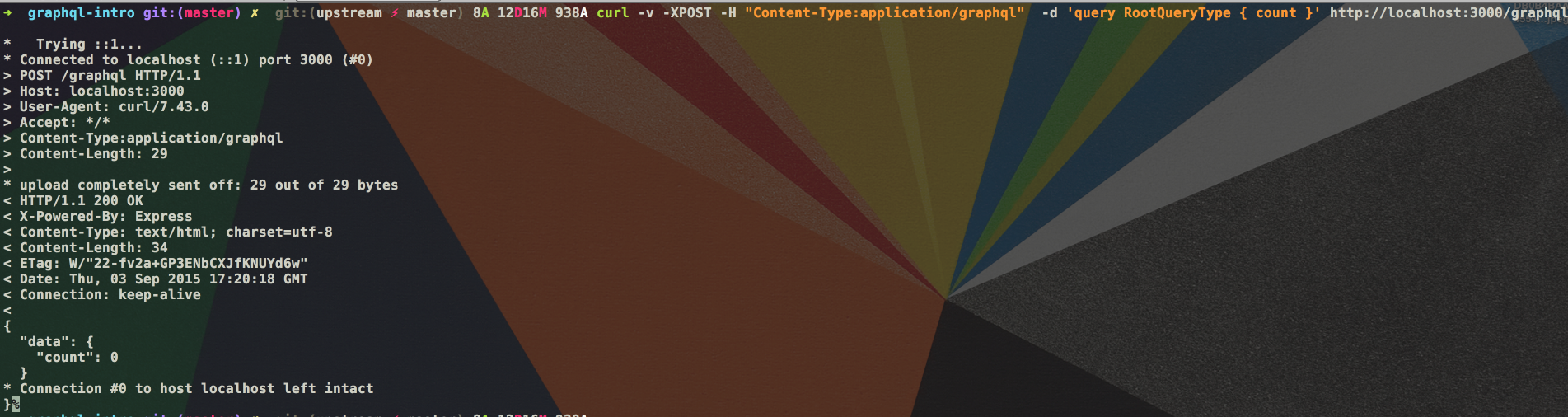
GraphQL 查询还可以省略掉 query RootQueryType 前缀,即:
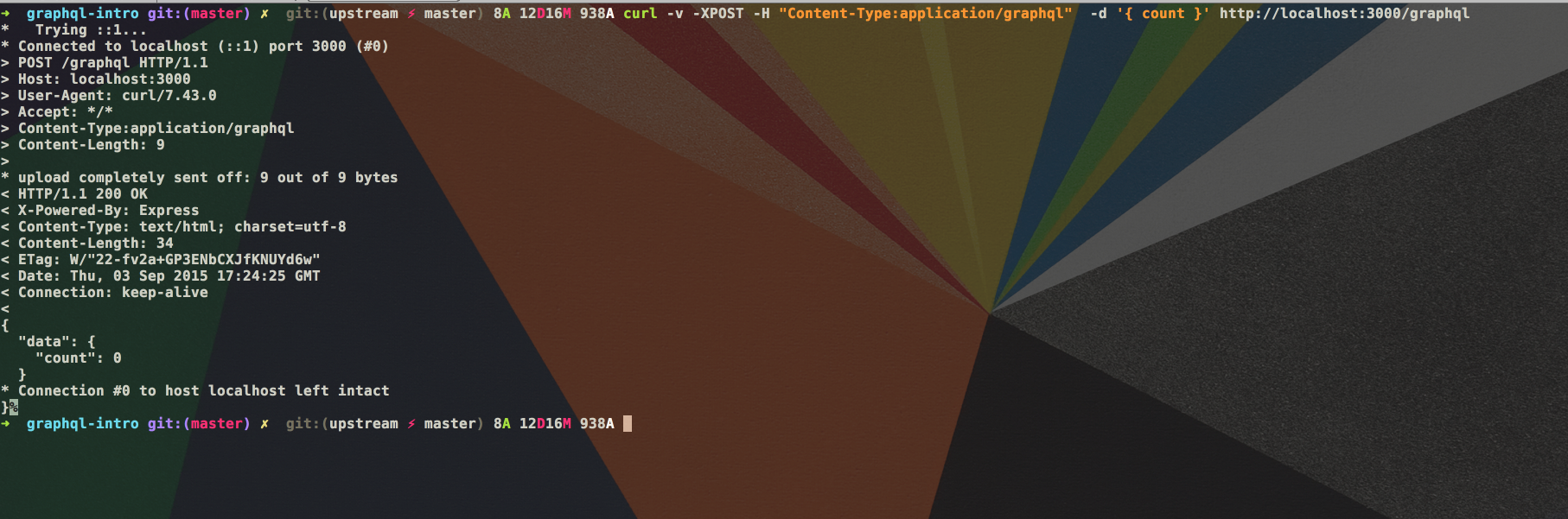
检查服务器
GraphQL 最让人感兴趣的是可以编写 GraphQL 查询来让 GraphQL 服务器告诉我们它支持那些查询,即官方文档提到的自检性(introspection)。
例如:
curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d '{__schema { queryType { name, fields { name, description} }}}' http://localhost:3000/graphql
|
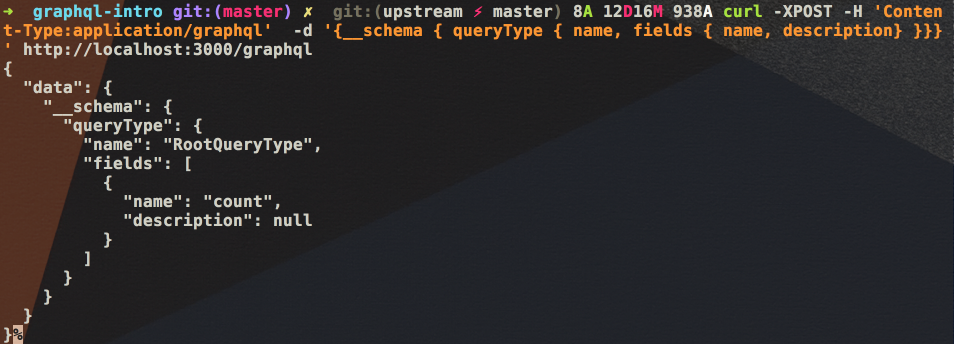
而我们实际的 GraphQL 查询请求内容为:
{
|
基本上每个 GraphQL 根域都会自动加上一个 __schema 域,这个域有一个子域叫 queryTyp。我们可以通过查询这些域来了解 GraphQL 服务器支持那些查询。我们可以修改 schema.js 来为 count 域加上 description:
let schema = new GraphQLSchema({
|
验证一下:
curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d '{__schema { queryType { name, fields { name, description} }}}' http://localhost:3000/graphql
|
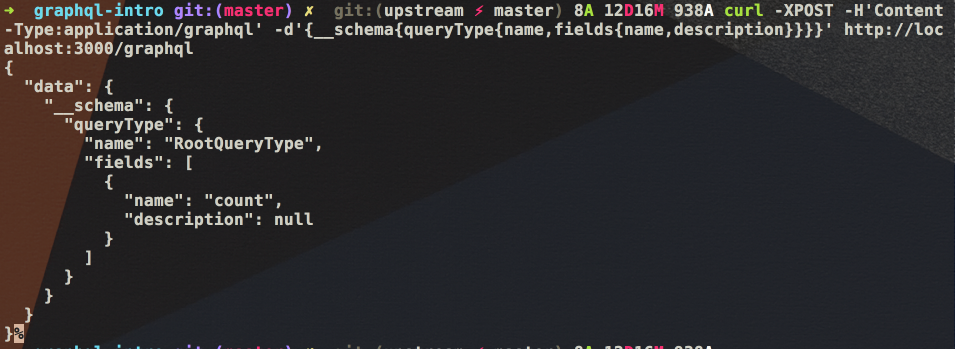
变异(mutation,即修改数据)
GraphQL中将对数据的修改操作称为 mutation。在 GraphQL Schema 中按照如下形式来定义一个 mutation:
let schema = new GraphQLSchema({
|
mutation 查询和普通查询请求(query)的重要区别在于 mutation 操作是序列化执行的。例如 GraphQL 规范中给出的示例,服务器一定会序列化处理下面的 mutation 请求:
{
|
请求结束时 theNumber 的值会是 2。下面为我们的服务器添加一个 mutation 查询,修改 schema.js 为如下所示:
//schema.js
|
验证:
curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d 'mutation RootMutationType { updateCount }' http://localhost:3000/graphql
|

搭建好 GraphQL 服务器后,我们来模拟下业务场景的实际需求,对于电商平台来说,最常用的就是商品信息,假设目前的商品数据模型可以用下面的 GraphQLObject 来表示:
var ItemType = new GraphQLObjectType({
|
查询商品的 schema 如下所示:
var ItemSchema = new GraphQLSchema({
|
通过如下 query 可以查询 id 为 12345 的商品信息:
query ItemQuery(id: 12345){
|
商品详情页展示时需要加上优惠价格信息,我们可以修改 ItemType,为它加上一个 promotion 字段:
var ItemType = new GraphQLObjectType({
|
商品详情页的查询为:
query ItemQuery(id: 12345){
|
ItemSchema 无需修改,只要在 ItemService 的返回结果中加上 promotion 就可以了。这样接口的修改对于原有业务是透明的,而新的业务也能基于已有的代码快速开发和迭代。
再假设有一个新的页面,只需要用到宝贝的图片信息,业务方可以使用下面的查询:
query ItemQuery(id: 12345){
|
服务器代码不用做任何修改。
4.总结
至此我们已经实现了一个 GraphQL 基础服务器。在实际业务中数据模型肯定会更加复杂,而 GraphQL 也提供了强大的类型系统(Type System)让我们能够轻松地描述各种数据模型,它提供的抽象层能够为依赖同一套数据模型的不同业务方提供灵活的数据支持。关于 GraphQL 在淘宝更多的生产实践,请持续关注我们博客未来的系列文章。
参考资料
- GraphQL Introduction
- Introducing Relay and GraphQL
- GraphQL Specification
- Introducing Relay and GraphQL译文
- GraphQL Overview - Getting Started with GraphQL and Node.js
- what is relay
- facebook engineer answers about relay, graphql
- Your First GraphQL Server
- https://medium.com/@clayallsopp/your-first-graphql-server-3c766ab4f0a2
- https://blog.risingstack.com/graphql-overview-getting-started-with-graphql-and-nodejs/
- https://github.com/davidchang/graphql-pokedex-api
- http://nginx.com/blog/introduction-to-microservices/
- https://code.facebook.com/posts/1691455094417024/graphql-a-data-query-language/
- http://graphql.org/blog/
- https://github.com/chentsulin/awesome-graphql