import javax.swing.*;
public class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
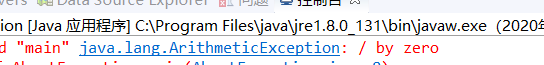
被零除 输出by zero
谁先出异常,就先去catch捕捉那个异常,try。。catch注释后,发现finally都会执行。
1.把可能会发生错误的代码放进try语句块中。
2.当程序检测到出现了一个错误时会抛出一个异常对象。异常处理代码会捕获并处理这个错误。
catch语句块中的代码用于处理错误。
3.当异常发生时,程序控制流程由try语句块跳转到catch语句块。
4.不管是否有异常发生,finally语句块中的语句始终保证被执行。
5.如果没有提供合适的异常处理代码,JVM将会结束掉整个应用程序。
public class ThrowDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
double data = 100 / 0.0;
System.out.println("浮点数除以零:" + data);
if(String.valueOf(data).equals("Infinity"))
{
System.out.println("In Here" );
throw new ArithmeticException("除零异常");
}
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
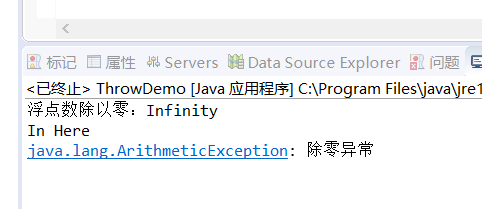
因为浮点数在除0时,他不是把他当做0而是看做是最小值,因此得出的结果为极大值。
多态
可以有多个catch语句块,每个代码块捕获一种异常。在某个try块后有两个不同的catch 块捕获两个相同类型的异常是语法错误。
使用catch语句,只能捕获Exception类及其子类的对象。因此,一个捕获Exception对象的catch语句块可以捕获所有“可捕获”的异常。
将catch(Exception e)放在别的catch块前面会使这些catch块都不执行,因此Java不会编译这个程序。
资源泄露:当一个资源不再被某应用程序使用,但此程序并未向系统声明不再使用此资源时发生这种情况
finally语句块主要用于解决资源泄露问题,它位于catch语句块之后,JVM保证它们一定执行。
注意:finally语句块中也可能发生异常,如果这种情况发生,先前的异常被放弃。
public class CatchWho {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
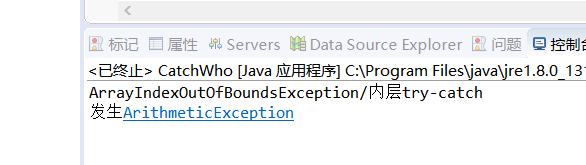
内层的try抛出异常,会被最近的符合要求的catch捕获,之后又抛出一个新的异常,再被离他最近的符合要求的catch捕获
public class CatchWho2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
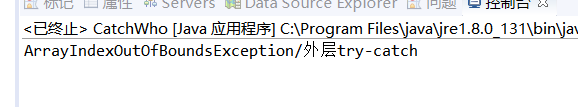
在最内层的异常抛出后,内层没有可以接受异常的catch,就跑到外层的try结构里,发现也没有,就跳出外层的try,被外层的catch接受
package 动手动脑;
public class EmbededFinally {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
//result=100/0; //Level 1
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
//result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}

通过不同的异常导致有些try语句块未能执行,其原因在于发生异常的try块外有无final语句,如果有就会执行,那么凡是在发生异常的try语句块里的finaly语句将都不会执行。
finally语句块一定会执行吗
当发生异常后,catch捕获后自动结束程序,那么之后的finaly语句块就不会被执行了
通过printStackTrace()打印方法调用堆栈,我们可以跟踪到程序的出错来源和传播路径